It's become something of an annual tradition at Datamation to end the year with a gigantic compilation of all the open source software we've surveyed over the past twelve months or so. (See 2010's
.) This year's retrospective is bigger than ever with 957 excellent open source applications featured.
The complete list is a lot to handle in one sitting, so we've divided it into categories. Also, please note that the projects in each category are listed in alphabetical order, not from best to worst or vice versa.
As always, if you'd like to add a project to list, feel free to do so in the comments section below.
Open Source Apps: Accounting
1.
Edoceo ImperiumWeb-based Imperium combines some business management features like CRM and job tracking with a full-featured double-entry accounting package. It's built in XHTML/CSS and JavaScript, and it integrates with Google Apps. Operating System: OS Independent
2.
FrontAccountingLike Imperium, FrontAccounting is Web-based and includes some ERP functionality. It prides itself on being powerful, yet simple. Operating System: OS Independent
3.
GnuCashA good option for small business owners, GnuCash combines the features of a business accounting package with the features of a personal financial manager. Key capabilities include double-entry accounting, investment management, invoicing, accounts payable, accounts receiveable, Quicken data import and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
4.
Lazy8 LedgerBest for very small businesses, Lazy8 Ledger offers an alternative to doing your books by hand or with a simple spreadsheet program. However, it lacks the advanced features that larger companies are likely to need. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
5.
LedgerSMBAlso designed for small to medium-sized businesses, LedgerSMB includes general ledger, accounts payable and accounts receivable capabilities. It was originally based on the SQL-Ledger code and also offers some basic ERP functionality. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
6.
osFinancialsWith an emphasis on simplicity, osFinancials aims to take the complications out of business accounting software. It can track up to 9999 accounts, 1 million creditors and debtors and 1 million stock items. Note: because it is developed by a team in the Netherlands, a lot of the osFinancials Web site and documentation is in Dutch, but English is also available. Operating System: Windows, Linux
7.
TurboCASHThis small business accounting package offers many similar features to QuickBooks and Sage. It tracks up to 10 bank accounts, 999 sets of books, 12000 accounts, 40000 debtors and creditors, and 64000 stock items. Operating System: Windows
8.
XIWAFirst released in 1999, XIWA is an older accounting program for Linux only. One benefit for owners of very small businesses is that it offers the option of using double-entry accounting or not, depending on the background of the user. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Appliances
9.
Turnkey LinuxTurnkey offers a variety of pre-configured appliances, including a NAS appliance. In addition, all Turnkey appliances come with TurnKey Linux Backup and Migration pre-installed. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Anti-Spam
10.
ASSPShort for "Anti-Spam SMTP Proxy," ASSP stops spam at your mail server. Key features include easy browser-based setup, support for most mail servers, automatic whitelisting, virus scanning through ClamAV, Bayesian filters, community-based gray-listing and more. Operating System: OS Independent
11.
MailScannerDownloaded more than 1.3 million times, MailScanner combines the power of two other open source tools—SpamAssassin and ClamAV—to protect mail servers. Extensive documentation is available on the site. Operating System: Linux, Unix
12.
SpamAssassin"The powerful #1 open-source spam filter," SpamAssassin from Apache uses an entire arsenal of techniques to find and block unwanted e-mail. You can deploy it on a mail server or locally on an individual e-mail account, but you will need to be fairly knowledgeable to set it up. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
13.
SpamBayesAfter you train SpamBayes by showing it which messages you like (the ham) and which messages you don't like (the spam), it will use special algorithms to sort your e-mail for you. It integrates with a wide variety of e-mail clients, including Outlook and Thunderbird. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Anti-Spyware
14.
NixoryNixory's job is to get rid of malicious tracking cookies. The new Active Shield mode removes cookies while your browser is open, without slowing down your surfing. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
15.
xpyFor the many users still running Windows XP, xpy tweaks the operating system settings to give you better privacy. For example, it disables communication with Microsoft, removes Windows Messenger, and makes some changes to Internet Explorer. Operating System: Windows XP
Open Source Apps: Anti-Virus/Anti-Malware
16.
ClamAVUndoubtedly the most widely used open-source anti-virus solution, ClamAV quickly and effectively blocks Trojans, viruses, and other kinds malware. The site now also offers paid Windows software called "Immunet," which is powered by the same engine. Operating System: Linux
17.
ClamTKLike ClamAV for Windows, ClamTK provides a front end for the ClamAV engine, this time for the Linux OS. It allows you to schedule system scans, but it does not provide real-time scanning for incoming files. Operating System: Linux
18.
ClamWinIf you're not on a network, ClamWin can provide good antivirus protection for a single system. It boasts more than 600,000 active users. Simply right-click on a file to scan it or use the scheduler to plan a full scan of your entire system. Operating System: Windows
19.
P3ScanThis transparent proxy server works with Clam AV and other anti-virus software to scan incoming and outgoing e-mail for viruses, worms, trojans, spam and harmful attachments. Operating System: Linux
20.
Rootkit HunterThis no-frills tool scans for rootkits and other malware on Linux system. While it does not provide live or scheduled scanning, the Web site explains how to set up your system to scan daily. Operating System: Linux, Unix
21.
ViralatorStill getting the occasional network virus even after you install anti-virus software? Viralator supplements the existing anti-virus software on your proxy server to block malware that might otherwise slip in when users access free webmail accounts. Operating System: Linux, Unix
Open Source Apps: Application Firewall
22.
AppArmorIncluded in both openSUSE and SUSE Linux Enterprise, Novell's application firewall aims to secure Linux-based applications while lowering IT costs. Key features include reports, alerts, sub-process confinement, and more. Operating System: Linux
23.
ModSecurityThe "most widely deployed WAF (Web Application Firewall) in existence," ModSecurity protects applications running on the Apache Web server. It also monitors, logs, and provides real-time analysis of Web traffic. Operating System: Windows, Linux
24.
SELinuxDeveloped by the NSA, Security Enhanced Linux adds mandatory access control features to the Linux OS. It enforces complete separation of information to make it more difficult to bypass application security mechanisms. Operating System: Linux, Unix
Open Source Apps: Astronomy
25.
CelestiaA great app for any space-obsessed kids (or adults) you may have in your house, Celestia lets you fly throughout the known universe seeing astronomical objects as they would appear at any date in history. It uses real images whenever possible to give you the feeling that you really are traveling through space. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
26.
KStarsKStars also lets you view the night skies, including "up to 100 million stars, 13,000 deep-sky objects, all 8 planets, the sun and moon, and thousands of comets and asteroids." If you're an amateur astronomer, you'll also like KStars' tools that help you plan your nightly viewing. (Note that in order to use KStars on Windows, you'll have to download
KDE for Windows.) Operating System: Windows, Linux
27.
PP3Ideal for educators, PP3 creates detailed star charts for use in PowerPoint presentations or books. Note that in order to use it, you will also need
LaTeX. Operating System: Windows, Linux
28.
StarChartThis app's website begins with a simple introduction: "There is a sky. There are things in the sky. This program draws maps of things in the sky." While the on-screen graphics on this app aren't as good as some of the other star-charting software, it does a good job of creating printed star charts for study. Operating System: Linux
29.
StellariumAnother educational astronomy app, Stellarium turns your system into a planetarium, displaying the night skies for any time you input. In fact, this app is actually used to power the displays at a number of planetariums. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Audio Tools
30.
AmarokKDE's audio player and manager integrates with a number of Web services, including last.fm, Ampache, Magnatune, MP3tunes, EchnoNest and others. Other unique features include dynamic playlists, bookmarking and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
31.
AqualungAqualung's claim to fame is "gap-free" playback of consecutive audio tracks—which is particularly nice when listening to concert recordings. It plays CDs, podcasts, audio streams and most types of audio files. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
32.
aTunesThis Java-based application plays CDs and audio files, helps organize your music and rips audio CDs. The interface is fairly basic, but it includes features like karaoke playback, shuffle, repeat, tag editing, playlists, and more. Operating System: OS Independent
33.
AudacityAudacity offers everything most amateur musicians and producers will need to get started recording and editing their own audio tracks. Its capabilities include pitch change, tempo change, spectrogram node, noise removal, import and export of various file types, unlimited undo and a library of built-in effects, like echo, phaser, wahwah, reverse, and others. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
34.
AC3FilterThis audio decoder and processor filter allows media players to play AC3 and DTS audio tracks from movies. It also allows you to mix audio tracks and adjust sound quality. Operating System: Windows
35.
CDexDownloaded more than 40 million times, CDex is an incredibly popular CD ripper. Key features include direct recording of multiple tracks, CD-Text support, advanced jitter correction, audio signal normalization and more. Operating System: Windows
36.
CdrtoolsCdrtools includes nine different open source tools for recording, reading and verifying CDs, DVDs and BluRay discs. Note that these are command line tools and do not come with a GUI. Operating System: Linux
37.
CoolPlayerBecause of its lightweight size, CoolPlayer offers "blazing fast" performance. Although it does offer some playlist capabilities, this is really just an audio player, not a full audio collection manager. Operating System: Windows
38.
DrumTrackTurn your keyboard into a drum machine with DrumCore. Key features include adjustable volume for each drum hit, randomization of drum hits/volume (to make it sound more like a human is playing), and MIDI import and export. Operating System: Windows
39.
EasyTAGEasyTAG allows users to view and edit the tag fields on MP3, MP2, MP4/AAC, FLAC, Ogg Vorbis, MusePack, Monkey's Audio, and WavPack files. It includes a tree-based browser and CDDB support for manual and automatic searches. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
40.
Free:acFormerly known as "BonkEnc," Free:ac makes it easy to rip CDs so that you can store and listen to them on your desktop, MP3 player or other mobile device. It can convert files to and from MP3, MP4/M4A, WMA, Ogg Vorbis, FLAC, AAC, WAV and Bonk formats. Operating System: Windows
41.
FrinikaIn addition to recording and editing your music, Frinika also helps you make music with a built-in synthesizer and midi support. The website includes a number of screenshots and demos so that you can see it in action. Operating System: OS Independent
42.
HydrogenDesigned for professionals, Hydrogen calls itself "an advanced drum machine for GNU/Linux" (although it does also work on OS X and Windows). It boasts an attractive, user-friendly GUI, a pattern-based sequencer with up 192 ticks per pattern, a sample editor, time stretch and pitch functions, timeline with variable tempo and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
43.
JajukAimed at users with large music collections, this powerful audio playback and management tool has been called "the most powerful jukebox out there" by critics. You can download it or using right from the Web interface. Operating System: OS Independent
44.
JukesNow more than a decade old, Jukes was designed for people who liked to keep their CD collections on their hard drive—back when that was an unusual thing. The interface is basic, but easy to use. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
45.
JuiceJuice makes it easy to capture and listen to podcasts, any time, anywhere. It includes a directory of thousands of online podcasts, so it’s also easy to find the one you want. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
46.
KMidTurn your PC into a karaoke player with this KDE app. It also plays Midi files and includes features like pitch control, a visual metronome and a piano player window. Operating System: Windows
47.
LAMEAlthough LAME stands for "Lame Ain’t No MP3 Encoder," the first line on its Web site states, "LAME is an MPEG Audio Layer III (MP3) encoder." It was intended as an educational tool for those interested in improving the speed and quality of MP3 files. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
48.
MMConvertThe "MM" in this app's name stands for "multi-media" and accordingly, it converts both audio and video among various file formats. You can use it from the command line or with a GUI. Operating System: Windows
49.
Linux MultiMedia StudioSuitable for amateur musicians and hobbyists, LMMS lets you use your PC to create musical tracks and then mix them together. Don't let the "Linux" in the name fool you—it's also available in a Windows version. Operating System: Windows, Linux
50.
Mixere> Designed for live performance, Mixere's feature set includes dynamic audio looping, auto-triggering, fully automated sliders, gradual mute/solo operations, crossfading and unlimited undo. Operating System: Windows 51. MixxxMixxx's advanced mixing engine gives professional DJs all the tools they need, like hot cues, looping controls and high-fidelity EQs. It also supports MIDI and vinyl controller input for DJs who are used to a traditional turntable/mixer setup. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
52.
MOCSimply select a directory, and the MOC (Music On Console) audio player will play all files in that directory. Supported file formats include MP3, Ogg Vorbis, FLAC, Musepack, Speex, WAVE, AIFF, and AU. Operating System: Linux/Unix, OS X
53.
MoosicIf you prefer your software without a GUI, Moosic might be right for you. It's a simple, client-server jukebox program that runs from the command line. Operating System: Linux/Unix
54.
MP3GainTired of constantly adjusting the volume when playing MP3s? MP3Gain uses statistical analysis to gauge how loud songs sound in the human ear, and then modifies the volume appropriately without degrading the quality of playback. Operating System: OS Independent
55.
Mp3spltMp3splt is an audio utility that does just one thing—it lets you cut mp3 and ogg files into smaller files and rename them. It’s especially useful if you need to split an entire album into individual tracks. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
56.
MuseScoreThis app makes it easy to create beautiful sheet music. And it plays back your creations with an integrated sequencer and synthesizer. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
57.
Pandora Radio Desktop AppYou don't have to upgrade to Pandora One in order to get a desktop app to listen to the free Pandora service. This lightweight app minimizes to your system tray and removes banner ads. Operating System: Windows
58.
pulpTunesWant to access your home iTunes library while you’re at work? Install pulpTunes and you can access your music from any Web-connected computer. Operating System: OS Independent
59.
Radio DownloaderIf your favorite online radio station only offers streaming content, you can turn it into a podcast you can listen to any time with Radio Downloader. It comes with built-in support for BBC content and a helpful "favourites" tab. Operating System: Windows
60.
SongbirdThis open source iTunes alternative lets you play audio files, manage your music collection and sync across PCs, Macs and Android-based smartphones and tablets. It also features an integrated music store from 7digital, concert notices and ticket purchase, and links to photos, videos and other related information on the Web. Operating System: Windows, OS X, Android
61.
StreamRipperStreamRipper allows you to record and save Shoutcast streams and other Internet audio. Its key feature is the ability to find silences and mark them as possible points of track separation. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix
62.
TuxGuitarTuxGuitar is both a tab editor and a player. Create your own multi-track guitar compositions and play them back. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
63.
ZinfAnother playback only app, Zinf describes itself as "a simple, but powerful audio player." It supports most types of audio file,s as well as streaming audio, and it integrates with MusicBrainz. Operating System: Windows, Linux
Open Source Apps: Backup
64.
AmandaProtecting more than a half a million systems, Amanda claims to be the "most popular open source backup and recovery software in the world." It's available in a variety of free and commercially supported versions, including a cloud-based solution from Zmanda. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
65.
Areca BackupIdeal for daily backup, Areca is user-friendly and very versatile. It supports compression and encryption, as well as incremental, differential, full and delta backup. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
66.
Backit DownThis app synchronizes files and folders so that you can backup or copy your drives. It works across networks or with external hard drives or USB drives. Operating System: Windows, Linux
67.
BaculaFor larger businesses, Bacula offers network backup and recovery capabilities. Although it's an enterprise-grade program, it's easy enough to set up and use that it's appropriate for small businesses as well. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
68.
ClonezillaSpecifically designed as a replacement for Norton Ghost and other Symantec backup products, Clonezilla is an open-source backup/imaging/cloning app that allows bare metal recovery and has unicasting and multicasting capabilities. It comes in two flavors: Clonezilla Live for backing up a single machine, and Clonezilla SE which can clone more than 40 systems at once. Operating System: Linux
69.
Create SynchronicityWhen zipped, this extremely lightweight backup utility occupies just 180KB. It offers a simple, very intuitive interface and fast performance. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
70.
FOGFOG creates a Linux-based server that can backup both Windows and Linux systems. It's a good choice for small organizations, because it's very easy to use but also very powerful with a number of advanced features. Operating System: Linux, Windows.
71.
PartimagePartimage is particularly useful if you need to recover from a complete system crash or if you need to install multiple images across a network. It's very fast and can restore to a partition on a different system. Operating System: Linux
72.
RedoWhile many backup solutions only store your data files, Redo saves a complete image of your system to a thumb drive or CD. It takes a little longer to create these backup files, but it gives you the ability to do a bare metal restore if your system experiences massive failure. Operating System: Windows, Linux
Open Source Apps: Billing
73.
ArgentumThis Web-based app offers basic client management, invoicing and time tracking functionality. It's free to download and host on your own Web server, or you can use the service in the cloud for $10 per month. Operating System: OS Independent
74.
jBillingDesigned for telecoms and companies that offer subscription-based services, jBilling boasts thousands of downloads per month. The software is available for free, but consulting, support and training require a fee. Operating System: OS Independent
75.
Simple InvoicesWith this Web-based invoicing system, you can easily send your clients PDF invoices or create basic reports that let you track your sales. You can download the free version to a PC or a server, or you can purchase access on an SaaS basis from one of the
third-party hosting providers listed on the site. Operating System: OS Independent
76.
SiwappThis Web app was designed to be as simple as possible and offers a very easy-to-use interface. It creates attractive, professional-looking invoices that you can send to your clients and easy-to-understand reports that you can use to manage your small business. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Biology
77.
ByoDynScientists building models of biochemical networks or pathways can use ByoDyn to estimate and analyze the parameters underlying these processes. In addition to the downloadable version, it can also be accessed online as a Web app. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
78.
GenoCADGranted, this is something the average user will likely never download, but the Virginia Bioformatics Institute has made this gene sequencing software available through an open source license. It's helping make possible some cutting edge scientific research. Operating System: OS Independent.
Open Source Apps: Blogging
79.
B2evolutionThis blog platform/content management system can support multiple blogs, multiple domains and multiple authors. It's extensible with skins and plug-ins, and the site offers a demo and links to sample sites. Operating System: OS Independent
80.
LifeTypeWith built-in multi-user authentication and multi-blog support, LifeType offers a blogging platform suitable for large enterprises. Key features include anti-spam filter, mobility support, integrated media management, easy installation and more. Operating System: OS Independent
81.
MovableTypeUsed by companies like NBC, NPR, Wells Fargo, Oracle and others, MovableType is a blogging platform that can operate as a full-fledged content management system. In addition to the open source version, it also comes in a free pro version for educational institutions or businesses with up to five users, as well as paid pro and enterprise versions for larger organizations. Operating System: OS Independent
82.
Nucleus CMSIt bills itself as a Content Management System, but in reality Nucleus is primarily a tool for setting up a blog and hosting it on your own server. Features include a built-in commenting tool, URLs optimized for readers, and multi-lingual support. Operating System: OS Independent
83.
WordPressCalling itself "both free and priceless at the same time," WordPress is the platform of choice for more than 60 million bloggers. It takes just five minutes to get up and running with your own WordPress blog, and a huge library of add-ons and themes makes it easy to customize it to your exact needs. It's also available as a hosted service through
WordPress.com Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Browsers
84.
ChromiumChromium is the open source project behind Google's
Chrome browser, and it's also the base for several other, less popular open source browsers. It's best known for being lightweight and fast. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, ChromeOS
85.
DoobleDooble is a newer browser built with a focus on security. Unlike the better-known browsers, it encodes all of your browsing information for better privacy. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
86.
FirefoxOne of the most popular open source downloads of all time, Firefox offers excellent security, performance and personalization capabilities. Key features in the most recent version include the "awesome bar," app tabs, desktop and mobile syncing, integrated search and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android, iOS
87.
K-MeleonBecause both use Mozilla's Gecko layout engine, K-Meleon and Firefox look and feel a lot alike. However, K-Meleon also lets you import your IE Favorites and Opera Hotlist, and it also supports mouse gestures like Opera. Operating System: Windows
88.
Qt Web BrowserBased on Nokia's Qt framework and Apple's WebKit rendering engine, this browser was designed to be lightweight, secure and portable. It's just 6MB, and it offers a highly customizable interface and a long list of privacy-protection features. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
89.
TorUsed by journalists, intelligence officers and other individuals who need to remain anonymous, Tor allows you to browse and communicate over the Internet without revealing your identity. It can also help you access Web services that have been blocked in particular countries. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Bugtrackers
90.
BugTracker.NETBoasting thousands of users, BugTracker.NET is easy to use and highly configurable. It supports Subversion, Git, and Mercurial, and the website includes a helpful demo and a link to comparisons of various bug tracking systems. Operating System: Windows
91.
BugzillaUsed by thousands of organizations, including Mozilla, Facebook, the Linux kernel, the Apache Project, The New York Times, Yahoo and NASA, Bugzilla makes it easy for software development teams to track issues and code changes. It's Web-based and offers advanced search capabilities, e-mail notifications, reporting, excellent security, custom fields and workflow, and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
92.
FlySprayFlySpray describes itself as "an uncomplicated, Web-based bug tracking system written in PHP for assisting with software development." It supports multiple databases, including MySQL and PGSQL, and it's easy to use. Operating System: OS Independent
93.
GNATSThe GNU project's bug tracking system stores issue and resolution information in a central searchable database and communicates with users via a variety of mechanisms. Although it's usually accessed via the
MantisBTThis Web-based bug tracker integrates with most SQL databases and can be accessed with any browser. It's easy to install and has an enormous list of features. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Business Rule Management System
95.
JBoss DroolsA competitor to commercial software like Blaze Advisor and JRules, Drools describes itself as a business logic integration platform for rules, workflow and event processing. It includes five separate modules: Drools Guvnor (BRMS/BPMS), Drools Expert (rule engine), Drools Flow (process/workflow), Drools Fusion (event processing/temporal reasoning) and Drools Planner (automated planning). Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Bulletin Board
96.
phpBBThe world’s most widely used open source forum creation software, phpBB, lets you set up an online community in just minutes. It includes the ability to send attachments, create unlimited sub-forums, add custom BBCodes, and many other features. Operating System: OS independent
Open Source Apps: Business Intelligence (BI)
97.
JaspersoftThe self-proclaimed "most widely used business intelligence software," Jaspersoft products offer reporting, dashboards, analysis and data integration capabilities. The link above primarily promotes the commercial versions of the software, which include paid support. More info on the community versions can be found at
JasperForge.org. Operating System: OS Independent
98.
JMagallanesIf you only need reporting capabilities, JMagallanes might be right for you. It leverages code from several other open source projects to create static reports, Swing pivot tables for OLAP analysis, and charts. Operating System: OS Independent
99.
OpenIOpenI was specifically designed for on-demand and SaaS deployments. It helps users visualize data from OLAP and relational databases through reports and dashboards. Operating System: OS Independent.
100.
OpenReportsAnother Web-based reporting-only BI tool, OpenReports offers flexible scheduling, a variety of output formats, fine-grained security controls, built-in auditing and more. The paid professional version adds capabilities like dashboards, conditional scheduling, and others. Operating System: OS Independent
101.
Palo BI SuitePalo offers planning, reporting, analysis, dashboards, consolidation and more. The community version essentially extends the capabilities of Excel or OpenOffice, while the paid premium verison adds more reporting and OLAP modules. Operating System: OS Independent
102.
PentahoPentaho likes to calls itself "the open source business intelligence leader." It claims to reduce BI costs by 90 percent, and it's also available on an SaaS basis. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
103.
RapidMiner"The world-leading open-source system for data and text mining," RapidMiner combines Data Integration, Analytical ETL, Data Analysis, and Reporting in a single solution. The enterprise versions offer an extended list of features, professional support and maintenance. Operating System: OS Independent.
Open Source Apps: Business Process Management/Business Performance Management (BPM)
104.
ActivitiThis newer project offers a lightweight, Java-based business process management platform. It aims to meet the needs of both business people and software developers. Operating System: OS Independent
105.
Bonita Open SolutionJava-based Bonita Open Solution consists of three separate parts: a process modeling tool, a BPM and workflow engine, and the user interface. The full version of the software is free, with training and three different levels of support available for a fee. Operating System: OS Independent
106.
ProcessMakerWeb-based ProcessMaker helps simplify workflows with tools for modeling workflows, automatic notification, reporting and optimization. It's available in a free community edition, a subscription-based enterprise edition or in a cloud-based version with a free trial. Operating System: Windows, Linux
107.
uEngineThe uEngine BPM suite includes three separate components: BPM Foundation with a process engine and modeling tool; the process portal with personalization, single sign-on, and dashboard capabilities; and the BP Analyzer with OLAP analyzing and charting abilities. It supports multiple languages, including English, but because it is developed by a Korean company, parts of the Web site and interface sound strange to native English speakers. Operating System: OS Independent.
Open Source Apps: Business Suites
108.
ADempiereThis community-based app offers ERP, CRM and POS functionality. It also integrates with several other open source apps as part of a full suite that adds Web 2.0, authentication, telephony, document management, BI, intranet and data repository capabilities. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others
109.
allocPSAThis web-based suite calls itself "the premier online professional services automation solution." Key features include bookkeeping, project management, a dashboard, time tracking, to do lists, CRM, calendar, and much more, all designed specifically to meet the needs of professional service organizations. It's also available on an SaaS basis starting at $199 per year. Operating System: OS Independent
110.
Compiere ERP + CRM Business SolutionOwned by Consona Corporation, Compiere boasts that it is the "most modern, adaptable and affordable ERP solution." It includes e-commerce, financial management, purchasing, materials management, order management, project accounting, sales, service, and performance management and reporting capabilities. It also comes in a paid enterprise version and is available on Amazon's cloud computing services. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
111.
Dolibarr ERP/CRMLike NetSuite and Sage, Dolibarr ERP/CRM meets the needs of SMBs, foundations and freelancers. The website offers screenshots and an online demo so that you can see how it works. The basic software is free, but additional modules and add-ons are available through the
Dolistore. Operating System: OS Independent
112.
PhreedomThis ERP suite is based on the PhreeBooks accounting software which is incorporated in the package. It includes contacts, inventory, payment, PhreeBooks accounting, reporting and shipping modules, and other add-on modules are also available. Operating System: OS Independent
113.
GNU EnterpriseGNU Enterprise contains a host of developer and ERP tools, including human resources, accounting, CRM, project management, supply chain management, and e-commerce features. Its modular design and open architecture make it easy to customize and easy to maintain. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
114.
JAllInOne ERP/CRMDespite its name, JAllInOne is primarily an ERP solution with some basic CRM functions. It provides all the standard ERP functionality and supports multiple users, multiple languages, and multiple companies. Operating System: OS Independent.
115.
JFireThis Java-based ERP system comes ready-to-use with a full set of features, but can also be customized to meet your company's unique needs. It includes both ERP and CRM functionality and also comes in a version for service-based businesses. Aditional information about the software can be found on the
jFire community site or on the
NightLabs site, which also offers support and services for JFire. Operating System: OS Independent
116.
OhioedgeOhioedge combines CRM and BPM features in a Java-based app. The site is light on documentation, but does include a helpful test drive that lets you see how the software can be used. Operating System: OS Independent
117.
opentapsOpentaps customers include Toyota, Honeywell and other well-known companies, and it supports e-commerce CRM, warehouse and inventory management, supply chain management, financial management and business intelligence. In addition to the free community version, it also comes in a paid professional version or a cloud-based version through Amazon Web Services; consulting and add-on modules are available as well. Operating System: Windows, Linux
118.
Plazma ERP + CRMThis multi-function suite for SMBs offers a lot of CRM capabilities, along with a few ERP functions. The interface is bare-bones but easy to use, and while it comes with quite a bit of documentation, no paid support is available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
119.
TNT ConceptThis app isn't designed to replace existing financial management applications; rather, it works alongside them and adds management and CRM functionality. It's available on an SaaS basis from Spanish company Autentia, which originally developed the software for its own internal use. Operating System: OS Independent.
Open Source Apps: CAD
120.
ArchimedesDesigned for architects, Archimedes is a Java-based CAD program with a fairly minimal feature set. Note that this is different than the GNU Archimedes program for semiconductor design and testing. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
121.
BRL-CADFor more than 20 years, the U.S. military has used BRL-CAD for solid modeling. Key features include interactive 3D solid geometry editing, high-performance ray-tracing support, network-distributed framebuffer support, image and signal-processing tools, path-tracing and photon mapping support, a system performance analysis benchmark suite, an embedded scripting interface, and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others
Open Source Apps: Charts
122.
ChartdroidChartdroid offers developers a native chart engine for Android. It creates bar, donut, line, pie and scatter charts and graphs. Operating System: Android
123.
GraphVizThis graph visualization program takes your text descriptions and turns them into graphical representations. It doesn't handle large graphs as well as aiSee, but works very well for most types of network diagrams. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
124.
HighChartsAlthough the project is only a few years old, this JavaScript-based charting library counts IBM, NASA, Siemens, HP, EMC, CBS, Hitachi, Ericsson, BMW, Nissan, Sony and MasterCard among its customers. It's available with an open source license for non-commercial use or a fee-based license for commercial use. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Chemistry
125.
AvogadroDesigned for advanced students, researchers and professional chemists, Avogadro describes itself as "advanced molecule editor and visualizer designed for cross-platform use in computational chemistry, molecular modeling, bioinformatics, materials science, and related areas." Operating System: Windows, Linux
126.
JmolThis java-based app lets students create diagrams of atoms, molecules, macromolecules, crystals, and more. The site includes a handbook and tutorials for helping you learn how to use the software. Operating System: OS Independent.
127.
KalziumAnother KDE app, Kalzium makes it easy to explore the periodic table. It also includes a molecular weight calculator, an isotopetable, a 3D molecule editor and an equation solver for stoichiometric problems. (Note that in order to use Kalzium on Windows, you'll have to download
KDE for Windows.) Operating System: Windows, Linux
128.
ProtoMolProtoMol is a framework for molecular dynamics simulation. It's designed to be highly flexible, easily extensible, and to meet high performance demands. Operating System: Linux, Unix, Windows.
Open Source Apps: Classroom Management
129.
iTALCIntelligent Teaching and Learning with Computers, aka iTALC, gives teachers the tools they need to manage a computer-based classroom without the high license fees of commercial software. Key features include remote control, demo viewing, overview mode, workstation locking and VPN access for off-site students. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
130.
MandoMando lets you create an interactive whiteboard. If you have your computer connected to a camera and a projector, you can use your laser pointer to control the computer in front of the class, just as you would use a mouse at your desk. Operating System: Linux.
Open Source Apps: Cloud Infrastructure
131.
AppScaleAppScale provides an alternative framework so that you can run apps created for Google App Engine on your private cloud or on a public cloud computing service like Amazon's EC2. It supports applications written in Python, Java and Go, and it works with a wide variety of datastores. Operating System: Linux
132.
CloudStackNow owned by Citrix, CloudStack seeks to enable "simple and cost effective deployment, management, and configuration of cloud computing environments." A commercially supported version is also available. Operating System: Linux
133.
Cloud FoundryVMware's platform as a service project supports Spring, Rails, Node.js, Scala and more. You can download the code or try the online beta service at
CloudFoundry.com. Operating System: OS Independent
134.
EucalyptusShort for "Elastic Utility Computing Architecture for Linking Your Programs To Useful Systems," Eucalyptus aims to help enterprises create their own on-premise private clouds. In addition to the free community version, it also comes in a commercially supported version. Operating System: Linux
135.
OpenNebulaWith more than 4,000 downloads per month, OpenNebula calls itself the "leading cloud management solution." It supports all major hypervisors and private, public and hybrid cloud computing models. Operating System: Linux
136.
OpenStackOriginally backed by NASA and Rackspace, this IaaS project now has 117 corporate supporters, including Dell, AMD, Intel, HP and Cisco. The goal of OpenStack is to offer a standardized set of tools for deploying and maintaining a public or private cloud. Operating System: Linux
137.
ownCloudAs the name suggests, this app lets you set up your "own cloud" so that you can access your stuff from anywhere. The Web interface makes it easy to find your files, music, calendar, contacts and bookmarks when you store them on your own server. Operating System: Windows, Linux
138.
QuantumThis OpenStack incubator project aims to enable network-connectivity-as-a-service for clouds built on the OpenStack platform. Just seven months old, the project already offers an version 1.0 API and a couple of plug-ins. Operating System: Linux
139.
ScalrWith Scalr, you can automatically scale up or down your usage of Amazon Web Services based on demand. The development version is available for free, while production and mission critical versions require a subscription. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Collaboration/Groupware
139.
CollabtiveDesigned as a replacement for Basecamp, Collabtive can even import Basecamp files. You can host it on your own server or use the hosted service. Operating System: OS Independent
140.
cyn.inAvailable as a free app, a hosted SaaS product or a paid enterprise on-premise appliance, cyn.in promises to "help teams to communicate faster and build collaborative knowledge." It offers wikis, social networks, blogs, file sharing repositories, micro blogs, discussion boards, and other tools in a unified framework. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
141.
Group-OfficeGroup-Office features a calendar, file sharing, e-mail, basic CRM capabilities, project management and mobile synchronization capabilities. You can choose to run the free or paid versions on your own mail server, or you can purchase Web-based service on a subscription basis. Operating System: OS Independent
142.
EGroupwareCalling itself "the leading Online Collaboration Tool," EGroupware includes CRM, project management, event management, document management, file server, incident tracking, and more, as well as traditional groupware functionality. Hosted and commercially supported versions are available, or you can download the community version for free. Operating System: OS Independent.
143.
Feng OfficeNow with more than 350,000 users, Feng Office provides Web-based groupware, plus project management, billing, and other features useful to services companies. You can download the free community version or use one of the professional versions on an SaaS basis. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
144.
IGSuiteThe Integrated Groupware Suite, or IGSuite, is another Web-based open source groupware system. In addition to calendaring, e-mail, etc., it also incorporates some basic CRM, ERP and CMS functionality. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix
145.
K-9K-9 is based on the e-mail client in Android, but adds some missing features. Those features include push IMAP support, attachment saving, BCC to self, signatures, flagging and more. Operating System: Android
146.
Open AtriumOpen Atrium describes itself as "a team collaboration tool with a kick of open source hotness." It includes blog, calendar, sharebox, notebook, case tracker and dashboard capabilities. Operating System: OS Independent
147.
phpGroupWareThis Gnu project offers more than 50 separate apps that enterprises can mix and match to meet their own communications needs. Capabilities include contact management, e-mail, calendar, Web content management, document management, project management, bug tracking, and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux
148.
Simple GroupwareThis Outlook-compatible enterprise groupware features email, calendaring, contacts, tasks, document management, project management, cell phone integration, full-text search and a library of extensions. It also uses the sgsML programming language so that in-house developers can build their own Web apps to extend its capabilities. Operating System: Windows, Linux
149.
SparkleShareSparkleShare aims to make it easy to share documents and collaborate on projects. Recently, it's becoming more popular as an alternative to services like Dropbox. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android
150.
TeamLabThis cloud-based app includes project management, business collaboration, document management, calendar, CRM and e-mail capabilities. You can host it on your own server, use the fee-based SaaS service or deploy it on Amazon EC2. Operating System: OS Independent
151.
TUTOSShort for "The Ultimate Team Organization Software," includes group calendar, email, time tracking, document management and project management. In addition, it also offers special features for developers, like a bug tracker, test support and some Scrum tools . Operating System: Linux
152.
ZarafaZarafa is primarily and open source collaboration and e-mail server, but it also offers a mobile device management plug-in that allows companies to remote-wipe lost devices. It runs on a Linux server, but provides e-mail that can be accessed from any browser or from BlackBerry devices. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Communication
153.
ElastixElastix is appliance software for Asterisk-based PBX systems. It combines a lot of the most popular Asterisk tools with a unique interface, utilities, and add-ons for a complete open-source VoIP system. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Compression
154.
7-zipIf you need to compress a file for e-mailing or any other purpose, 7-zip can make your files 30-70 percent smaller than WinZip. In addition, 7-zip can also read and write WinZip files, as well as several other compression formats. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
155.
CaesiumThis helpful app compresses images up to 90 percent, making it easier to e-mail them or upload them to your favorite Web site. It supports most common image formats, including JPG, PNG, GIF, BMP, and WMF. Operating System: Windows
156.
KGB ArchiverThe KGB Archiver offers both good compression and good encryption capabilities, with all files protected by AES-256 encryption automatically. It's also pretty fast, but you will need a fairly robust system in order to use it. Operating System: Windows
157.
PeaZipIf you need to compress, extract or encrypt a file, PeaZip does the job nicely. And it supports a huge number of archive file formats—it creates 12 different types and reads 133 different types. Operating System: Windows, Linux
Open Source Apps: Content Management and Wikis
158.
AIOCPThe All In One Control Panel (a.k.a. AIOCP) combines content management with e-commerce management and a development platform for creating Web apps. Support and services can be purchased from project owner
Tecnick.com.Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
159.
AlfrescoThis all-in-one enterprise content management app combines a Web CMS with document management, records management, and enterprise collaboration capabilities. Besides the open source community version, it also comes in a paid enterprise version or an on-demand cloud version. Operating System: Windows, Linux
160.
ArchonWinner of several awards, Archon simplifies the process of creating a searchable Web site to house archival materials. Administrators can input or edit information via Web forms, and the software automatically uploads and publishes the data. It's currently being used by more than 40 universities, zoos, historical societies, and other institutions. Operating System: OS Independent.
161.
ArmstrongFirst released in 2011, Armstrong is a content management system specifically designed to meet the needs of news organizations. It was developed by The Bay Citizen and the Texas Tribune. Operating System: OS Independent
162.
BIGACEWhile BIGACE is used by many smaller organizations, it's multi-site, multi-language, and multi-user capabilities make it a possibility for larger enterprises looking for a Web CMS. Key features include a WYSIWIG editor, templates and stylesheets, and permission management. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix.
163.
BitweaverBitweaver's claim to fame is a modular design that lets you pick and choose which features you need. Those features include articles, wikis, image galleries, calendar, user management, and more. Operating System: OS Independent.
164.
Daisy CMSJava-based Daisy can be used for Web sites, intranets, product documentation, knowledge bases, and more. It includes both a document repository and a wiki. Operating System: OS Independent.
165.
Devproof PortalDevproof includes modules for blogging, articles, downloads, and more that make it easy to set up your own portal. It's easy to use, but not as popular as some of the other content management systems. Operating System: OS Independent
166.
DotNetNukeUsed by more than 700,000 sites, DotNetNuke is a mature ASP.Net-based CMS with lots of documentation, add-ons, and other help available. It comes in both free community and paid professional and enterprise editions, with training and other services also available. Operating System: Windows
167.
DrupalUsed by Popular Science, New York Observer, The Economist, Harvard, MIT, the White House, MTV UK and hundreds of thousands of other sites, Drupal is one of the most popular Web content management systems available. It offers a huge list of features, and tens of thousands of modules and themes are available to help you customize your site. Operating System: OS Independent
168.
Family ConnectionsIf you love scrapbooking, you might also love setting up a family Web site. This app makes it easy to create a private site for sharing photos, calendars, recipes and keeping in touch with family members. Operating System: OS Independent
169.
Fedora CommonsFedora Commons allows you to manage, preserve, and link different types of digital content. For example, you can use it to create an archive of video, audio, and text files on a particular topic which users can then search or comment on. Operating System: OS Independent.
170.
Get SimpleDownloaded more than 90,000 times, this CMS offers great security, an extremely user-friendly interface, easy "undo," automatic backups and more. Because it's based on XML, it doesn't require a separate database, making it a good option for smaller organizations. Operating System: Linux
171.
ImpressPagesThis CMS's claim to fame is a drag-and-drop interface designed to make it easier for non-technical folks to create Web pages. It's SEO-friendly and based on PHP and MySQL. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android
172.
JoomlaCurrently, 2.7 percent of all websites on the Internet use the Joomla content management system. The latest version offers one-click updating, improved multi-language handling, batch processing of articles, auto-validation of form data and more. Operating System: OS Independent
173.
LiferayDownloaded more than 4 million times, Liferay boasts that it’s the "leading open source portal for the enterprise." Commercial support, training and consulting are available through the site. Operating System: OS Independent
174.
MagnoliaUsed by many Fortune 500 companies, Magnolia offers fast and easy content publishing, scalability, flexibility and proven performance. It comes in fee-based enterprise standard and enterprise pro editions, as well as the community version. Operating System: Windows, Linux
175.
MindTouchUsed by Autodesk, Fujistu, The Washington Post, HTC, Novell and other companies, MindTouch claims to be "the world’s most popular open source collaboration platform." The "Core" version is available under an open source license, while starter, standard and enterprise versions are available for a fee. Operating System: Windows, Linux
176.
Owl Intranet Knowledgebase Owl lets you create a knowledgebase or FAQ site. It's available in both a regular version and an "ultralite" version that does not use a database. Operating System: Windows, Linux
177.
PimcoreWinner of a 2010 Most Promising Open Source Award, Pimcore offers Web content management, product information management, asset management and rapid application development. It's based on the Zend framework and ExtJS. Operating System: Linux, Unix
178.
TomatoCMSTomato takes a widgets-based approach to website design, which makes page layout very easy. Like Pimcore, it's also built on top of Zend. Operating System: Linux
179.
TYPO3Downloaded more than 4 million times, the TYPO3 content management system combines a rich feature set with usability. Key features include multimedia support, detailed user permissions, and scalability. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix
180.
WebGUIThis CMS offers a framework for creating your own Web apps, as well as a full suite of modules, including wikis, photo galleries, message boards, event management, ecommerce, surveys, donations and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix, OS X
181.
Wolf CMSThis newer CMS prides itself on being lightweight, fast and easy to use. However, note that it is easiest to use if you have some PHP coding skills. Operating System: Windows, Linux
182.
XOOPSShort for "eXtensible Object Oriented Portal System," XOOPS has grown far beyond its origins as portal software to support a wide range of sites, from small one-person blogs to large, multi-purpose enterprise websites. It features a modular design and is driven by a MySQL database. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Crafts
183.
Scheme MakerFor crafty types, Scheme Maker takes photos or graphics and turns them into patterns for knitting or cross-stitching. We bet you know someone who would get a kick out being able to put a picture of their favorite dog on a sweater. Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
184.
CitrusDBCitrus is a customer care and billing solution aimed at subscription-based products such as Internet service, telecommunications, and consulting. It tracks customer information, service records, custom billing cycles, and support tickets. Operating System: OS Independent
185.
CiviCRMSimilar to Orange Leap, CiviCRM was particularly designed for advocacy groups, NGOs and non-profit organizations with similar needs. It includes modules for case management, fundraising, event management, membership management, e-mail communications and marketing, and it integrates with both Drupal and Joomla. Operating System: OS Independent
186.
ConcourseSuiteJava-based ConcourseSuite combines CRM with Web content management and collaboration capabilities. In addition to the free community download, it's also available on a paid basis in the cloud. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
187.
CovideCovide promises up to 30 percent improvements in user productivity. In addition to CRM functions, it also includes some CMS, groupware, VoIP, calendar and e-mail functionality. Like Salesforce.com, it's available in a SaaS version. Operating System: Windows, OS X, Unix
188.
Daffodil CRMDaffodil CRM provides a complete picture of the entire customer lifecycle and includes tools for sales force automation, sales forecasting, efficient opportunity tracking, customer satisfaction, and performance management. The Daffodil site primarily promotes the commercially supported version, but you can download the free, open-source version from
SourceForge. Operating System: OS Independent.
189.
openCRXThis CRM solution provides account management, price and product management, groupware, and issue tracking capabilities. You can access it through any browser, and it integrates with most ERP and database applications. Operating System: OS Independent
190.
Orange LeapOrange Leap helps non-profit organizations management their communication with donors, supporters and other constituents. Paid support is also available. Operating System: Windows
191.
SellWinCRMThis CRM tool is designed primarily for your sales force rather than your customer service staff, and includes a phone client that is very helpful for mobile employees. Despite the "Win" in the name this is a multi-platform tool; in this case, "Win" refers to actual sales wins, not Windows. Operating System: OS Independent
192.
SourceTapThis very flexible sales force automation tool helps companies forecast sales, recognize trends, share information and close more deals. It offers dual licensing options, and it can also be purchased on an SaaS basis. Operating System: Windows, Linux
193.
SplendidCRMSplendidCRM tracks accounts, sales, leads, e-mail marketing campaigns, projects, tasks and more. For Windows users only, it can be deployed on-premise in free or commercial versions or used in the cloud on an SaaS basis. Operating System: Windows.
194.
SugarCRM"One of the world's most used CRM systems," Sugar helps you communicate with your customers and manage sales and customer service interactions. If you don't want to host the free version on your own server, you can also purchase on an SaaS basis. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
195.
vtiger CRMUsed by more than 100,000 companies, vtiger offers lead management, support automation, campaign management, inventory management, e-mail integration, and mobile support for a very low total cost of ownership. Download and host it yourself, or use the SaaS version for just $12 per user per month. Operating System: Windows, Linux
196.
X2ContactsNow in beta release, X2Contacts offers sales management with a social-networking focus. It's aimed at SMBs and offers a blog-style interface that makes it easy to see and record sales contacts. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Databases
197.
CassandraThis Facebook-created NoSQL database isn't unknown, but it is new, having finally been released in version 1.0 in October 2011. The 1.0 version offers faster performance, easier use and superb scalability. Operating System: OS Independent
198.
FirebirdFirst created in 1981, this RDBMS boasts "excellent concurrency, high performance, and powerful language support for stored procedures and triggers." Professional support is available through several of the companies that support the Firebird Foundation. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X, Solaris
199.
KexiCalling itself “a long-awaited competitor for programs like MS Access or Filemaker,” KDE's Kexi offers a set of features similar to both applications. Those features include tools for importing files from spreadsheets, Access, CSV files, MySQL or PostgreSQL or for exporting to CSV files, MySQL or PostgreSQL. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
200.
MySQLMany of the open source e-commerce solutions on our list require the MySQL database in order to function. It comes in both a free edition and paid editions which are supported by Oracle. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
201.
RiakRiak isn't exactly a RBDMS, but it isn't exactly NoSQL either. It is a "highly scalable, fault-tolerant distributed database" that's designed for virtualized and cloud environments. In addition to the open source version, it also comes in a subscription-based enterprise version. Operating System: Linux, OS X
202.
PostgreSQLAnother good option for storing your e-commerce data, PostgreSQL claims to be "the world's most advanced open source database." Commercial support and hosting are available through third-party providers. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
203.
VoltDBVoltDB describes itself as "the NewSQL database for high velocity applications." It was recently named one of Gartner's Cool Vendors for 2011. In addition to the free community version, it also comes in several commercially supported versions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Database Administration Tools
204.
MonoQLSimilar to phpMyAdmin, MonoQL offers an Ajax-based Web application for managing SQL databases, including MySQL and Microsoft SQL. Capabilities include database and table design, data browsing, data editing and advanced queries. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Data Destruction
205.
BleachBitBleachBit protects your privacy in several ways: it cleans your cache, erases your Internet history, deletes cookies and gets rid of logs, temporary files and other junk you didn't even know your system was storing. It also includes a "shredder" to eliminate completely all traces of files you want to delete. Operating System: Windows, Linux
206.
Darik's Boot And NukeIf you're getting rid of an old PC or you have other reasons for wanting to destroy all the data on a hard drive, DBAN is for you. It securely deletes all information from all drives it can detect on your system so that those files cannot be recovered. Operating System: OS Independent
207.
Disk CleanerThis small utility cleans all the “junk” out of your temporary files, cache etc. It's also handy for protecting your privacy when using public machines. Operating System: Windows
208.
EraserWhile DBAN erases your entire drive, Eraser securely deletes selected files and folders only. The website suggests it's ideal for eliminating all traces of "passwords, personal information, classified documents from work, financial records, and self-written poems." Operating System: Windows
209.
FileKillerFileKiller works much like Eraser, but it gives the user the option of determining how many times the old data is overwritten. It's also very fast. Operating System: Windows
210.
WipeIf you need a tool like Eraser, but you're running Linux, check out Wipe. It also securely deletes files and folders by writing over the old data several times. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Data Loss Prevention
211.
OpenDLPThis tool for businesses or other organizations with large networks scans all the Windows systems on a network and identifies which systems contain sensitive data. That information is then sent back via a secure connection to a centralized Web app so that administrators or security consultants can see the results. Operating System: Windows
212.
MyDLPAnother tool for larger organizations, MyDLP monitors incoming and outgoing traffic on your network looking for sensitive data leaks. It's available in a free community edition or a paid enterprise edition. Operating System: Windows, Linux, VMware
Open Source Apps: Data Warehouse (DW)
213.
ApatarApatar software helps companies integrate their data from various on-site and on-demand applications, including Salesforce.com, Quickbooks, and others. In addition to the free software, the company offers commercial support, training, and integration consulting services, as well as some on-demand integration services and some pre-built data integration solutions. Operating System: Windows, Linux
214.
DataCleanerDataCleaner profiles, validates, and compares data in order to ensure its quality. It can work with nearly any kind of datastore, including Oracle, MySQL, XML files, Microsoft SQL, Excel spreadsheets, and more. Operating System: OS Independent.
215.
Clover ETLDesigned for those with "modest data transformation and ETL requirements," the community edition of CloverETL makes it easy to move data between different types of databases and spreadsheets. For those with more advanced needs, CloverETL also offers a variety of fee-based versions. Operating System: OS Independent.
216.
KETLThis "premier" extract, transform, load (ETL) tool offers excellent scalability, which allows it to compete against commercial tools. It integrates with most popular security and data management tools. Operating System: Linux, Unix.
217.
LucidDBLucidDB was specifically designed to serve the analytics needs of data warehouse and business intelligence projects. It was created with "flexible, high-performance data integration and sophisticated query processing in mind." Operating System: Windows, Linux.
218.
MailArchivaThis app helps organizations meet their compliance requirements for storing e-mails long term. The enterprise edition adds a number of features not available in the open source edition, as well as offering faster performance for companies with a lot of users. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
219.
TalendThe "recognized market leader in open source data integration," Talend offers a unified platform for data management that includes data integration, data quality and master data management tools. In addition to the free community versions of its products, Talend also offers paid support, training, commercial versions with additional features, and other services. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix.
Open Source Apps: Desktop Enhancements
220.
Classic ShellIf you've upgraded to Windows 7 (or Windows Vista) and miss some of the features from older versions of Windows, this app can bring them back. It gives you a classic start menu, classic explorer, a toolbar in Windows Explorer and many other features. Operating System: Windows
221.
CompizCompiz can be used as either a compositing manager to add fancy effects to your windows or as a full windows manager. Included effects include drop shadows, the desktop cube and expo view. Operating System: Linux
222.
ConsoleFor developers and others who like to work from the command line, Console adds capabilities that aren't available through cmd.exe. For example, it allows users to open multiple tabs, change the font and window style, use a text selection tool, and more. Operating System: Windows
223.
Dave’s Quick Search DeskbarAre the Google deskbar and "I'm feeling lucky" button not fast enough for you? Try Dave's Quick Search Deskbar. It lets you search the Internet without opening a browser first, and it has lots of helpful features that speed up search even more. Operating System: Windows
224.
DropItIf your file system is a mess, DropIt gives you an easier way to clean it up than using the file copy-and-paste capabilities of Windows Explorer. With this app, you can create an icon on your desktop that sends files to the folder of your choice. Just drag your file to icon and it will move the file where you want it to go. Operating System: Windows
225.
Electric SheepOne of the most interesting screensavers ever created, Electric Sheep connects your system to thousands of others around the world to create abstract animations known as "sheep." The name comes from the Philip K. Dick novel Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
226.
EmergeThis replacement for the Windows shell offers a minimalist interface based on applets. It lets users access programs via a right click instead of the Start Menu, and it offers an application launcher and virtual desktop capabilities. Operating System: Windows
227.
EnlightenmentCompatible with both Gnome and KDE, Enlightenment is a fast, modular windows manager. The project also includes a large interface development library, some parts of which are usable on Windows, OS X and other OSes. Operating System: Linux
228.
FlorenceIf you can't use your hands for some reason, or if you spilled Red Bull on your keyboard and are waiting for it to dry out, Florence can help you keep on typing. This app for the Gnome desktop puts a virtual keyboard on your screen that you can click with your mouse. Operating System: Linux, OS X
229.
FluxboxAlthough it's not too flashy, this window manager is lightweight and fast. Key features include tabbing, editable menus, an application dock and more. Operating System: Linux
230.
GeoShellIf you don't like the way your Windows interface looks, GeoShell can replace it with skinnable versions of the start menu, taskbar, system tray, etc. It also requires fewer resources than Windows Explorer, and it has a whole host of plug-ins that can add other features like RSS readers, weather forecasts and more. Operating System: Windows
231.
Google WallpaperIf you get bored having the same image on your desktop for more than five seconds or so, this app might be for you. You type in a keyword, an interval of time and whether or not you want to use "Safe Search." The app then pulls up random pictures from Google and uses them as your wallpaper for the period of time you set. Operating System: Windows
232.
icewmIcewm's stated goals include "speed, simplicity, and not getting in the user's way." It currently supports 25 different languages. Operating System: Linux, OS X
233.
izuluNo window near your cubicle? This app automatically changes the background on your desktop to match current weather and time. Operating System: Linux
234.
Karsten SlideShowLike the “My Pictures Slideshow” screensaver that comes with Windows, this app shows your photos when your desktop is inactive. But unlike "My Pictures" this app makes it easy for you to decide which pictures and videos to include and which to leave out. Operating System: Windows
235.
KWinThe default window manager for the KDE desktop, KWin puts an emphasis on reliability and good looks. The latest version supports compositing, that is, 3D window effects. Operating System: Linux
236.
KysrunMuch like Launchy (below), Kysrun starts your applications or opens bookmarks or documents with a couple of keystrokes. It also starts searches on Google, Wikipedia or IMDB and solves math problems. Operating System: Linux
237.
LaunchyIf you hate to use the mouse, Launchy is for you. It lets you open applications, documents, folders, bookmarks and more with just a few keystrokes. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
238.
LCARS 24If you're a Trekkie with an old PC sitting in your basement or garage, you might want to install this app on that old system. It provides a talking alarm clock and other apps all based on the graphics from the Enterprise's displays. Operating System: Windows, DOS
239.
LotseEscherFans of the artist M. C. Escher will enjoy this animated version of his Print Gallery drawing. If you like it, you may also like this developer's other screensavers: LotsaGlass, LotsaSnow and LotsaWater. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
240.
MatrixglFor those who love the Matrix movies, this screensaver features falling green characters that create images of characters from the The Matrix Reloaded. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
241.
MetacityThe default window manager for Gnome 2.x, Metacity is designed to be as usable and unobtrusive as possible, and might be described as a little plain. The project owners themselves say, “Many window managers are like Marshmallow Froot Loops; Metacity is like Cheerios.” Operating System: Linux
242.
Pixel CityThis app generates new night-time cityscape artwork every time it runs. Check out the demonstration video link on the site to see how it works. Operating System: Windows
243.
PNotesThis fast and lightweight app lets you leave yourself virtual sticky notes on your desktop. It also offers features like scheduling, audio notes, encryption, password protection, tabs, smilies, transparency and more. Operating System: Windows
244.
Really Slick ScreensaversIf you're looking for a screensaver that's a little bit out of the ordinary, check out Really Slick. It includes a dozen different colorful (and sometimes nausea-inducing) screensavers. Operating System: Windows
245.
SharpEnviroFormerly known as "SharpE," SharpEnviro makes the desktop highly configurable, including the option of having up to 20 different toolbars. It supports multiple monitors and is very easy to use. Operating System: Windows
246.
Startup ManagerThis app lets the user control which applications and processes start up when you turn on your system. It's particularly useful if you'd like to speed up the process or if you always open the same programs. Operating System: Windows
247.
StickerSticker is a Windows 7-compatible electronic post-it note app. Unlike some similar apps, it lets you put notes directly on the desktop as if they were icons. Operating System: Windows
248.
topBlockThis screensaver's graphics aren't as impressive as some of the others on our list, but it's fun if you like Lego blocks. Operating System: Windows
249.
Wikiquote ScreensaverIf you prefer a screensaver that's a little more philosophical, check out this app. You type in a topic and press save, and it will pull up random Wikiquotes on the topic. Operating System: Windows
250.
WallyLike the Google Wallpaper app, Wally changes out the photo on your screen after a set period of time. But this app let's you pick photos from your own hard drive or from remote sources like Google, Flickr, Yahoo, Photobucket and many others. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
251.
WhorldWhorld generates interesting geometric patterns that can be used for a screensaver or for VJing. It gives you a huge number of options and controls, and you can even extend them by using one of the downloadable patches or creating a patch of your own. Operating System: Windows
252.
VirtuaWinMost Linux/Unix windows managers make it easy to switch between desktops, but to accomplish the same thing on Windows, you usually have to log out and log back in as another user. This app lets you save up to nine different desktops and switch between them quickly. It's helpful if you're multi-tasking and need one set of apps for one project and other set for a different project. Operating System: Windows
253.
WindowsPagerWindowsPager offers very similar functionality as VirtuaWin, with a different interface for switching between workspaces. Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Desktop Publishing
254.
MiKTeXAn update of TeX, MiKTeX is a typesetting program with a complete set of fonts, utilities, and macros. According to the original developer, it was "intended for the creation of beautiful books—and especially for books that contain a lot of mathematics." Operating System: Windows, Linux
255.
ScribusSuitable for professional designers, Scribus desktop publishing offers features like color separations, ICC spot color support and PDF creation. Despite the advanced features, there is plenty of help available, so it's also suitable for amateurs. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X
256.
SiSUAfter creating documents in the text editor of your choice, you can use SiSU (Structured information, serialized units) to publish them in the format of your choice and make them searchable. Supported formats include plain-text, HTML, XHTML, XML, ODF, LaTeX, and PDF. Operating System: Linux/Unix
Open Source Apps: Desktop Search
257.
BeagleIf you don't know the name of the file you're looking for, Beagle can help you find it. It indexes and searches the text of your documents, emails, web history, IM/IRC conversations, contacts, calendar, and other files to find the keywords you're looking for. Operating System: Linux
258.
DocFetcherInstead of wasting time searching every file on your system, DocFetcher searches only your documents for the keywords you enter. It supports plain text, html, Microsoft Office, OpenOffice.org, AbiWord, pdf and several other types of files. Operating System: Windows, Linux
259.
PinotPinot combines both desktop search and Web search into a single app. It also allows advanced queries (probabilistic search, boolean filters, wildcards, date ranges, time and size) and supports Chinese, Japanese and Korean text searches. Operating System: Linux
230.
RecollRecoll can search the text of most document types, including e-mails, attachments and compressed files. It supports a variety of query types, and it provides a preview of searched documents. Operating System: Linux
231.
TrackerPart of the Gnome desktop, Tracker combines traditional search by name and file location with more advanced search capabilities that let you look for document text or tags. If you choose, you can use it to add metadata tags to all of your files, which makes it easier to organize your files and find what you're looking for. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Developer Tools
232.
AmdatuStill in the very early stages of development, Amdatu offers a "rapid application development platform and runtime for open, service oriented and cloud-aware Web applications." It leverages several Apache Foundation tools and is built on Java. Operating System: OS Independent
233.
Anjuta DevStudioGNOME's IDE supports C and C++ development on Linux systems. It includes an application wizard, interactive debugger, source code editor, version control, GUI designer and more. Operating System: Linux
234.
Appcelerator TitaniumTitanium helps create apps that work not only on the largest mobile platforms, but also on all of the major desktop platforms. It supports HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Ruby, and Python. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS, Android
235.
ATPadThis Notepad replacement includes a number of features for developers, like a tabbed interface, line numbering, word wrapping, text coloring and more. It's won a number of awards. Operating System: Windows.
236.
Cloud9 IDELaunched in 2010, the Cloud9 IDE offers an online alternative to Eclipse for JavaScript development. It also supports HTML/CSS, Coffeescript, Ruby, PHP and other programming languages. The source code is available, and Cloud9 offers the IDE on a development-as-a-service basis, with a free subscription available for open source developers. Operating System: OS Independent
237.
Code::BlocksThis cross-platform C++ IDE is highly extensible, making it easy to add the features you want. It includes built-in compiling and debugging capabilities, plus an easy-to-use interface. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
238.
DartFirst unveiled in October of 2011, Dart is Google's new programming language designed as an alternative to JavaScript. Currently, the company is seeking feedback on the language, which is still in the very early stages of development. Operating System: OS Independent
239.
Dev-C++Dev-C++ is a C/C++ IDE with support for all GCC-based compilers. Key features include integrated debugging, project management, customizable syntax editor, code completion and others. Operating System: Windows
240.
EclipseIn addition to the well-known Java IDE, the Eclipse site offers a number of other development tools and educational materials. You'll also find plug-ins that extend its capabilities to support C, C++, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, and other programming languages. Operating System: OS Independent
241.
EvolutilityWith Evolutility, users can build custom Web apps in just minutes, without writing any C#, HTML, CSS, Javascript, or SQL. If you have a database, this app can put it on the Web quickly and easily. Operating System: Windows.
242.
Game EditorIf you're not really a programmer, but you think you have an idea for a game that might be the next big hit on the iPhone, this tool might help. It's a cross-platform game creator, and the site offers advice for those just starting out. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS, others.
243.
FLOW3Very recently released in version 1.0, FLOW3 is a PHP development framework from the creators of the TYPO3 content management system. It's designed to support the principles of Agile development, Domain Driven Design, Extreme Programming and Test-Driven Development. Operating System: Windows, Linux
244.
GCCThe "GNU Compiler Collection" offers front ends and libraries for C, C++, Objective-C, Fortran, Java, and Ada. It's probably the most widely used compiler for code that will run on multiple operating systems. Operating System: OS Independent
245.
GestaltGestalt offers a developers a way to write Ruby and Python scripts in in (X)HTML pages. It's SEO-friendly and lets you use some advanced HTML5 technologies on your Web apps. Operating System: OS Independent
246.
GladeGlade lets developers quickly create interfaces for the GTK+ toolkit and the GNOME desktop environment. It saves those interfaces in XML so they can be accessed by applications written in a wide variety of programming languages. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
247.
HibernatePart of the JBoss Enterprise Middleware Suite, Hibernate provides object/relational persistence for Java and .NET. It also includes the ability to write queries in SQL or the Hibernate version of SQL (HQL). Operating System: OS Independent
248.
Intel Threaded Building BlocksThis library helps C++ developers take advantage of the benefits of multi-core processing systems, even if they don't know a lot about threading. It's available in both a commercial and an open source version. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
249.
IPFacesThis tool aims to make it faster, easier and cheaper for experienced ASP.Net, Java or PHP developers to create native form-oriented apps. Commercial support, training and other services are available. Operating System: OS Independent for the developer; creates apps for iOS and BlackBerry
250.
JavadocJavadoc uses the comments you embed in your Java code to create an HTML documentation file. By default it describes the public and protected classes, nested classes (but not anonymous inner classes), interfaces, constructors, methods and fields. It's included in Oracle's Java developer kits. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
251.
JoThis HTML5 mobile app framework creates both Web and native apps for iOS, Android, webOS, BlackBerry and Chrome OS. It relies heavily on CSS3, and it works with PhoneGap. Operating System: iOS, Android, webOS, BlackBerry, Chrome OS
252.
jQueryjQuery calls itself "the write less do more JavaScript library," and that's a pretty apt description. It simplifies HTML document traversing, event handling, animating, and Ajax interactions for rapid web development. Operating System: OS Independent
253.
JQTouchThis jQuery plugin enables mobile Web development for the iPhone and Android devices. It's easy to install, customizable and offers theme support. Operating System: iOS, Android
254.
KDevelopKDE's integrated development environment (IDE) includes a source code editor, project managers, GUI designer, front ends for the GNU Compiler Collection and GNU Debugger, and more. It offers code completion for C/C++, as well as some support for Perl, Python, PHP, Java, Fortran, Ruby, Ada, Pascal, SQL, and Bash. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
255.
KurogoA fork of the MIT Mobile Framework, Kurogo is a new mobile development platform with a focus on "clean integration, exceptional user experience and deep customization." It comes in two versions: one for mobile Web apps and one for iOS. Operating System: OS Independent
256.
Lazarus Lazarus offers a complete and easy-to-use programming environment for FreePascal. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, FreeBSD
257.
MinGW"Minimalist GNU for Windows" ports the GCC compilers and GNU Binutils for Windows. It allows you to use GNU tools to build Windows apps from Windows or Linux systems. Operating System: Windows, Linux
258.
MonoDevelopDesigned for .NET developers, this IDE from Novell makes it easier to create C# applications for multiple platforms. It also supports Java, Boo, Visual Basic.NET, Oxygene, CIL, Python, Vala, C and C++. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
259
MoSync SDKWith MoSync, you can build cross-platform mobile apps with familiar tools—C or C++ and the Eclipse IDE. Commercial support and training are also available. Operating System: Android, iOS, Windows Mobile, Symbian
260.
MUSCLEMUSCLE stands for "Multi-User Server Client Linking Environment." In a nutshell, it makes it possible for cross-platform applications to communicate with each other over the network. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, BSD
261.
NetBeansAlthough known as a Java tool, NetBeans also supports JavaFX, PHP, JavaScript, Ruby, Groovy, Grails and C/C++. Its goal is to help users quickly develop web, enterprise, desktop, and mobile applications. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
262.
Nette FrameworkNette Framework promises developers "you will write less, have cleaner code and your work will bring you joy." It's a PHP-based framework for writing Web applications, and it supports AJAX, SEO, DRY, KISS, MVC and code reusability. Operating System: Windows, Linux
263.
NuGetThis extension for Microsoft's Visual Studio makes it easy to install and update open source libraries for the .NET platform. And the
NuGet Gallery makies it easy to find those open source libraries. Operating System: Windows
264.
Open64Formerly known as Pro64, Open64 was created by Intel and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. It includes compilers for C, C++ and Fortran90/95 compilers for the IA-64 Linux ABI and API standards. Operating System: Linux
265.
Open BlueDragonIf you'd like to create Web apps using the ColdFusion Markup Language (CFML), but don't want to spend thousands of dollars on your development tool, Open BlueDragon gives you an open source option. It describes itself as "the world's first truly open source GPL Java and Google App Engine CFML runtime." Operating System: Windows, Linux
266.
OWASPThe “Open Web Application Security Project” includes a number of documents, applications, and tools for developers concerned about app security. Key projects include WebGoat, ESAPI Security Library for Java, and numerous standards and guides. Operating System: OS Independent
267.
PhoneGapPhoneGap claims to be the "only open source mobile framework that supports six platforms." It allows you to use HTML5 and JavaScript to create truly cross-platform apps that are able to access the native features of the various smartphone platforms. Operating System: requires OS X for the developer; creates apps for iOS, Android, BlackBerry WebOS, Symbian, Bada
268.
php ClamAVThis package allows you to incorporate the ClamAV engine into your PHP5 scripts. Operating system: Linux
269.
phpDocumentorLike Javadoc, phpDocumentor turns code comments into readable documentation for users, only in this case for the PHP language instead of for Java. It's very fast and includes a variety of templates. Operating System: OS Independent
270.
phpMyAdminWritten in PHP, this utility handles the administration of MySQL over the Web. phpMyAdmin performs many database administration tasks like running SQL statements, adding and dropping databases, and adding, editing or deleting tables or fields. Operating System: OS Independent
271.
PrototypeThis JavaScript framework tries to make it easier to create dynamic Web apps. It offers a class-style OO framework, easy DOM manipulation, and what it humbly calls "the nicest Ajax library around." Operating System: OS Independent
272.
RestkitThis Objective-C framework "aims to make interacting with RESTful web services simple, fast and fun." It uses an API and a object mapping system to help reduce the amount of code you need to write when creating apps for the iPhone or iPad. Operating System: iOS
273.
RhodesDesigned for enterprise application developers, Rhodes is a Ruby-based framework that enables developers to write applications once and turn them into native apps for each of the various platforms. Commercial support is available and the company behind the project (Rhomobile) offers a number of other related enterprise mobility solutions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X for the developer; creates apps for iPhone, Android, Windows Mobile, BlackBerry, Symbian, Windows Phone 7
274.
Ruby on RailsDesigned for rapid application development using Agile methodologies, Ruby on Rails offers "Web development that doesn't hurt." It's used by the developers behind thousands of apps, including Twitter, Basecamp, Github and Groupon. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
275.
Sencha TouchThis mobile JavaScript framework assists in the development of mobile Web apps that look and feel like native apps for iPhone, Android or BlackBerry. Note that it only supports WebKit browsers like Chrome and Safari. Operating System: OS Independent
276.
SharpDevelopLike MonoDevelop, SharpDevelop (or #develop) was created as an alternative to Visual Studio for Microsoft's .NET platform. It supports C#, VB.NET and Boo. Operating System: Windows
277.
soapUIWith more than 2 million downloads, soapUI claims to be the most popular Web services and SOA testing tool in the world. It performs functional testing of SOAP, REST, HTTP, and JMS services, as well as databases. Operating System: OS Independent
278.
SonarIn its first year of release, this Web-based platform for managing code quality quickly racked up 30,000 downloads. Now in its second year, Sonar gets 4,000 downloads per month and is notable for its ease of use and excellent reporting tools. Operating System: OS Independent.
279.
Ultimate++This rapid application development framework includes both a C++ library and an IDE designed to handle large applications. Its emphasis is on speeding up the development process and includes "BLITZ-build" technology that makes C++ rebuilds up to four times faster. Operating System: Windows, Linux
280.
WakandaAccording to its website, Wakanda is "an open source platform for building business Web applications with nothing but JavaScript." It's still in preview status, but is already getting kudos from end users for its ability to speed up and simplify the business application development process. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
281.
wxWidgetsThis cross-platform development toolkit enables programmers to write applications in C++, Python, Perl, and C#/.NET that work on several different operating systems. In addition to an easy-to-use GUI, wxWidgets offers online help, streams, clipboard and drag and drop, multithreading, database support, HTML viewing and printing, and many other features. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix, OS X
282.
XML Copy EditorXML Copy Editor doesn't have as many features as some comparable apps, but it is very fast and lightweight. It's simplicity also makes it easier to use than some of the more feature-heavy applications. Operating System: Windows, Linux
283.
ZendZend offers both a Web application server (Zend Server) and an IDE (ZendStudio) for PHP developers. Both are available in free, open source or paid versions, and the company also offers training and some additional commercial products and services. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
284.
ZKZK claims to be the "leading enterprise Java Web framework," and it supports the development of both Web and mobile apps. It's been downloaded more than 1.5 million times. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Dictionary/Translation Tools
285.
GlobalSightGlobalSight is a translation management system designed to streamline the process of localizing content for multi-national organizations. It's available on an SaaS basis, with prices that vary depending on the number of translation vendors you need to track. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
Open Source Apps: Diet/Exercise
286.
iDietTrying to decide which diet to try? iDiet makes it easy to compare a lot of different diets, including Atkins, Summer Fresh, The Zone, Body for Life, Jenny Craig, based on nutritional guidelines. Once you pick a diet, the Java-based app helps you set goals and track your progress. Operating System: OS Independent
287.
SportsTrackerNo matter what sport you participate in (running, cycling, lifting weights, tennis, etc.), SportsTracker can help you track your training plan, type of activity, body weight, time spent exercising, etc. It also integrates with several brands of heart rate monitors, so you can track your heart rate data as well. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Distributed Computing
288.
HadoopHadoop offers a variety of tools for working with large amounts of data in distributed computing environments. Notable users include Yahoo, Facebook, Google, Hulu, IBM, LinkedIN, The New York Times and others. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Document Management Systems (DMS)
289.
EpiwareAthough it primarily offers Web-based document management, Epiware also includes project management capabilities, as well as group calendaring, wikis and a newsfeed. Commercial support is also available. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
290.
InforamaWith Inforama, you can create document templates, import data from databases and spreadsheets, create PDFs, and automatically store documents in a central repository. It's available in a Community Edition (for a single machine) or an Enterprise Edition, both of which are free and open source. Operating System: OS Independent.
291.
KnowledgeTreeThis Web-based collaboration and file sharing tool offers features like search and preview, workflow and document alerts, Microsoft Office integration, document auditing, electronic signatures, scanning and capture, and more. It's available in five different cloud-based options, as well as the free open-source
community edition. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
292.
LogicalDOCLogicalDOC aims to make it easy for workers to collaborate on and share all types of documents. Features include version control, a task manager, Outlook integration, and smartphone support. Operating System: OS Independent.
293.
OpenDocManLike many others in this category, OpenDocMan includes automated workflow capabilities, as well as search, security, file expiration, revision history and more. You can download and host it for free or purchase it on an SaaS basis. Operating System: OS Independent.
294.
OpenKMThis document management system includes a JBPM workflow capability to make sure your files get routed for the appropriate sign-offs and approvals. It offers advanced search and security capabilities, and professional-level support is available for a fee. Operating System: OS Independent.
Open Source Apps: Earth Science
295.
Seismic Toolkit (STK)This app makes it easier for scientists and researchers to analyze data from seismic events. It includes tools for filtering and plotting data, evolutive polarization, and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Open Source Apps: eBook Reader
296.
FBReaderWant to read an e-book, but don't have a Nook, Kindle or iPad? This ebook reader supports multiple file formats and works on netbooks and Linux-based PDAs, as well as desktops. Operating System: Linux, Windows, BSD
Open Source Apps: E-Commerce
297.
Broadleaf CommerceJava-based Broadleaf claims to be "the most cost-effective enterprise e-commerce solution available." While Broadleaf does not offer commercial support directly, consulting firm
Credera does offer support and related services. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
298.
dashCommerceWith tens of thousands of downloads every year, dashCommerce is a very popular e-commerce engine. It offers a drop-in provider model for payment, shipping, tax and coupon providers; unlimited products; single-page checkout and more. Operating System: Windows
299.
DigistoreBased on osCommerce (see below), Digistore offers a full list of e-commerce features and requires no coding knowledge to set up and manage. Customization and consulting are available from the Digistore team, and the site also includes links to third-party vendors who offer hosted solutions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
300.
EclimeBased on osCommerce, Eclime offers fast performance and a template-based design that's difficult to mess up. It also offers SEO capabilities, media playlist support, wishlists and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
301.
eShopThis WordPress plug-in offers good, basic e-commerce features, but lacks some of the more advanced features in other e-commerce solutions. It does integrate with most payment processing systems. Operating System: OS Independent
302.
Fishop.NETThis ASP.Net-based package offers a "no frills" solution that is easy to install and highly customizable. It's also available on an SaaS basis (with prices in Euros). Operating System: Windows
303.
Free Simple ShopAs the name implies, this project offers a simple shopping cart engine that can be incorporated into more complex sites. It's based on PHP and MySQL, and it integrates with Google Analytics. Other features include an inventory control system, support ticket system, automatic payment notifications, search-friendly URLs and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
304.
InterchangeInterchange has been around since 1995, and it supports a wide range of uses, including sales, content management, customer service, reporting and analysis, personalization, B2B, parts re-ordering, auctions, supply chain management, project management, online collaboration and even an MP3 jukebox. Professional support is available from a variety of third-party partners. Operating system: Linux, OS X
305.
JadaSiteJava-based JadaSite offers enterprise-class e-commerce features like BIRT reporting, product import/export, AJAX-based components, a WYSISYG editor, multi-currency, multiple language support and more. Paid support packages are not available, but JadaSite does offer consulting services for installation, customization, upgrades, etc. Operating System: OS Independent
306.
JAllInOne eCommerceThis eCommerce platform is designed to integrate with the JALLInOne ERP/CRM suite. Key features include fast search, catalog browsing, support for promotions and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
307.
JigoshopAnother plug-in for WordPress, Jigoshop boasts lightweight code, advanced reporting and "out-of-the box awesomeness." Paid support is available. Operating System: OS Independent
308.
MagentoAcquired by eBay earlier this year, Magento boasts more than 100,000 users, including OfficeMax, Harbor Freight Tools, K-Swiss and The North Face. It's available in three different editions—free community and paid professional and enterprise—as well as a hosted SMB solution called Magento Go. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
309.
Modern MerchantDescribing itself as "smart and simple," Modern Merchant offers a no-frills, easy-to-use e-commerce shopping cart. It's easy to install and extensible with a variety of plug-ins. Operating System: Linux
310.
nopCommerceOne of the few .NET-based open source e-commerce options, nopCommerce is highly customizable with a pluggable architecture. It was designed to be search-engine-friendly and gets high marks for usability. Operating System: Windows
311.
OpenCartNominated for a 2011 Packt Publishing award, OpenCart offers a long list of features and user-friendly operation. Commercial support is available from a variety of international third-party partners. Operating system: Windows, Linux, OS X
312.
Order PortalAimed at manufacturers, distributors and rental companies, Order Portal is best for established companies that are looking to add an online presence. It also integrates with a larger Web Business Suite available from the same company. Operating System: Linux
313.
osCMaxAnother osCommerce fork (see below), osCMax aims to be easy enough for small startups and advanced enough for larger operations. It offers unlimited products and categories, vouchers and coupons, Web-based administration, support for multiple payment processors, spreadsheet-based data entry and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux
314.
osCommerceMore than a decade old, osCommerce powers nearly 13,000 online shops. Highly customizable, it offers more than 6,700 free add-ons to extend its capabilities. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
315.
Oxid eShopThis flexible e-commerce solution offers marketing integration, search engine optimization, easy admin management, an integrated CMS, couponing, reviews, ratings and more. In addition to the community version, it also comes in paid professional and enterprise versions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
316.
PliciThis French project offers a "powerful and extensible" e-commerce solution. Check out the website for a helpful demo of Plici in action. Be warned that much of the documentation is in French, but English translations are available. Operating System: Windows, Linux
317.
PrestaShopWinner of the 2010 Packt Best Open-Source E-Commerce Application Award, PrestaShop runs more than 100,000 e-commerce shops worldwide. Commercial support, training, customization and other services are available through the site. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
26.
SatchmoDjango-based Satchmo calls itself "the webshop for perfectionists with deadlines." The site offers links to more than 100 stores created with the software, so you can see it in action for yourself. Operating System: Linux, OS X
318.
Self CommerceA German project, Self Commerce is based on xt:Commerce (see above) and the Smarty template engine. Much of the website documentation is in German, but English versions of the software are available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
319.
SimpleCart (js)This very lightweight (under 20kb) JavaScript-based shopping cart offers very fast setup and doesn't require a separate database. However, in order to use it, you will need to know HTML. Operating System: OS Independent
320.
SpreeThis newer e-commerce platform calls itself "the world's most flexible." In addition to the free download, it's also available as a Rackspace-powered SaaS solution, and the site also offers discounts and easy sign-up for payment processing. Operating System: OS Independent
321.
Tomato CartThis fork of osCommerce (see below) includes unlimited product categories, a review and ratings system, search box with auto-completion, product image zoom, 26 built-in payment methods, one-page checkout and more. Hosting with support is available from several third-party partners. Operating System: Windows, Linux
322.
UbercartUbercart is an e-commerce add-on for the Drupal content management system. It offers a configurable product catalog, single page checkout, anonymous checkout, an integrated payment system and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
333.
VirtueMartThis add-on for the Joomla CMS offers advanced features like encryption, flexible tax models, shipping address management, multiple currencies and languages and more. The site has a demo and a number of links to live shops that use its shopping cart engine. Operating System: Winodws, Linux, OS X
334.
WordPress eCommerce Plug-InDownloaded more than 1.3 million times, WordPress's eCommerce plug-in is a tried and true way to add e-commerce capabilities to your blog. Support, additional themes and other features and services are available for a fee. Operating System: OS Independent
335.
X-CartDownloaded more than 400,000 times, X-Cart is 100% PCI-DSS compatible, SEO-friendly, and it supports many payment processers and shipping carriers. In addition to the free community version, it also comes in paid Pro and Gold editions, with additional modules and services available for sale as well. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
336.
xt:CommerceSmarty-based xt:Commerce is a mature, German e-commerce solution with an English version available. In addition to the free community version, it also comes in premium supported versions with prices in euros. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
337.
Zen CartDesigned by "a group of like-minded shop owners, programmers, designers, and consultants," Zen Cart puts the emphasis on ease of use. Key features include a newsletter manager, support for coupons and gift certificates, XHTML templates, multiple payment and shipping methods and more. Operating System: OS Independent
338.
ZenMagickThis fork of Zen Cart (see below) offers features like unlimited products and categories, multi-currency and multi-language support, extensibility and simple PHP-based templates. Commercial support is available through Mixed Matter. Operating System: OS Independent
339.
ZeuscartThis open source shopping cart boasts a rich interface, good usability, comparison-driven shopping, SEO-friendly URLs, gift cards, coupons and more. Paid support services, including installation and upgrade help, are available. Operating System: Windows, Linux
Open Source Apps: Educational Testing
340.
Safe Exam BrowserIf you're worried about your students cheating during a test, this app locks down the browser. While it's activated, it runs in fullscreen mode and prevents students from access other apps, the Internet, shortcuts, etc. Operating System: Windows
341.
iTestWith iTest, teachers can easily give students different versions of the same test because all questions can be drawn at random from a database. The website includes a large library of screenshots that show exactly how the software works. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
342.
TCExamClaiming to be "the most commonly used free CBA software in the world," this Web-based testing program greatly simplifies the process of creating, administering and grading tests. It's free for non-commercial use, or you can purchase a commercial license that includes support. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Elementary Education
343.
ChildsPlayFor pre-school to kindergarten aged children, ChildsPlay includes 14 simple games, most of which teach numbers, letters, etc. It also includes some "just for fun" games like versions of Pacman and Pong. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
344.
GComprisDesigned for children up to age 10, GCompris includes 100 separate games and educational programs. For example, it includes geography, math, reading, and science games, as well as chess, memory, connect 4 and Sudoku. Operating System: Windows, Linux
345.
GPaintFor older children, GPaint offers a step up that is easier to use than professional drawing programs without being too childish. It's part of the Gnu desktop. Operating System: Linux
346.
KLettresBecause you're never too young for open source, KLettres teaches preschoolers to identify letters and their sounds. It also includes a "grown-ups" mode that aims to teach adults the basic building blocks of 25 different languages. (Note that in order to use KLettres on Windows, you'll have to download
KDE for Windows.) Operating System: Windows, Linux
347.
Little WizardIf you’re the kind of parent who believes children are never too young to learn how to code, check out this development environment for the grade-school crowd. Using only the mouse, Little Wizard users learn about programming concepts like variables, expressions, loops, conditions, and logical blocks. Operating System: Windows
348.
TuxMathIn this game, players solve arithmetic problems in order to prevent meteors from smashing Tux the penguin in his igloo. It offers a variety of types of problems for students with different skill levels. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
349.
Tux PaintAnother app for elementary and preschool students, Tux Paint is a kid-friendly drawing program. Features include a variety of drawing tools, fun stamps and silly sound effects. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: E-mail
350.
EvolutionOften called "the Outlook of Linux," Evolution offers e-mail, calendar and other capabilities from an interface that looks a lot like the Microsoft product. Other notable features include built-in spam filtering, advanced search capabilities, encryption support, and iCalendar support. Operating System: Linux
351.
Thunderbird with
LightningMade by Mozilla, the organization behind Firefox, Thunderbird is a tabbed, searchable e-mail client with an emphasis on customization capabilities. If you want an integrated calendar, you'll also need to download the Lightning add-on. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
352.
ZmailZmail describes itself as a "fake e-mail program" that allows you to send e-mail from anyone to anyone. It's useful for testing mail servers or for sending e-mail without using your regular account. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: E-mail Marketing
353.
OpenEMMOpenEMM boasts that it offers 95 percent of the features of commercial e-mail marketing software, as well as some features the commercial products don't have. A hosted version is available through
Agnitas. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
354.
phpListThe "world's most popular open source email campaign manager" has launched a beta of its new hosted service. For now, users can send up to 300 messages per month (50 per day) for free through the hosted service. The full-featured paid version is slated to launch before the end of the year. Operating System: OS Independent.
Open Source Apps: Encryption
355.
APGShort for "Android Privacy Guard," APG ports the OpenPGP encryption software for Android devices. Use it to encrypt, decrypt and sign files and e-mail. Operating System: Android
366.
AxCryptUsed by more than 2.2 million people, AxCrypt calls itself the "leading open source file encryption software for Windows." It integrates seamlessly into the Windows File Explorer—just right-click to encrypt a file and protect it with a password, or double-click to decrypt. Operating System: Windows
377.
CryptThis encryption tool is extremely lightweight (44KB) and fast, and you don't have to install it to use it. However, that speed and light weight is due to the fact that it doesn't have a GUI, so you'll need to be comfortable working from the command line ot use it. Operating System: Windows
378.
FreeOTFEShort for "free on the fly encryption," this tool creates encrypted virtual disks on your hard drive. It can run from a thumb drive, and it supports multiple hash and encryption algorithms. Operating System: Windows
379.
Gnu Privacy GuardGnuPG (aka GPG) allows Linux users to sign and encrypt their data or digital communications. This is a command line tool, but several front ends (including some we've featured on this list) are available. Operating System: Linux
380.
GPGToolsThis project ports GPG for Mac users. Note that not all of the features will work with OS X Lion yet. Operating System: OS X
381.
Gpg4winAs you can tell by the name, this version of GPG encrypts files and e-mail on Windows systems. This version is a little bit easier for the less technically inclined to use than some of the others. Operating System: Windows
382.
LUKS/cryptsetup"Linux Unified Key Setup" or "LUKS" provides a standard format for hard disk encryption that works on all Linux distributions. The cryptsetup project makes LUKS usable on the desktop. Operating System: Linux
383.
MailCryptThis app applies PGP or GnuPGP encryption to your e-mail and Internet usage. If you use Windows NT, be sure to read the warning note on the Web site. Operating System: OS Independent
384.
MCryptThis replacement for the Unix crypt allows developers to add a wide range of encryption functions to their code, even if they don't know a lot about cryptography. The Web site contains a list of supported algorithms that are included in the Libmcrypt library. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix
385.
NeoCryptMuch easier to use, NeoCrypt offers right-click integration with Windows Explorer. It supports 10 different encryption algorithms, including AES and BlowFish, and it offers batch encryption capabilities. Operating System: Windows
386.
Open SignatureThis digital signature project supports all Open SC cards and aims to be the first single app that can be used with cards from multiple countries. Open Signature originally focused on cards used in Italy but has branched out. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix
387.
SecureFoldersAs you might guess from the name, this app lets you secure your folders. It gives you the option of hiding, locking, and/or encrypting folders to keep them safe from prying eyes. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
388.
SteghideIf you really want to feel like a spy, you can use Steghide to conceal hidden messages in audio or text files. It works with JPEG, BMP, WAV and AU files. Operating System: OS Independent
389.
TrueCryptDownloaded nearly twenty million times, this popular encryption tool can protect an entire drive or an entire partition of a drive. And its parallelization and pipelining techniques mean you won't notice any performance delays on your encrypted drive(s). Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
390.
Apache OFBizIn addition to e-commerce and ERP functionality, the Apache Open for Business Suite includes CRM, supply chain management, enterprise asset management, point-of-sale and other capabilities. It offers small businesses advanced e-commerce features along with excellent flexibility. Operating System: OS Independent
391.
EdgeERPThis fork of WebERP (see below) offers flexibility and the ability to integrate with many other types of software. Small businesses can use it to manage sales quotes, orders, invoicing, receivables, inventory, purchases, payables, banking, and general ledger accounting. Operating System: OS Independent
392.
ERP5In addition to ERP functionality, this app adds CRM, MRP, SCM, accounting, HR and PDM capabilities. It comes in a version for mobile phones, and it also available in commercially supported and SaaS versions. Operating System: Linux
393.
NeogiaThis French ERP suite includes B2B and B2C e-commerce capabilities. It's designed for small to mid-size companies. Operating System: Windows, Linux
394.
OpenbravoWith more than 2 million downloads, Openbravo boasts that it is the "world’s leading Web-based open source ERP solution." In addition to the free community version, it also comes in paid basic and professional editions that can be deployed on-site or in the cloud. Operating System: OS Independent
395.
OpenERPThis full-featured app includes modules for CRM, accounting, point of sale, project management, warehouse management, human resources, purchasing, manufacturing, marketing, invoicing and an application builder. It's available in a free community edition, a paid enterprise edition for on-site deployment, or a subscription-based online edition. Operating System: Windows, Linux
396.
]project-open[Used by more than 1,000 companies around the world, project-open (or "po") combines ERP and project management functionality. The core modules are free, but additional modules and support require a fee. Operating System: Windows, Linux
397.
Postbooks/xTuple ERPxTuple's ERP suite includes accounting, sales, CRM, purchasing, product definition, inventory and distribution, light manufacturing and reporting capabilities. The Postbooks edition is available with either an open source or a commercial license, and the Standard, Project, Manufacturing or Enterprise editions are available only with a commercial license. It's also available in the cloud, and information about other related services is also on the website. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X
398.
SQL-LedgerAnother Web-based application, SQL-Ledger features double-entry accounting and ERP features and, as you might guess, stores data in a SQL database server. Paid support is available at a variety of price points. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
399.
webERPThis popular app is downloaded an average of 5,000 times per month. While it can be used by any type of business, webERP is particularly well suited to the needs of wholesalers, distributors and manufacturing companies. Commercial support and hosting are available through third-party organizations. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Family Tracing and Reunification
400.
RapidFTRIn crisis situations like earthquakes and other disasters, children often get separated from their families. This mobile app makes it easier to collect, share and manage information about these children so that they can be reunited with their families more quickly. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: File Managers
401.
Java File ManagerBecause it's based on Java, this file manager works with most operating systems. It's very simple and offers a less cluttered interface than many of the other two-panel file managers. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
402.
KrusaderThe KDE file manager, Krusader is a twin-panel commander-style file manager. It boasts extensive support for archived files, advanced search, batch re-naming, file content comparisons and more. Operating System: Linux
403.
muCommanderThis Java-based, commander-style file manager is both lightweight and fast. It includes compression tools, a bookmark manager and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
404.
PCManFMBuilt for the Lightweight Desktop Environment (LXDE), PCManFM is so fast and lightweight that it opens in just one second or less on most systems. It features a tabbed interface, drag & drop support and bookmarks support. Operating System: Linux
405.
SurFWith its unique, tree-based view of files, SurF makes it very easy to move around your files and folders. It also includes a text search tool, real-time highlighting of new and changed files, network support and more. Operating System: Windows
406.
TuxCommanderThis Linux-only file manager requires no installation, so it's completely portable. It offers a tabbed, two-panel graphic interface and support for files larger than 4GB. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: File Sharing
407.
ABC (Yet Another BitTorrent Client)Based on BitTornado (which in turn is based on BitTorrent), ABC offers multiple downloads in a single window, super-seed mode, prioritized queuing system and other features. Note that this client hasn’t been updated in several years, but you can still download the latest version. Operating System: Windows
408.
ANts P2PFor P2P users who are concerned about security, ANts encrypts all files as they are transmitted and routes data through several intermediate nodes in order to protect the privacy of the uploader and the downloader. The website includes multiple tutorials for those who are new to anonymous file-sharing. Operating System: OS Independent
409.
Ares P2PAres supports BitTorrent and ShoutCast, as well as the Ares peer-to-peer network. It includes a built-in player, a library organizer, chat rooms and more. Operating System: Windows
410.
BitTornadoBitTornado offers a slightly different interface for accessing P2P networks via the BitTorrent protocol. The latest version adds encryption capabilities for security. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
411.
BitTorrentBoasting "powerful features and a world of content," BitTorrent lets users download multimedia files from a wide variety of torrent sites. The website includes plenty of help for those who are new to file sharing. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
412.
BT++This app aims at improving the original BitTorrent client. Current features include multiple downloads in a single window, minimize to the system tray, and automatic re-starting of interrupted torrents. In the future, developers plan to add enhanced bandwidth throttling and better OS/browser integration. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix
413.
DC++A good option for P2P newbies, DC++ provides an interface to connect to the Direct Connect/Advanced Direct Connect network. It's been downloaded more than 50 million times, and the site includes a lot of tutorials and other documentation for new users. Operating System: Windows
414.
eMule/eMule PlusOne of the most popular projects on SourceForge, this client for the eDonkey and Kad networks gets more than a million downloads a week. It calls itself "one of the biggest and most reliable peer-to-peer file sharing clients around the world." Operating System: Windows
415.
MuteSimilar to ANts, Mute is an anonymous P2P client. The interface is very basic, but the website provides a lot of good documentation, including understandable explanations of how anonymous file-sharing works. Operating System: OS Independent
416.
PeerBlockThis fork of PeerGuardian 2 (which is no longer in active development) protects your privacy while using peer-to-peer networks by blocking computers on "known bad" lists. It's been downloaded more than a million times. Operating System: Windows
417.
RetroShareMost file sharing networks open you up to all kinds of security and privacy concenrs, but RetroShare lets you set up a secure file sharing network only among those you trust. It encrypts all communication via OpenSSL and GPG, and it supports e-mail, chat, file sharing, streaming, VoIP, and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, BSD
418.
Shareaza P2PShareza humbly calls itself "most luxurious and sophisticated file sharing system you'll find." It supports four separate P2P networks: eDonkey2000, Gnutella, BitTorrent and Gnutella2, and it offers previews, chat, user comments and ratings. Operating System: Windows
419.
StealthNetLike MUTE, the StealthNet network routes file sharing requests through multiple network nodes in order to provide anonymity. It offers fast download speeds and a user-friendly GUI. Operating System: OS Independent
420.
Vuze/a> One of the most popular BitTorrent clients, Vuze makes it easy for novices to get started downloading hi-def video while offering plenty of features for advanced users. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix, OS X 421. WasteWaste allows small groups of users to chat and download files securely and anonymously. Transmissions are encrypted using RSA and Blowfish algorithms. Operating System: Windows, Linux, BSD, OS X.
Open Source Apps: File Transfer
422.
ConnectbotWith this SSH client, you can connect securely to your corporate network to transfer files to your phone. Substantial documentation is available on the site. Operating System: Android
423.
FileZillaFileZilla comes in a server version that runs on Windows only, or a desktop client version that works on multiple platforms. In addition to regular FTP transfer, it also supports secure file transfer via FTPS or SFTP. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
424.
FireFTPThis add-on gives you an intuitive FTP client for the Firefox browser. It supports FTP or SFTP only. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
425.
WinSCPAward winning WinSCP offers a client for transferring files via SFTP, SCP, FTPS or FTP protocols. It includes two different interfaces: Explorer (which looks like Internet Explorer) and Commander (which looks like Norton Commander). Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Flashcards
426.
AnkiAnki supports images, audio, videos and scientific markup, so you can use it to memorize anything from names and faces, geography, vocabulary, information for medical or law exams or even guitar chords. It also works with most mobile OSes, so you can use it on your smartphone or tablet. Operating System: OS Independent.
427.
FlashQardFlashQard uses the Leitner method of presenting flashcards, which focuses your time and attention on the facts that you haven't yet mastered. There are several pre-made sets of cards available and it also supports the KDE vocabulary sets used for Parley. Operating System: Windows, Linux
428.
GeniusGenius can help you memorize almost anything—foreign language phrases, vocabulary words, historical events, legal definitions, even formal speeches. It uses a "spaced repetition" method that takes your previous answers into account when quizzing you on the material to be learned. Operating System: OS X
429.
jVLTJava-based jVLT is a flashcard program specifically designed to help users learn the vocabulary for a foreign language. You can download flashcard sets for learning a number of different languages, including German-Czech, English-Czech, Finnish-Russian, Czech-English, German-Czech, German-French, Thai-English, Spanish-French, French-English, and practical Chinese reading. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
430.
The Mnemosyne ProjectThis flashcard app boasts an intuitive interface, support for foreign alphabets and scientific symbols, an efficient scheduling algorithm and three-sided flashcards, which are helpful for learning a foreign language. It's available in a mobile version, and if you use the program, you also have the option of uploading your usage statistics so they can be incorporated into a research project studying long-term memory. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android, BlackBerry
431.
ParleyKDE's vocabulary training program works like a traditional flashcard program, but gives you the option of creating other types of tests, like mixed letters (anagrams), multiple choice, conjugation tests, synonym/antonym tests, fill in the blank and more. You can also find a very extensive library of pre-made cards for Parley at
KDE for Windows. Operating System: Windows, Linux
432.
PaukerPauker is designed to help you exercise your ultra-short-term, short-term, and long-term memory. It's Java-based and works on smartphones and other mobile devices, as well as desktops and laptops. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Foreign Language Instruction
433.
PythonolPythonol is designed to help English speakers learn Spanish. It includes multiple tools and games for learning vocabulary, conjugation, pronunciation, idioms, reading comprehension and more. Note that it comes in separate versions for adults and children. Operating System: Windows 98, Linux
434.
Step Into ChineseWhile it's not as full-featured as Rosetta Stone, Step Into Chinese does include information to help you learn the characters, meanings, and pronunciation of more than 26,000 modern Chinese words and concepts. It also has a helpful flashcard feature for learning through repetition. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
435.
ZkanjiThis Japanese learning tool includes dictionaries, a flashcard tool and stroke animations. It also has thousands of example sentences and inflection/conjugation information. Operating System: Windows.
436.
ZWDisplayZWDisplay aims to help Mandarin students become better readers of the language. It includes both English-Chinese and Chinese-English translation capabilities and a built-in flashcard app. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Forensics
437.
Live ViewThis Java-based tool creates a VMWare virtual image of the machine you are analyzing so that you can interact with it without changing the underlying image or disk. Developed by CERT and the Software Engineering Institute at Carnegie Mellon, it's an excellent tool for forensic examiners. Operating System: Windows.
438.
ODESSAAlthough it hasn't been updated in several years, the Open Digital Evidence Search and Seizure Architecture, aka "ODESSA," offers several different tools that can be useful in analyzing digital evidence and reporting on findings. The site also offers several white papers related to the topic. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
439.
The Sleuth Kit/Autopsy BrowserThe Sleuth Kit includes a set of digital investigation tools that run from the command line. For those that prefer a graphical interface, the Autopsy Browser provides a front-end to the tools. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Games
440.
0 A.D.Now in its sixth alpha release, 0 A.D. looks and feels a lot like Microsoft's Age of Empires series. The high-quality graphics are particularly noteworthy, and we assume the game will continue to improve and eventually enter beta and general release status. Operating System: Linux, Windows, OS X
441.
Advanced Strategic CommandCreated "in the tradition of the Battle Isle series," Advanced Strategic Command is a turn-based strategy game where combat units fight it out on a map made of hexagonal spaces. It offers both single- and multi-player play. Operating System: Linux, Windows
442.
Alien ArenaSimilar to games like Quake and Unreal Tournament, this "furious frag fest" has been downloaded more than 1 million times since its debut in 2004. It offers great graphics and a sci-fi theme. Plus, it has a large and loyal community, so it's easy to find players for an online match nearly any time. Operating System: Linux, Windows, OS X
443.
AssaultCubeBased on the Cube engine (see below), AssaultCube is another multi-player first-person shooter with realistic graphics. With low latency and a lightweight file size, it can run easily on older system or slow network connections. Operating System: Linux, Windows, OS X
444.
AssaultCube ReloadedThis fork of the popular first-person shooter integrates some of the best features of Battlefield, Quake and Call of Duty into AssaultCube, while maintaining a lightweight footprint. Other improvements include ricochet shots, new weapons, improved radar and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux
445.
Battle for WesnothThis turn-based strategy game is set in a high-fantasy world full of elves, necromancers, orcs and warriors. It includes multiple scenarios for gameplay or you can play against up to eight other people in multiplayer battles. Operating System: Linux, Windows, OS X, iOS
446.
BosWarsSet in a futuristic world, BosWars is a real-time strategy game where you must build up your economy and your military at the same time. You can play alone or connect to other opponents over a LAN or over the Internet. Operating System: Windows, Linux, BSD, OS X
447.
BZFlagShort for "Battle Zone Capture the Flag," BZFlag is a very popular 3D tank game. It was originally based on the arcade game Battlezone, and several servers make it possible to connect to online multiplayer games. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
448.
CommanderStalinCommanderStalin is based on the BosWars code, but instead of playing in a future world, this game is set in the Soviet Union under Stalin's rule. Build up your society quickly so that you'll be able to defend against the inevitable attack from Nazi Germany. Operating System: Windows, Linux
449.
CrossfireWith more than 150 monsters, about 3000 maps to explore, 13 races, 15 character classes, a system of skills, and many artifacts and treasures, this cooperative multiplayer graphical RPG and adventure game puts you in an elaborate, magical world. However, the graphics and game play are decidedly retro. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
450.
CubeThis first-person shooter offers a variety of interesting landscapes and maps with superb 3D graphics. You can play single-player or multi-player online games, and you can also create your own maps. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
451.
Dakar 2011In this newer racing game, you drive in the Dakar rally through 14 different stages based on real maps. It includes six different vehicles and 140 different opponents. Operating System: Windows, Linux
452.
EgobooAlthough it's still under development, Egoboo has been downloaded more than 400,000 times. In this role-playing adventure game, you crawl through a dungeon hoping to save Lord Bishop from the evil Dracolich. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
453.
EnigmaBased on the old Oxyd Atari game, Enigma is an addictive puzzle game where the object is to find sets of matching stones. It has more than 1,000 levels to keep you challenged. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X
454.
Excalibur: Morganna's RevengeWith an elaborate storyline, EMR takes players on a time-traveling journey through a wide variety of landscapes. It's fast, action-packed and offers 42 solo levels and 27 multi-player levels. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
455.
Fish Fillets NGThis is an open-source, cross-platform remake of the older Fish Fillets freeware puzzle game for Windows. The goal is to free the two trapped fish on each level, while the two fish make witty remarks about the game. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X
456.
FlightGearLike many of the best commercial flight simulators, FlightGear offers a very realistic flying experience with more than 20,000 real-world airports. It offers multiple types of aircraft with extremely accurate controls and operation. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others
457.
Foobillard++This is also a remake of an earlier open source game. Check out the screenshots on the site to see the excellent graphics for this billiards game. Operating System: Windows, Linux
458.
FreeColIn this turn-based strategy game, you establish a colony in the New World while building up your economy and your military. It was originally based on the older game Colonization and feels very similar to the game Civilization. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
459.
FreeCivAnother game that's similar to Civilization, FreeCiv begins in prehistoric times and requires you to manage your community so that you survive through modern times. Unlike many similar games, it supports many different languages. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
460.
FreeOrionInspired by the Master of Orion games, FreeOrion describes itself as a "turn-based space empire and galactic conquest game." It offers both single- and multi-player games. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
461.
Frets on FireExtremely similar to Guitar Hero, Frets on Fire includes hundreds of songs created by the community, allows you to create your own songs and imports songs from Guitar Hero I and II. You can use a generic guitar controller or joystick to play, or you can use your keyboard as a "guitar." Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
462.
Frozen BubbleSometimes called "the most addictive game ever created," Frozen Bubble offers single-player, two-player or networked multi-player games. Shoot the bubbles to create chains of matching colors and eliminate them before time runs out. Operating System: Windows, Linux
463.
Get Sudoku PortableStumped by a Sudoku puzzle? Enter the values you know into this app and it will help you keep track of the possible answers for all of the other boxes. Operating System: Windows
464.
GlestIn this 3D real-time strategy game, the forces of Tech (machines and warriors) battle against the forces of magic (mages and summoned creatures). It's won multiple awards, and has a very active user community. Operating System: Windows, Linux
465.
GLtronInspired by the movie Tron (and all the other games inspired by the movie), GLtron requires players to ride lightcycles around a course, leaving "wall" trails behind them. Crash into a wall, and you're dead. The goal is to be the last rider still alive. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
466.
GnomeGamesThis is the collection of casual "five-minute" games for the Gnome desktop. It includes AisleRiot (a solitaire collection), GNOME Chess, GNOME Mahjongg, GNOME, Klotski, Iagno (Reversi), Nibbles, Quadrapassel (Tetris) and more. Operating System: Linux
467.
HedgewarsThis slightly silly game features "the antics of pink hedgehogs with attitude as they battle from the depths of hell to the depths of space." It offers turn-based action for up to eight players. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS
468.
KDE GamesThe collection of games that ships with the KDE desktop includes dozens of arcade, board, card, dice, logic and strategy games. It includes versions of tetris, breakout, golf mahjong, battleship, sudoku and others. Operating System: Windows, Linux
469.
LinCity NGAs you might guess from the name, this is an open source version of SimCity. (The "NG" version is an update of the older LinCity game.) To win, build up your city to create a sustainable economy or evacuate all of the population on spaceships. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
470.
Liquid WarLiquid War has been called the "most original Linux game," and it truly is unique. You control an army of liquid and try to defeat your opponents by eating them. The graphics aren't great, but it's worth checking out. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
471.
Linley's Dungeon CrawlFor those who like their games really old-school, Dungeon Crawl is similar to the old DOS game Rogue. You must maneuver your way through an underground maze to retrieve the Orb of Zot while defeating various monsters and overcoming other obstacles. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
472.
MegaGlestThis app is a fork of popular Linux game Glest, which is no longer under active development. It updates and adds new features to the real-time strategy game where users control the warring armies of Tech and Magic. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
473.
MicropolisBased on the original code for SimCity, Micropolis offers the familiar city-building scenario with somewhat dated graphics. It's also part of the One Laptop Per Child project. Operating System: Linux, Unix
474.
NeverballIn this puzzle/skill game, you must quickly tip various platforms in order to roll a ball through an obstacle course with 141 levels of increasing difficulty. The download also includes Neverputt, a golf game that uses the same physics and graphics engine. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
475.
NexuizDownloaded more than 5 million times, this very popular first-person shooter is included in many Linux distributions. A team is now working on a re-make that will soon bring Nexuiz to many gaming consoles. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
476.
OoliteInspired by the game Elite, Oolite is a single-player space simulator that requires you to pilot ships around the universe, creating space stations around inhabited planets. Along the way, you'll need to fight off enemy ships. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
477.
OpenArenaFor mature audiences only, OpenArena is a deathmatch first-person shooter with seventeen characters and 12 weapons to choose from. It has a large userbase, so it's easy to connect to an online game. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
478.
OpenCityInspired by the open source project FreeReign, OpenCity is another city development simulator. It also uses a lot of concepts from SimCity2000, although it isn't a clone of that game. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
479.
OpenTTDThis clone of Transport Tycoon Deluxe adds a number of features not found in the original commercial game, including multi-player games for up to 255 players. As in the original, the goal is to make a lot of money transporting passengers and freight by land, water and air. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
480.
PingusPingus is a lot like the puzzle game Lemmings—except that it features penguins instead of lemmings. Direct your horde of penguins through the course by typing in simple commands. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
481.
PokerTHThis version of Texas Hold 'Em lets you play against up to 10 live or computer-generated players and features very nice graphics. It's been downloaded millions of times and is one of the most popular open source games around. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
482.
PushoverIn Pushover, you control an ant who scales various levels, pushing over dominos in the correct sequence to reach the next level. The graphics are old-school, but the puzzles are fun. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
483.
PySolFCA fork of the discontinued PySol Solitaire project, PySolFC includes more than 1,000 solitaire card games. Key features include multiple cardsets and tableau backgrounds, sound, unlimited undo, player statistics, a hint system, demo games and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
484.
Red EclipseFirst released in March of 2011, Red Eclipse is a newer shooter built on the Cube engine. It offers multiple game modes, excellent graphics and both single- and multi-player action. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
485.
Rigs of RodsExtremely popular, Rigs of Rods is a vehicle simulator that uses a soft-body physics engine to provide very accurate simulations. In order to run it, you will need a fairly up-to-date system. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
486.
Rocks'N'DiamondsOne of the oldest games created for Linux, Rocks'N'Diamonds is similar to the old Boulder Dash game. Pass through the levels by collecting diamonds while avoiding monsters and traps. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
487.
RyzomThis MMORPG is set 2000 years in the future on the world of Atys. The source code is available and it's free to play, but you'll need a subscription if you want to advance past level 125. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
488.
Scorched3DScorched 3D modernizes the classic DOS artillery game Scorched Earth. You can play against up to 24 other players at a time over a LAN or online. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
489.
Secret Maryo ChroniclesFor Mario Bros. fans, this game resurrects the old 2D graphics from the original game. Jump and run to collect mushrooms, fireplants and stars, but look out for the poison mushroom. Operating System: Linux, OS X
490.
Seven Kingdoms: Ancient AdversariesIn this real-time strategy game, you choose to play as the Japanese, Chinese, Mayans, Persians, Vikings, Greeks, or Normans against up to six other civilizations. Unique features include an advanced espionage system, magical creatures called fryhtans and a taxation system. Operating System: Windows
491.
ScummVMScummVM allows you to port many classic point-and-click adventure games to nearly any platform you like, including many mobile platforms. Supported games include Simon the Sorcerer 1 and 2, Beneath A Steel Sky, Broken Sword 1 and Broken Sword 2, Flight of the Amazon Queen, Monkey Island, Day of the Tentacle, Sam and Max, and dozens of others. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, and many others
492.
SimutransSimilar to Transport Tycoon Deluxe and OpenTTD, this app allows you to build up a city full of a variety of transportation networks. Just stay out of debt, or your game will soon be over. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
493.
Smash BattleAlthough it's only a few years old, this game features old school, 2D graphics. Two to four players jump from platform to platform trying to shoot each other without being killed. Operating System: Windows, Linux
494.
SokoSolveLike all Sokoban (Japanese for "warehouse keeper") games, SokoSolve requires you to pull, never push, crates one at a time until you achieve the desired configuration. The 2D play is simple but surprisingly addictive. Operating System: Windows
495.
Steel Storm Episode ISet in a futuristic world, Steel Storm is a top-down shooter with fast-paced action that doesn’t take too long to play. Note that while Episode I has an open source license, Episode II is a commercial product. Operating System: Windows, Linux
496.
StepManiaDance Dance Revolution fans can test their rhythm skills for free with StepMania. Connect your own dance pads or just use the keyboard to keep up with the beat. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix, OS X, XBox
497.
Stunt RallyStunt Rally is also a racing game, and it offers 57 tracks, 9 scenarios and 8 cars. There's also a track editor, so you can create your own courses, complete with loops and curves. Operating System: Windows, Linux
498.
SuperTuxKartThis 3D racing game features Tux the Penguin racing around 20 different tracks. The graphics are less than fabulous, but it does offer several different game modes and multi-player capabilities. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
499.
T^3 PortablePlay Tetris in 3D! It's simple, familiar and fun. Operating System: Windows
500.
TeeworldsTeeworlds combines cartoon-ish 2D graphics with deadly action in a side-scrolling game for 2 to 16 players. Shoot the other players with your pistol, bash them with your mallet or hunt for more powerful weapons as you battle your opponents. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
501.
TORCSAnother racing game,Tthe Open Race Car Simulator (TORCS, for short) features more than 50 different cars, more than 20 tracks, and 50 opponents. You can play against up to four other people from your system, but it does not yet support online multiplayer races. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
502.
TremulousThis team-action game pits human versus aliens and combines elements you find in a first-person shooter with elements of a real-time strategy game. The graphics and storyline are impressive, and it's won a number of awards. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, XBox
503.
Tux RacerDownloaded more than a million times, Tux Racer allows you to guide Tux the Linux penguin through a variety of snow-covered courses. Collect herring while you deal with hazardous weather conditions and speed down steep mountains. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
504.
UFO:Alien InvasionThis game transports players to the year 2084, where they must control a secret group defending earth from an alien invasion. It's inspired by the X-COM games, but isn't a remake. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
505.
Ultrastar DeluxeSimilar to SingStar for Playstation, this competitive karoake game awards points based on how well you sing. You'll need a microphone to play, and up to six people can play at the same time. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
506.
Unknown HorizonsA cross between a city building simulator and a real-time strategy game, Unknown Horizons starts you off with a ship, a few sailors and a handful of resources that you must use to build a thriving civilization. It's still an alpha release but is playable. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
507.
VDriftBuilt with drift racing in mind, this racecar game offers great graphics, more than 40 real-world tracks and nearly 40 real-world cars. It's single-player only, but you can race against up to 3 AI opponents. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
508.
Vega StrikeVega Strike describes itself as a "3D action-space-sim that lets you trade, fight, and explore in a vast universe." It's a beta release but very playable, and the graphics are very good. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
509.
WarMUXThis artillery game describes the style of play as "convivial mass murder." The goal is to inflict maximum damage to your opponents using dynamite, grenades, baseball bats and bazookas. The scenery is cartoonish, and the characters are open source software mascots. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
510.
WarsowEnter a cartoon-ish future world where you must shoot rocketlauncher-wielding pigs and lasergun-carrying cyberpunks. This first-person shooter moves very fast with lots of running, jumping and bouncing off the walls. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
511.
Warzone 2100In this real-time strategy game, you must re-build the world after it's been nearly destroyed by nuclear war. It has a very large research tree and focuses on artillery, radar, and counter-battery technologies. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
512.
WidelandsSimilar to The Settlers and The Settlers II, Widelands is yet another real-time strategy game that requires you to build your economy and military strength to overcome competing civilizations. It features four worlds, three tribes, and single- or multi-player games. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
513.
WinBoard PortablePlay the standard chess game you know or one of the variants like xiangqi (Chinese chess), shogi (Japanese chess), Makruk, Losers Chess, Crazyhouse, Chess960 and Capabanca Chess. You can play on your own or connect to other players on the Internet. Operating System: Windows
514.
XMotoIn this 2D platform-style game, you ride motocross past various obstacles while collecting strawberries. Thanks to an active user community, it has more than 2500 custom levels available for download. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
515.
XPilotInspired by games like Thrust and Asteroids, XPilot is an old school 2D space battle game. It's been forked many times, and versions are also available for smartphones. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
516.
Yo Frankie!Because it was created to show off the capabilities of the open source 3D modeling tool Blender, the graphics on Yo Frankie! are particularly impressive. It's a platform style game in which you control a sugar glider or monkey who must make it through a course full of obstacles. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
517.
Zero-KSet in a futuristic world, this real-time strategy game requires players to build up armies of mechanical beings. Some of its unique features are a flat technology tree and the ability to transform the landscape with the characters you control. Operating System: Windows, Linux
518.
ZombiesThe objective of this game is simple—kill the zombies before they kill you. It's turn-based and includes gore settings so you can choose how much blood splatters around. Operating System: Windows, OS X
Open Source Apps: Gateway Security Appliance
519.
Endian Firewall CommunityLike Untangle, the open source version of Endian allows you to turn an older PC into a gateway security appliance. It includes a firewall, anti-virus, anti-spam, Web content filtering, a VPN and more. Operating System: Linux
520.
UntangleWith Untangle, you can turn an old PC in to an appliance that protects your privacy and secures your network (or you can purchase a pre-configured appliance directly from the company). It's currently used by more than 1.7 million people at more than 30,000 organizations around the world. Operating System: Linux
521.
NetCop UTMAvailable as either a free open source download for up to five concurrent users or in an enterprise version for unlimited users, NetCop offers the same functions as Endian and Untangle and the commercial UTMs. However, it is not available as a pre-configured appliance. Operating System: Linux.
Open Source Apps: Genealogy
522.
GenealogyJThis Java-based genealogy app lets you view family information as a family tree, in a table, on a timeline, or by geographic location. It's appropriate both for people looking for a hobby and more serious historians. Operating System: OS Independent
523.
GrampsIf tracing your genealogy is your idea of a good time, you might enjoy this app which also has one of the most fun acronyms ever—Gramps is short for "Genealogical Research and Analysis Management Programming System." Not only is the tool itself helpful, but the site also include more than 1,000 pages of content about tracking your relatives. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
524.
PhpGedViewWorking on your family tree? PhpGedView makes it easy to collaborate online with the rest of your family to trace your genealogy. Note that you'll need your own Web server in order to set it up. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Geography/GPS
525.
Marble Another KDE app, Marble is a combination atlas/virtual globe that integrates with Wikipedia so that students can learn more about places that interest them. It also includes topographic maps, a satellite view, street maps, earth at night and temperature and precipitation maps, and many teachers find it useful in the classroom. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
526.
WorldWind WorldWind was
originally packaged to be very similar to Google Earth. The link here takes you to an SDK that allows you to incorporate WorldWind into your own apps. It also includes links to several interesting apps that use WorldWind. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Graphics Editors
527.
Art of IllusionThis 3D modeling and rendering software isn't as full-featured as Maya (or Blender), but it's capabilities are robust enough for beginners and amateurs. The interface is fairly easy to use and it has good online documentation, including some tutorials. Operating System: OS Independent
528.
BlenderSuitable for professionals, Blender is a free open source 3D content creation suite. It includes tools for 3D modeling, shading, animation, rendering and compositing. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
529.
DiaIf you need to outline the steps necessary for a project, create a system diagram or draw an org chart, Visio is for you. It supports common graphic file formats, as well as a space-saving custom XML format. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
530.
GimpShort for "GNU Image Manipulation Program," GIMP is a professional-quality image manipulation program that's intuitive enough for amateurs to use. It includes a full suite of painting and image re-touching tools, layers and channels, sub-pixel sampling, quickmask, file format conversion tools, animation capabilities and much more. For the Windows version, you'll need to download
Gimp-win. Operating System: Windows, Linux
531.
InkscapeAnother tool for graphics professionals, Inkscape is a vector graphics drawing program with many advanced features. The Inkscape website also includes links to a library of open source clip art that you can use freely in your illustrations. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
532.
K-3DAnother 3D modeling and animation option, K-3D claims it "excels at polygonal modeling, and includes basic tools for NURBS, patches, curves and animation." Like Art of Illusion, it's suitable for amateurs. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
534.
PencilPencil lets you create traditional 2D animations using your computer. It's best for home users and hobbyists who love the look of the old-school cartoons. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
535.
PixelitorSimilar to Photoshop and the open source graphics program Gimp, Pixelitor lets users perform advanced editing of photos and graphics. And because it's Java-based, it works on multiple platforms. Operating System: OS Independent.
Open Source Apps: Human Resource Management (HRM)
536.
Open ApplicantOpen Applicant helps HR professionals and hiring managers sort through potential candidates to find the best applicant for a job. The application is free to download, but enterprise level support, customization, an SaaS version, and other services can be purchased from the company. Operating System: OS Independent
537.
Orange HRMWith more than 1 million users, Orange claims to be the "world’s most popular Open Source Human Resource Management Software." It tracks time and attendance, leave, recruiting performance, and employee information, and it's also available in an SaaS version. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X
538.
WaypointHRWhile not as mature as Orange, Waypoint also tracks employee records, pay, performance, leave and other HR information. Also, like Orange, it's available in a hosted "On Demand" version. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Instant Messaging
539.
AdiumPidgin (see below) doesn't work on a Mac, but this nearly identical app does. Operating System: OS X
540.
aMSNConceived as an MSN Messenger clone (before Microsoft changed the name to Windows Live Messenger), this app includes offline messaging, voice clips, photo support, custom emoticons and more. A large library of plug-ins and skins is also available on the site. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
541.
KopeteKDE's IM client supports AIM, ICQ, Windows Live Messenger, Yahoo, Jabber, Gadu-Gadu, Novell GroupWise Messenger and other networks. It also offers tools for archiving and encryption and a unique notification system that only lets "important" message through. Operating System: Linux
542.
Miranda IMSmall and fast, Miranda is very light on system resources. Like many of the other IM clients on our list, it supports multiple networks, including AIM, Facebook, ICQ, IRC, Yahoo and others. Operating System: Windows
543.
PidginThis universal chat client allows you to IM with friends on numerous different networks, including AIM, ICQ, Google Talk, Jabber/XMPP, MSN Messenger, Yahoo, and others. It's available in dozens of languages, and numerous plug-ins extend its capabilities. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix
544.
PsiPsi is an open-source IM client for the Jabber network, which includes GoogleTalk, LiveJournal, and a number of international networks. It’s completely customizable and supports about 20 different languages. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: IT Inventory Management
545.
GLPIThis app creates a database that tracks all of the technical resources of your organization. It also includes some management functions that allows admins and help desk to staff track open jobs, respond to alerts, etc. Operating System: OS Independent
546.
OCS Inventory NGThis "next generation" inventory tool helps you discover all the hardware and software in use on your network, which you can then track with a tool like GLPI (see below). It can also help you easily deploy scripts or software across your network. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Library
547.
LibLime KohaKoha humbly describes itself as "the most functionally advanced open source ILS on the market today." A variety of paid services, including hosting, support, implementation and consulting are also available on the site. Operating System: OS Independent
548.
OpenBiblioThis automated library system includes online public access catalog (OPAC), circulation, cataloging, and staff administration functionality. It's not as full-featured as some of the other library apps, but it gets the job done, and the site has lots of documentation. Operating System: OS Independent
549.
VuFindDesigned and developed "by libraries for libraries," VuFind aims to make searching your library's catalog easy and intuitive. Key features include modular design, faceted results, "more like this" suggestions, author biographies and more. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Linux Desktop Environments
550.
GnomeOne of the two most popular Linux desktop environments, Gnome is the default desktop for Fedora, Ubuntu, and several other distributions. It's best known for being easy to use. Operating System: Linux
551.
KDE Plasma DesktopThe second of the two most popular Linux desktop environments, KDE has a reputation for being "prettier" than some of the other desktop environments and feels very similar to Windows and OSX. The KDE community is one of the largest open source communities, so plenty of help is available for new (or experienced) users. Operating System: Linux
552.
LXDEThe "Lightweight X Desktop Environment" claims it has a "beautiful interface," but if truth be told, it's much more concerned about speed than looks. Because it uses so few computing resources, it's a good choice for netbooks and cloud-computing environments. Operating System: Linux
553.
XfceAnother lightweight option, Xfce also offers very fast performance and doesn't make any claims about its beauty. It offers a modular design, so users can install just the components they choose in order to create a completely customized desktop experience. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Log File Monitoring and Analysis
554.
AnalogThe self-proclaimed "most popular logfile analyzer in the world," Analog quickly generates usage statistics for Web servers. It can be used in conjunction with
Report Magic to create more attractive graphs. Note that this project has not been updated in a while, but it is still used to analyze traffic on many servers. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
555.
AWStatsAWStats uses the log files from your Web, streaming, FTP or mail server to create easy-to-read graphical reports. It runs from the command line or as a CGI. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
556.
BASEThe "Basic Analysis and Security Engine," or BASE, use a Web-based interface to analyze alerts from Snort IDS. Features include role-based user authentication and Web-based setup. Operating System: OS Independent
557.
IPtables Log AnalyzerThis app makes it easier to understand the log files from your Shorewall, or SUSE Firewall, or Netfilter-based firewall logs. It organizes rejected, acepted, masqueraded packets, etc. into an attractive HTML page. Operating System: Linux
558.
SnareThe Snare project encompasses a number of different tools and agents, all of which assist in the filtering, collection and monitoring of server log files. Commercial support and the proprietary Snare Server are also available on the same site. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others
559.
WebalizerLike AWStats and Analyzer, Webalyzer analyzes the statistics from Web servers. By default, it creates yearly and monthly usage reports which can be viewed from any browser. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Logic/Debate
560.
ArgumentativeSimilar to mind mapping software, Argumentative helps you create an "argument map" that outlines the premises of an argument in a visual way. It's particularly helpful for projects with a lot of writing – like creating a book, website, software documentation, etc. Operating System: Windows.
Open Source Apps: Mail Servers
561.
CitadelCalling itself the "leader in true open source email and collaboration," Citadel features a unique "rooms" architecture that makes it versatile and flexible. It's available as a standard download, a VMware appliance or on a hosted basis. Operating System: Linux
562.
EximThis MTA was developed at the University of Cambridge and is still widely used in the UK. It's best for servers that are unlikely to have large volumes of mail because it doesn't have a central queue manager. Operating System: Linux, Unix
563.
PostfixOriginally developed by IBM Research, Postfix is a secure mail transfer agent that is very similar to Sendmail (see below). It's fairly fast and can handle a large volume of mail. Operating System: Linux, Unix, OS X, Solaris
564.
ScalixUsed by more than 1,300 corporations with more than 2 million mailboxes, Scalix offers an alternative to a Microsoft Exchange server. It offers e-mail and calendaring, with excellent Outlook support. It's available in a free community version or paid small business, enterprise or hosting versions. Operating System: Linux
565.
SendmailWhile it's not as widely used as it once was, Sendmail continues to be a very popular mail transfer agent. Newer features include support for filters, authentication and external database look-ups. Operating System: Linux
567.
SME ServerBased on CentOS and Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SME Server offers file and printer sharing, a mail server, network firewall, automatic backup, remote access and more. Installation and basic configuration take only about 20 minutes, and there's quite a bit of documentation for the project available on the site's wiki. Operating System: Linux
568.
SOGoSOGo is a groupware server that allows users to access e-mail and shared calendar data via the Web, a BlackBerry device, or an e-mail client like Thunderbird. The latest version adds native Outlook support. Operating System: OS Independent
569.
ZimbraThe self-proclaimed "leader in open source e-mail and collaboration," Zimbra offers a mail server that provides an alternative to Exchange, as well as a desktop client that offers an alternative to Outlook. It's available in a variety of free and paid editions, including hosted versions and versions designed to run in a virtualized or private cloud environment. Operating System: Linux, Unix, OS X
Open Source Apps: Mapping
570.
OpenLayersThis alternative to Google Maps and Bing Maps provides free APIs that can put dynamic, JavaScript-based maps on any website. It's sponsored by the Open Source Geospatial Foundation. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Math
571.
ApophysisIf you're a math geek, you probably know what fractal flames are. If not, it's probably enough to know that this app lets you create and edit very strange algorithmically generated images. Operating System: Windows
572.
Dr. GeoThe award-winning Dr. Geo helps both elementary (age 10 and up) and more advanced students learn basic geometric principles by interacting with geometric shapes. Check out the video on the website to see it in action. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
573.
GeniusThis tool began as a simple calculator but has morphed into a powerful tool with many similar features as Mathematica (although it doesn't have Mathematica's full feature set). It has its own language (GEL), which can be used by researchers to create new functions. Operating System: Linux, OS X
574.
GeoGebraGeoGebra combines tools for learning dynamic geometry, algebra and calculus. It offers an intuitive GUI and a video tutorial which make it a little more user friendly than some of the similar math apps. Operating System: OS Independent
575.
gnuplotIf you're comfortable working from the command line, you can use gnuplot to create 2D and 3D graphs of mathematical functions. Extensive help is available on the website, and there's even a book on Gnuplot that you can buy. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X, and others
576.
GraphCalcWhy buy a handheld graphing calculator, when GraphCalc will do all the same things (and more) for free. According to the website, "GraphCalc can be your first, last, and only line of offense against the mathematics that threaten to push you over the brink of insanity. It slices, dices, shreds and purees functions that leave other calculators wondering what hit them." Operating System: Windows, Linux
577.
KigThis KDE app for geometry students and teacher makes it easy to draw and explore geometric shapes. It can also import files from Dr. Geo and Cabri. (Note that in order to use Kig on Windows, you'll have to download
KDE for Windows.) Operating System: Windows, Linux
578.
MandelbulberIf you're geeky enough to know what a Mandelbulb is, you might enjoy this app which renders 3D fractals. More information about the app can also be found on the
FractalForums site. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
579.
MaximaThis "computer algebra system," handles differentiation, integration, Taylor series, Laplace transforms, ordinary differential equations, systems of linear equations, polynomials, and sets, lists, vectors, matrices, tensors, and more. It also creates 2D and 3D graphs of mathematical functions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
580.
SageLike Mathematica, Sage can solve a wide variety of higher-level math problems and is suitable for advanced students and researchers. You'll get the most functionality out of it if you know the Python programming language. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
581.
ScilabUsed by many industrial engineers and university researchers, Scilab can perform hundreds of mathematical operations. It also comes with an API for those who want to use its capabilities to create their own applications. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
582.
TTCalcIf you need to work with numbers that are too big for the standard Windows calculator to handle, TTCalc is the solution. It includes most arithmetic and trigonometric functions, and it's accurate to 306 valid decimal digits. Operating System: Windows
583.
Ultimate CalcThis scientific and graphing calculator solves complex equations and offers an easy-to-use interface. It supports plug-ins and scripts to extend its capabilities. Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Microfinance
584.
MifosThis Web-based management information system (MIS) aims to help microfinance institutions streamline their operation. It offers portfolio and transaction management, on-the-fly financial product creation, in-depth client management, integrated social performance measurement, and a reporting engine. Operating System: OS Independent
585.
OctopusRated as "one of the most user-friendly solution with highly ergonomic windows display" by the World Bank/CGAP, Octopus offers a robust, secure MIS for microfinance organizations. It's available both in a free community version or a supported professional edition. Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Mind Mapper
586.
FreeMindThis tool is excellent for brainstorming sessions, creating diagrams, outlining the steps of a project, process management and more. The best way to see how it works is to take a look at the screenshots on the website. Operating System: OS Independent
586.
The GuideThis tool lets you organize your notes in a hierarchical, tree-based format. It's similar to a mind mapper, but not as complex. Operating System: Windows
587.
XMindSimilar to FreeMind, XMind has one numerous awards, and it's been downloaded more than 1.7 million times. It also comes in an paid enterprise version that adds Gantt charts, privacy/sharing features, company themes and more export options. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Open Source Apps: Mobility Tools
588.
Brm Bluetooth RemoteThis app turns your J2ME-enabled phone into a remote control for your PC. It controls most media players, PowerPoint, a remote keyboard and more. Operating System: Windows
589.
F-DroidF-Droid offers a catalog of dozens of open source apps for the Android platform. It you don't want to install them all, you can also download the individual apps separately. Operating System: Android
590.
FunambolFunambol includes a number of mobile-related tools in one package: a data synchronization service, a device management service, client connectors and a software development kit. The site also acts as a forge hosting multiple projects built with Funambol tools. Operating System: Android, iOS, Windows Mobile, Symbian
591.
LISPmobThis is an open source version of the LISP-Mobile Node implementation, which provides mobile devices greater ability to roam while remaining connected to the Internet. It was originally developed by Cisco and is now maintained by Barcelona Tech University. Operating System: Linux
592.
QuincyKitQuincyKit collects information about app crashes and reports them to your server. It automatically generates reports about similar types of crashes and gives you the option of collecting user feedback. Operating System: OS X, iOS
593.
TizenStill in the extremely early stages of development, Tizen is the mobile OS meant to replace Meego. Development is being led by Intel, Samsung and the Linux Foundation; a first release is expected in the first quarter of 2012. Operating System: N/A
Open Source Apps: Modeling
594.
ArgoUMLThe self-proclaimed "leading open source UML modeling tool" supports all standard UML 1.4 diagrams and comes in 10 different languages. Because it's based on Java, it runs on any platform, and it can export diagrams in six different file formats. Operating System: OS Independent
595.
StarUMLDesigned as an alternative to Rational Rose and other commercial modeling tools, StarUML supports both the latest UML standards and Model Driven Architecture (MDA). It's very user-friendly and features a plug-in architecture. Operating System: Windows
596.
ModelioThe code behind Modelio has actually been in development for more than 20 years, but parent company Modeliosoft just recently released it under an open source license. It offers a UML modeler, BPMN support, Java code generator, and support for XML, HTML and Jython. Operating System: Windows, Linux
Open Source Apps: Multimedia Tools
597.
AmpacheAmpache is both a video/audio player and a streaming server. With it you can set up a multimedia server that will allow you to access your audio and video files from any Internet-connected device. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
598.
AmpJukeThis streaming server boasts easy operation and speed. It automatically fetches album covers, images and lyrics from various Web services, and it enables sharing of your favorites lists. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
599.
BansheeAnother mobile-friendly option, Banshee syncs with smartphones and tablets and integrates with the Amazon MP3 store. Other key features include smart shuffle, automatic cover art, smart playlists, queuing and a podcast guide. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android, iOS
600.
CamStudioIdeal for teachers and trainers, CamStudio records what you're doing on your computer so that you can play it back as a video. It also records audio and includes some basic editing capabilities. Operating System: Windows
601.
Darwin Streaming ServerDeveloped by Apple, this QuickTime alternative was the first ever open source RTP/RTSP streaming server. The code has not been updated in a while, but it is still available for download. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
602.
Data CrowIf you're the extremely organized type, you'll love Data Crow. It helps you organize all of your content—CDs, DVDs, books, electronic files—and even includes a loan registration feature so that you can keep track of which friends borrowed your stuff. Operating System: OS Independent
603.
InfraRecorderThis CD and DVD burner creates audio, data or mixed mode discs. It can record disc images and it supports a wide variety of audio file formats. Operating System: Windows
604.
kPlaylistLike the others in this category, kPlaylist lets you set up your own multimedia server so that you can listen or view your files over the Web and share them with your friends. Features include user authentication, Flash player support, randomizer function and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux
605.
MediaInfoMediaInfo finds tags and technical data for audio and video files, as well as some text files. It supplies the title, artist, director, number of tracks, and much, much more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, and others
606.
Media Player Classic Home CinemaThis app looks a lot like Windows Media Player, and it's very lightweight while still offering a lot of features. Notable capabilities include playback and recording of television, remote control for Android smartphones and support for most audio, video and image file types. Operating System: Windows
607.
MediaPortalLike XBMC, Media Portal helps turn your PC into a home theater PC (HTPC). It plays CDs and DVDs, records TV like a DVR, supports remote controls and offers a huge library of plug-ins that can extend its capabilities further. Operating System: Windows
608.
MMConvertIn addition to converting audio files, this app also handles many video files types, including asf, wmv, wma, avi, mp3, wav, mkv, mka, and ogg. Note that you may also need to download some codecs in order to convert some files. Operating System: Windows
609.
MiroMiro makes it easy to sync the audio and video files on your PC with your iPad or an Android device. In addition to playing and converting most multimedia file types, Miro also offers torrent downloading and a music and app store. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android, iPad
610.
MplayerWinner of numerous awards, Mplayer plays an impressively long list of multimedia file types. It installs without a GUI by default, but several front-ends are available. In addition, other developers have created versions for Windows and Mac. Operating system: Linux
611.
UMPlayerShort for "Universal Media Player," UMPlayer claims to "play everything." Key features include built-in codecs, playback for damaged files, a YouTube player/recorder, skinnable interface, subtitles search and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
612.
VideoLANThis is the server-side solution that goes along with the VLC Media Player. It can stream all of the multimedia formats that VLC can read. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
613.
VLC Media PlayerOne of the most popular open source multimedia players, VLC plays nearly all types of audio and video files. It offers a user-friendly GUI and fast performance, and it can often play damaged files. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others
614.
XBMC Media CenterDesigned for home theater PCs (HTPCs), XBMC supports most types of remote controls, so it's easy to use while sitting on the couch. It plays most audio and video file types, including CDs and DVDs, and it automatically organizes your multimedia content. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
615.
xineThis media player is very fast, extensible and skinnable, and it supports most video file types. Work on a Windows version is underway. Operating System: OS X, Linux
Open Source Apps: Multiple Function Security Solutions
616.
Bastille LinuxFormerly known as Bastille Linux, Bastille UNIX hardens your system to decrease the likelihood of a successful attack. Along the way, it asks you questions about your computer use and provides additional information about security topics, so that you're not only protecting your system, you're also educating yourself. Operating System: Linux, Unix, OS X.
617.
Network Security Toolkit (NST)Like INSERT, NST includes a whole lot of tools and a complete Linux distribution that fits on a CD-ROM. In this case, you get nearly 100 tools and the Linux copy is based on Fedora. Operating System: OS Independent.
618.
OSSIMShort for "Open Source Security Information Management," OSSIM combines 12 separate open source security tools, including Snort, Nessus, Nagios, and others. The dual goals are to prevent intrusions and give administrators a complete, detailed view of the entire network. Operating System: Windows, Mac, Linux, Unix, BSD, Solaris
619.
Security and Privacy CompleteThis app gives you control over a number of system settings and settings for Windows Media Player, Internet Explorer, and Firefox. A handy tooltip feature lets you know what each function does and why you might want to enable or disable it. Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Music Education
620.
GNU SolfegeIf you wish you had a better ear for music, this app can help. It includes exercises to help you identify and sing pitches, intervals, chords, rhythmic patterns and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
621.
Impro-VisorThis "Improvisation Advisor" helps aspiring jazz musicians learn to compose their own solos. In addition to teaching students to understand improvisation, it can also improvise on its own or transcribe music. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
622.
LenMusThis program includes exercises for learning music theory and aural training. It also includes a barebones score editor for writing your own compositions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Network Firewalls
623.
Devil-LinuxThis Linux distribution functions as both a network firewall and an application server. It also includes many open source network and sever monitoring tools. Operating System: Linux
624.
FireHOLFireHOL describes itself as "a language to express firewalling rules." It lets you configure an iptables based firewall using four basic commands. Operating System: Linux.
625.
FirestarterUnlike most of the open-source firewalls, Firestarter can protect a single PC, as well as a network. Best of all, you can probably install it and be up and running in just a couple of minutes. Operating System: Linux
626.
IPCopThis software for home or SOHO networks turns an old PC into a Linux-based firewall. It's fairly easy to configure and maintain if you're technically minded. Operating System: Linux.
627.
LEAFThe "Linux Embedded Appliance Framework" (aka LEAF) can be used as an Internet gateway, router, firewall, or wireless access point. This app requires a little more know-how than some of the other choices in the category, but is still a good option. Operating System: Linux
628.
m0n0wallLike most of the other apps in this category, m0n0wall allows you to create your own firewall, but unlike most of the other firewalls here, this one runs on FreeBSD, not Linux. It occupies just 12MB and can be loaded from a compact flash card or a CD. Operating System: FreeBSD.
629.
pfSenseThis project is a fork of m0n0wall. While m0n0wall was created to be used on embedded hardware, pfSense was designed to make it easier to use on a full PC. It's been downloaded more than 1 million times and protects networks of all sizes from home users to large corporations. Operating System: FreeBSD.
630.
Sentry FirewallThis app can operate as a network firewall, server or IDS node. It boots directly from a CD, making it very easy to set up a firewall quickly. Operating System: Linux.
631.
ShellTerAn iptables-based firewall, ShellTer offers quite a bit of customization capability. Features include port forwarding, blacklisting, whitelisting, and more. Operating System: Linux.
632.
ShorewallShorewall, aka "Shoreline Firewall," configures the Netfilter in Linux, making it easy to manage your own firewall. You can use it either to secure a network or on an individual Linux system. Operating System: Linux.
633.
SmoothWall ExpressBecause it's designed to be used by people with no knowledge of Linux, SmoothWall Express is an excellent option if you aren't a technical whiz, but want to tackle setting up your own network. Operating System: Linux
634.
Turtle FirewallAnother tool for helping you create your own Linux-based network firewall out of an old system, Turtle can be managed via a Web interface or by modifying XML files directly. The website offers a helpful manual with info for both newbies and those with experience with firewalls and networking. Operating System: Linux.
635.
VuurmuurLike many of the other projects in this category, Vuurmurr leverages the built-in firewall capabilities in Linux. This one comes with a basic GUI, but you're still going to need to be fairly technical in order to use it. Operating System: Linux.
Open Source Apps: Network Management
636.
CloseTheDoorThis tool allows network and security managers to identify all listening ports for their listening ports for IPv4 and IPv6 networks. It provides information and allows you to shut down remote attacks. Operating System: Windows
637.
OpenNMSOpenNMS bills itself as "the world’s first enterprise grade network management application platform developed under the open source model." It offers a vast list of features for automated and directed discovery, event and notification management, service assurance and performance management. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS
638.
Zenoss CoreZenoss combines a configuration management database with availability and performance monitoring, event management and reporting. It also includes a Web portal and dashboards so that administrators can see what's happening with their IT systems at a glance. Operating System: Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Network Monitoring/Scanning/Intrusion Detection
639.
AFICKLike Tripwire, "Another File Integrity Checker," or AFICK for short, detects changes in files caused by network intruders. It's easy to install and can be used from the command line or a GUI. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
640.
Angry IP ScannerAlso known as "ipscan," Angry IP Scanner scans IP addresses and ports very quickly. It can generate reports that include NetBIOS information (computer name, workgroup name, and currently logged in Windows user), favorite IP address ranges, web server detection, and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
641.
CactiThis tool offers a user-friendly interface to manage and graph network data stored in a RRDTool database. If you have a large network, you'll probably want a separate plug-in to collect data, such as
Spine. Operating System: Windows, Linux
642.
GangliaSpecifically designed for high performance computing systems such as clusters and grids, Ganglia uses a highly scalable hierarchical architecture. It was built for the UC Berkeley Millennium Project, and you can view a demo of that network's operation from the site. Operating System: Linux, others
643.
KismetKismet is a combination wireless network detector, packet sniffer, and IDS. Often used to detect unprotected or hidden networks, it's a valuable tool for checking the security of your wireless network, as well as monitoring network activity. Operating System: Windows, Mac, Linux, Unix, BSD
644.
KnockerThis simple TCP security port scanner works on multiple platforms and is easy to use. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix.
645.
MuninMunin is designed to help network administrators spot trends and figure out the root cause of performance problems. And in case you're wondering, the name comes from Norse mythology and means "memory." Operating System: Linux, OS X
646.
NagiosThe "industry standard in open source monitoring," Nagios provides alerts that can help IT respond to problems before they can cause costly outages. Well-known users include Unisys, Wells Fargo, BT, iRobot, and the Office of the President of the United States. Commercial support and maintenance packages are available from Nagios Enterprises. Operating system: Linux, Unix
647.
NDTNDT is short for "Network Diagnostic Tool," and it does just that—diagnosing network performance problems. It's a client/server app that requires a Linux server; however, the client can run on any system with Java installed. It's not as robust as some of the other full monitoring tools on our list, but it does this one thing very well. Operating System: Linux
648.
Net-SNMPAs you might guess from the name, this tool uses SNMP v1, SNMP v2c and SNMP v3 protocols to monitor the health of network equipment. Because it focuses only on SNMP it's not as complete as the commercial monitoring software or many of the other open source options on our list. Operating System: Windows, Linux
649.
NSATShort for "Network Security Analysis Tool," NSAT performs bulk scans for 50 different services and hundreds of vulnerabilities. It provides professional-grade penetration testing and comprehensive auditing. Operating System: Linux, Unix, FreeBSD, OS X.
650.
Open Source TripwireThe standard version of Tripwire is no longer open source, but this project is built on the open source code from 2000. It alerts IT managers when changes have been made in network files in order to help them detect intrusions. Operating System: Linux.
651.
Opsview CommunityOpsview aims to "unify your monitoring" so that you can track your physical, cloud and hybrid infrastructure from one place. An enterprise version, additional enterprise modules, support, training and consulting services are available for a fee. Operating System: Linux
652.
OSSECThis intrusion detection system offers log analysis, file integrity checking, policy monitoring, rootkit detection, real-time alerting and more. Enterprise users can get paid support for OSSEC from Trend Micro. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others
653.
Pandora FMSThe "FMS" stands for "Flexible Monitoring System," and it's apt because Pandora can monitor applications, servers, network equipment, or even stock market trends. It features an attractive GUI and can create graphs based on both real-time and stored historical data. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
654.
SECAlthough we put this app in the Network Monitoring category, the Simple Event Coordinator (SEC) actually works with many different applications. To use it, you set up a set of rules that specify what actions you want to occur whenever a particular event occurs. Operating System: OS Independent.
655.
SniffDetThis tool implements a number of different open-source tests to see if any of the machines in your network are running in promiscuous mode or with a sniffer. Note that some of the documentation for this app is in Portuguese. Operating System: Linux.
656.
SnortThe "most widely deployed IDS/IPS technology worldwide," Snort boasts millions of downloads and more than 400,000 registered users. It uses signature, protocol and anomaly-based inspection to detect and prevent intrusions on your network. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others.
657.
tcpdump/libpcapThese command line tools provide packet capture (libpcap) and analysis (tcpdump) capabilities. It's a powerful tool, but not particularly user-friendly. Operating System: Linux.
658.
WinDumpWinDump ports the tcpdump tools so they can be used on Windows systems. The project is managed by the same company that owns Wireshark. Operating System: Windows.
659.
WiresharkThe self-proclaimed "world's foremost network protocol analyzer," Wireshark has won quite a few awards and become a standard in the industry. It allows users to capture and view the traffic on their networks. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
660.
ZabbixCalling itself the "ultimate open source monitoring solution," Zabbix provides a huge range of monitoring, alerting and visualization features. Several different levels of commercial support are available, as well as training and other services. Operating System: Windows (agent only), Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Network Simulation
661.
GNS3Useful for research, designing networks, or studying for certifications, GNS3 allows users to experiment with Cisco and Juniper configurations. It also simulates simple Ethernet, ATM and frame relay switches. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Office Productivity
662.
AbiWordThis full-featured word processor offers nearly all of the same features as Microsoft Word, and it even reads and saves in Word-compatible formats. The newer versions of the software also offer free online collaboration for groups working on the same document through
AbiCollab.net. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
663.
EdhitaThis is a simple text editor and file transfer program for iPad only. It's missing the fancy features that would make it a full word-processing program, as well as the text highlighting and completion features you would find in code editors, but it gets basic jobs done. Operating System: iPad
664.
GnumericThis spreadsheet app for the Gnome desktop has been praised as more accurate than the leading proprietary spreadsheet. It can read existing files from Excel and similar programs, but is not meant to be a clone of any commercial program. Operating System: Windows, Linux
665.
KOfficeKDE's office suite includes KWord (word processing), KCells (spreadsheets), Showcase (presentations), Kivio (diagrams and flowcharts) and Artwork (vector graphics). The interface is quite a bit different than Microsoft Office's, but it is still easy to use. Operating System: Windows, Linux
666.
LibreOfficeLibreOffice is a community fork of OpenOffice.org. It has all the same capabilities as OpenOffice.org, plus a few new features all its own. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
667.
LyXLyX lets you format your document based on its structure. You mark text as a title, subtitle, etc., and then worry about the formatting later. It makes it easier to ensure continuity throughout long documents and deal with some of the difficulty of creating a document on a netbook or other device with a very small screen. Operating System: Linux, Unix, Windows, OS X
668.
NeoOfficeIn 2003, there was no version of OpenOffice.org for Macs, so the NeoOffice team created one. Even though OpenOffice.org and LibreOffice now offer versions for OS X, development has continued on NeoOffice, and it offers very stable operation and some Mac-specific features that aren't found in the other suites. Operating System: OS X, iOS
669.
OI NotepadIn addition to creating, editing and sending notes, this note-taking application allows users to add tags, filter and sort notes. Open Intents, the organization behind this app, also offers several other open source Android apps from the same site. Operating System: Android
670.
OpenOffice.orgThis alternative to Microsoft Office includes word processor (Writer), spreadsheet (Calc), presentation (Impress), graphics (Draw), math/science notation (Math) and database (Base) software. It both reads and writes to Microsoft Office formats, making collaboration easy. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
671.
OpenOffice Document ReaderWith this app you can view (but not edit) documents created with OpenOffice or LibreOffice on your phone. Features include zoom, copy and spreadsheet support. Operating System: Android
672.
Text EditThis simple text editor lets you write, edit and save short documents on your Android phone. You can select the font size and type, change colors and e-mail the documents you create. Operating System: Android
673.
VuDroidWith VuDroid, users can view PDF and DJVU documents from their Android devices. Features include zoom by slider drag, fast orientation change and more. Operating System: Android
674.
WriteTypeIf your children use your home office PC to write school reports (and of course, they do), you may want to check out WriteType. It's a word processor with special features for young students, like word completion, read back, highlighting, grammar and spell check, and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux
675.
X-OOo4KidsOpenOffice.org for Kids offers a simplified version of OpenOffice.org designed to be used by those aged 7-12. The advantage of this version, even if you're not a kid, is that it loads and runs very quickly and requires very little space on your portable drive. Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Online education/eLearning
676.
ATutorThis standards-based course management system has been used by many educational institutions to create award-winning websites. It was designed with an emphasis on accessibility and is very easy to use. Operating System: OS Independent
677.
Canvas LMSThe Canvas learning management system is designed to be as user-friendly as possible, with an intuitive interface and features like the SpeedGrader that help instructors save time. The software is also available on an SaaS basis from corporate sponsor
Instructure. Operating System: Linux, Unix, OS X
678.
ChamiloAfter just 18 months in existence, this open source learning management system racked up half a million users. The website includes a helpful demo so that you can try the software out before downloading. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X
679.
ClarolineClaroline has a very international community, with users in 93 different countries. It allows instructors to publish documents in nearly any format, and it's designed to foster collaborative learning. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
680.
CoFFEEShort for "Collaborative Face-to-Face Educational Environment," CoFFEE aims to help groups of students work together on problem-solving activities. It includes a set of tools for collaboration, shared work, individual work, and communication that can be managed and monitored by the instructor. Operating System: OS Independent.
681.
eFrontDesigned to be easy-to-use and visually appealing, eFront offers a very polished interface and all of the capabilities you would expect in an online course management system. In addition to the free version, it's also available in commercially supported versions with special features for educational institutions or enterprises. Operating System: Windows, Linux
682.
ILIASAnother international favorite, the ILIAS website includes links to organizations using ILIAS in 20 different countries. It's standards-based and includes features like webcasting, tests and assessments, support for multiple authentication methods, a SOAP interface, online surveys, integration with Google maps and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux
683.
MoodleOne of the most popular online course management systems, Moodle currently has more than 43 million users accessing course content on more than 53,000 sites. It includes modules for wikis, forums, databases, assessments, document delivery and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
684.
SakaiOriginally sponsored by Stanford, the University of Michigan, Indiana University and MIT, the Sakai CLE (collaboration and learning environment) is now used by more than 350 institutions. It is a combination learning management system, research collaboration system and ePortfolio solution. The source code is available for free, or you can purchase access to a hosted version through Sakai's commercial affiliates. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: OpenCourseWare
685.
eduCommonsA number of universities around the world aren't just utilizing open-source software, they're "open-sourcing" the content of their courses by making it freely available online. EduCommons is a content management system designed for these OpenCourseWare projects. Operating System: OS Independent.
686.
OCW ConsortiumIf learning something new without all the pressure of homework due dates and scheduled tests is your idea of fun, visit the OpenCourseWare Consortium. This isn't an open-source app; instead, it's a collection of university-level class materials that a variety of institutions have chosen to make "open source." Participating institutions include MIT, Notre Dame, the University of Michigan, and many others. Operating System: OS Independent.
Open Source Apps: Operating Systems and Kernel Modifications
687.
aLinuxFormerly known as Peanut Linux, aLinux is designed to be both fast and multimedia-friendly. Its graphic interface provides an easy transition for former Windows users
688.
andLinuxA good option for Windows users who would like to try out some Linux applications, andLinux runs Linux applications on Windows 2000, 2003, XP, Vista, or 7 machines
689.
ArchBangThis Arch variant uses the Openbox Window Manager. It's fast and lightweight, and offers many of the same customization capabilities as Arch
690.
Arch LinuxArch is definitely not for Linux newbies, but its simple design makes it a favorite among long-time Linux users who are comfortable with the command line. By default, it installs a minimal base system but provides plenty of options for customization
691.
Bodhi LinuxBodhi puts the focus on user choice and minimalism. It uses the Enlightenment desktop environment and a "software store" that makes it easy to find and install the open source applications you want to use
692.
CentOSShort for "Community ENTerprise Operating System," CentOS is based primarily on Red Hat code. It's the most popular version of Linux for Web servers, accounting for about 30 percent of Linux-based Web servers
693.
ChakraBased on ArchLinux, Chakra uses the KDE desktop. It uses a unique "bundles" system to let users access Gtk apps without actually installing them on the system
694.
Chrome OS/Chromium OSGoogle's operating system goes by two names, which can make things confusing. Officially, "Chromium OS" is the open source version used primarily by developers, and "Chrome OS" is the name for the version of the operating system Google plans to include on netbooks for end users. And just to make things even more confusing, both projects share a name with Google's Web browser. For now, Chromium OS (the only version available for download) is really only suitable for advanced users and developers
695.
CrunchBangSometimes written #!, CrunchBang is a lightweight distribution based on Debian. It's a popular option for netbooks like the Asus Eee
696.
DebianDebian is the foundation for many other Linux distributions, including Ubuntu. In addition to the core operating system, it includes 29,000 packages of open source software for a wide variety of purposes
697.
DreamLinuxThis distro can be installed on your desktop or run easily from a USB drive. DreamLinux installs the Xfce desktop environment by default, but it also supports Gnome
698.
DSLAt just 50MB, this distro lives up to its name – Damn Small Linux (DSL). As you might expect, it's very fast and runs on older PCs, as well as fitting onto small USB drives and business card CDs
699.
Easy PeasyDesigned for use on netbooks, EasyPeasy boasts millions of users in more than 166 countries. It was built to support social networking and cloud computing, and it offers very low power consumption for longer battery life on mobile devices
700.
EdubuntuThis version of Ubuntu Linux was specifically designed for use in schools. It includes many of the education-related applications on this list, including the KDE education apps, GCompris and School Tool
701.
eyeOSBuilt for cloud computing, eyeOS makes an entire desktop, including office productivity applications, accessible from a Web browser. It also serves as a platform for creating new Web apps
702.
FedoraFedora offers a community-supported (free) version of Linux that's very similar to and managed by
RedHat. Critics have called it an "amazingly rock-solid operating system."
703.
FrugalwareLike Slackware, Frugalware is best for users who aren't afraid of the command line, although it does have some graphical tools. It's designed with simplicity in mind
704.
FusionFusion describes itself as a "pimp my ride" version of Fedora. It offers good multimedia support and an interesting look and feel. It's best for more advanced Linux users who are looking for cutting edge, experimental applications
705.
GentooFirst released in 2002, Gentoo boasts "extreme configurability, performance and a top-notch user and developer community." It uses the Portage package management system, which currently includes more than 10,000 different applications
706.
GoboLinuxGoboLinux's claim to fame is that is doesn't use the Unix Filesystem Hierarchy Standard, but instead stores each program in its own sub-directory in the Program directory. That means that it's a little bit easier to use for Linux newbies or experienced Linux users who like to install applications from the original source code
707.
gNewSenseSupported by the Free Software Foundation, gNewSense is based on Ubuntu with a few changes, like the removal of non-free firmware. The name started as a pun on "Gnu" and "nuisance" and is pronounced guh-NEW-sense.
708.
IllumosWhen Oracle discontinued development of OpenSolaris, some of the developers who had been working on the project forked it to the Illumos project, where development and bug fixes continue. If you are looking for a free version of Solaris, this is the option for you. To download the software, visit the OpenIndiana page above.
709.
Joli OSJoli installs in just ten minutes and is optimized for cloud computing applicatons. Use it to breathe new life into an old PC, or you can run it alongside Windows
710.
KnoppixSuitable for beginners, Knoppix is an easy-to-use distribution based on Debian. It runs from a live CD, and if you don't want to go to the trouble to burn your own (or you don't know how), you can buy one for less than two bucks
711.
KubuntuAs the name suggests, Kubuntu is a Ubuntu fork that uses the KDE desktop instead of the Unity desktop. It's an excellent choice for new Linux users
712.
Linux MintLinux Mint boasts that it is the fourth most popular operating system for home users, behind Windows, OS X, and Ubuntu. It has a reputation for being very easy to use and it includes about 30,000 packages.
713.
LubuntuLubuntu is lighter, faster, and uses less energy than its namesake, making it a good choice for mobile devices, including netbooks. It uses the LXDE desktop instead of the Unity desktop
714.
MageiaIn 2010, a group of Mandriva developers began this community-driven fork following some ownership changes at the company that owns the Mandriva project. It's currently in beta, but the first official release is due in a few weeks
715.
MandrivaOwned by a publicly traded French company, Mandriva claims more than 3 million users worldwide. It's available in several editions, desktop and server, paid and unpaid, including a unique Instant On version that boots up with minimal functionality in less than 10 seconds
716.
MeeGoBased on Intel's Moblin and Nokia's Maemo, MeeGo is known as a smartphone OS, but it can also be used on netbooks and other mobile devices. With Nokia moving to Windows Phone 7 for future headsets, MeeGo's future is uncertain
717.
MEPISDebian-based MEPIS (also known as simplyMEPIS) is particularly popular with those new to Linux. It's available in free downloadable versions, or you can purchase a CD which makes trying or installing the software easy.
718.
MoonOSDeveloped in Cambodia (English is supported), MoonOS is based on Ubuntu, but has a different file hierarchy system and appshell framework. It's designed for speed, great looks and low memory use
719.
Musix GNU+LinuxAs its name implies, Musix is geared for multi-media enthusiasts, particularly those involved in audio editing. It can boot from a live disk or be installed on a system
720.
openSUSE.
This is the free version of Novell's
SUSE. It comes in both desktop and server versions, and you can find a great deal of documentation and support online
721.
PCLinuxOSDesigned to be easy to use, PCLinuxOS can be run on a Live CD or installed on a desktop or laptop. It supports seven different desktops, including KDE, Gnome, Enlightenment, XFCE, LXDE, and others
722.
PeppermintA good choice for netbooks or older PCs, Peppermint is designed to work with cloud and Web apps. The name might make you think it's based on Mint, but it's not. It's actually based on Lubuntu, which of course, is based on Ubuntu
723.
Pinguy OSBuilt for new Linux users who need something that's even easier to use than Ubuntu, Pinguy OS makes it easy to find and use the programs average users need most often. It's also available in a DVD version for $5.99
724.
Puppy LinuxSmall and fast, Puppy is designed to be installed on a USB thumb drive that users can take with them and boot from any PC. It takes up about 100 MB, boots in less than a minute, and runs from RAM for maximum speed
725.
quantOSThis variation of Linux Mint has been hardened for greater security. It includes integration with the Tor network and leverages several other security- and privacy-related open source projects.
726.
Red Hat Enterprise LinuxThe Red Hat company calls itself "the world's open source leader," and its server version of Linux is a particular favorite with enterprises. It's available only with a paid subscription, but does have a community version--Fedora.
727.
SabayonNamed after an Italian dessert, Sabayon aims to be the "cutest" Linux distribution — "as easy as an abacus, as fast as a Segway." It's based on Gentoo, and it supports the KDE, Gnome, LXDE and Xfce desktop environments
728.
Salix OSSalix compares itself to a bonsai tree in that it is "small, light and the product of infinite care." It comes in four different versions for the Xfce, LXDE, Fluxbox and KDE desktop environments
729.
Scientific LinuxCreated by the folks at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory and the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), as well as various scientists and universities, Scientific Linux (SL) aims to prevent scientists at each of these different institutions from having to recreate a Linux distribution that meets their needs. It's basically the same as Red Hat Enterprise Linux with a few slight modifications
730.
SlackwareFirst released in 1993, Slackware is one of the oldest Linux distributions. Popular with the geekiest of geeks, it relies heavily on command-line tools and is very similar to UNIX
731.
SUSENovell's version of Linux for enterprises is available only with a paid subscription (although you can download the very similar openSUSE for free). It claims to be "the most interoperable platform for mission-critical computing–across physical, virtual and cloud environments."
732.
Tiny Core LinuxOne of the smallest Linux distros available, Tiny Core weighs in at just 10MB in its GUI version. The command line version, Micro Core, is even smaller – just 6MB
733.
UbuntuCanonical's Ubuntu has become one of the most popular Linux distributions. It's very easy for Linux newbies to learn, and it comes in desktop, server and cloud versions
734.
UnityInstead of being built for end users, Unity is built to give developers or advanced Linux users some modular pieces they can use to create a customized distribution. Despite its name, it has nothing to do with the Unity desktop used by Ubuntu; instead, the Unity OS uses the OpenBox graphical environment
735.
Vector LinuxVectorLinux's credo is "keep it simple, keep it small and let the end user decide what their operating system is going to be." In addition to the free download, it's also available in a supported "deluxe" edition
736.
XubuntuAnd this is the version of Ubuntu that uses the Xfce desktop environment. It's available in both desktop and server versions
737.
Ylmf OSLike Zorin, Ylmf's interface looks a lot like Windows, in this case the Windows XP classic look. Created by Chinese developers, it's available in either Chinese or English, and it's based on Ubuntu
738.
ZenWalkOriginally based on Slackware and called "Minislack," ZenWalk has evolved to become a modern, fast, lightweight distribution that's easy to use. It's available in five versions: standard, core, live, Gnome and Openbox
739.
Zorin OSUnlike most Linux distributions, Zorin was designed to look and feel as much like Windows as possible – only faster and without as many bugs. It's available in both free and paid verions
Open Source Apps: Organization Management
740.
ATHENADesigned for cultural and arts organizations, ATHENA offers business management software with modules for ticket sales, accounting, donor and sponsor information, fundraising and marketing and more. The same software is available online with a subscription through
Artful.ly. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Password Crackers
741.
OphcrackFor those occasions when passwords can't be recovered any other way, Ophcrack can help systems administrators figure out lost passwords. It uses the rainbow tables method to crack passwords, and it can run directly from a CD. Operating System: Windows
742.
Figaro's Password ManagerThis Linux-only password safe encrypts passwords with the blowfish algorithm. It also features a password generator and can act as a bookmark manager as well. Operating System: Linux
744.
KeePassUsing the same password all the time is dangerous, but remembering multiple passwords can be difficult. KeePass offers a solution—an encrypted database that stores all of your passwords. All you have to remember is one master password. Operating System: Windows
745.
KeePassDroid,
7Pas,
iKeePass,
KeePass for BlackBerryThe open source password safe KeePass has been ported to all of the major mobile operating systems. It saves all of your passwords in an encrypted database so that you only have to remember one master password. Operating System: Android, iOS, Windows Phone 7, BlackBerry
746.
KeePassXOriginally, this project ported KeePass so that it could be used with Linux. Now, it supports multiple operating systems and adds a few features not in the original KeePass. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
747.
PasswordMakerInstead of re-using the same password over and over, use PasswordMaker to generate completely secure passwords using a one-way hash algorithm. All you need to remember is the name of the site you're visiting and your master password. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
748.
Password SafeWith a very simple interface, Password Safe offers a bare-bones password management system. It also offers the option of storing different sets of passwords—for example, your work and home passwords—in different databases with different master passwords. Operating System: Windows
749.
PWGenIf your password is easy to remember, it's probably also easy to guess. This app randomly generates strong passwords for better protection. (But because these passwords are hard to remember, it's best to use PWGen with a password safe.) Operating System: Windows
750.
Secrets for AndroidLike KeePass, Secrets saves your passwords in a master database. However, this app also gives you the option of saving other secret information in the same secure database so that it can't be accessed if your phone is lost or stolen. Operating System: Android
751.
WebKeePassHave your own Web server? This version of KeePass lets multiple users access a KeePass database from any Web-connected system. It's ideal for small businesses. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: PDF Tools
752.
jPDF TweakThis Java-based program lets you merge, split, reorder, sign, and encrypt previously existing PDF files. Operating System: OS Independent
753.
PDFCreatorThis helpful app lets you create a PDF file from virtually any Windows program. It also creates PNG, JPG, TIFF, BMP, PCX, PS and EPS files as well. Operating System: Windows
754.
PDFeditYou don't have to purchase expensive Adobe software in order to make modifications to existing PDF files. PDFedit lets you edit text, delete and renumber pages, add markup and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux
755.
SkimIf you need to read a lot of pdf files, for example technical or scientific papers, Skim makes it easier to read and take notes digitally instead of printing out pages and making notes by hand. You can also use it to give presentations using a pdf file instead of a traditional presentation program. Operating System: OS X
756.
SumatraThis alternative to Adobe Reader boots up fast and offers a very simple interface. In addition to PDF files, it also reads XPS, DjVu, CBZ and CBR files. Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Personal Financial Management
757.
BuddiCalling itself “personal budget software for the rest of us,” Buddi offers very simple installation and operation for users with little financial background. It's won multiple awards, but does not offer the same type of advanced features as Quicken. Operating System: OS Independent
758.
ChartsyThis stock charting and screening platform features a modular architecture that lets you install only the capabilities you need. The project owners plan to add trading capabilities in the future, but they aren't operational yet. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
759.
GrisbiWhile it doesn't offer double-entry accounting, Grisbi offers some business accounting features in addition to all the features you would expect in a personal finance manager. It's available in multiple languages and can handle multiple currencies, Operating System: Windows, Linux
760.
HomeBankUnder development since 1995, HomeBank offers an intuitive interface and easy-to-use reporting capabilities. Like many of the other apps on our list, it can import financial data from other sources, autocompletes entries whenever possible and provides budgeting capabilities. Operating System: Linux
761.
iFreeBudgetThis budgeting, accounting and expense tracking app also comes in an Android version. Its best for small businesses or home users. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Android
762.
JGnashJava-based JGnash supports double-entry or single-entry bookkeeping, account reconciliation, PDF report generation, multiple currencies, check printing and more. It can also import data from commercial financial software or online banking systems. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
763.
JStockFor active investors, this app offers a stock watchlist, portfolio management, alerts, filters, charts, chat and more. It can track 26 stock markets around the world, and it can save your data in the cloud if you like. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
764.
KMyMoneyKDE's personal finance software is particularly user-friendly, with an interface that's easy for anyone who's used Quicken or similar software to understand. Previous versions of the software only worked on Linux, but the latest version also supports Windows (though it isn't completely stable). Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
765.
LightWalletIf you have trouble remembering to save receipts or enter transactions in your budgeting software, LightWallet is for you. This Java-based personal finance package installs on your mobile phone, so you can enter transactions while you're on the go instead of having to remember what you bought when you get back home. Operating System: OS Independent
766.
Market Analysis SystemReady to get really serious about investing? This app tracks a huge number of metrics and analyzes market data, flagging you when certain criteria are met. You can run it on a single PC or in a client/server setup. Operating System: Windows, Linux
767.
Money Manager ExThis app claims to offer "all the basic features that 90% of users would want to see in a personal finance application." Notable features include AES encryption, the ability to run from a thumb drive without an install, depreciation tracking, international support and import from CSV and Quicken file formats. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
768.
StockManiacManage your own investments? StockManiac incorporates a feed reader/comment system with a stock tracker so that you can track your thoughts about your stocks while you track your stocks. It's not suitable for day trading, but works well for average personal investors. Operating System: OS Independent
769.
UnkleBillThis newer financial software offers double-entry accounting to track your personal or small business accounts. It offers multiuser functionality and creates PDF reports. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
770.
YapbamJava-based Yapbam (short for "yet another bank account manager") is cross-platform, portable and extensible. It can import data from other software and online banking, automatically generates reports and includes a currency converter. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Photography Tools
771.
Coppermine Photo GalleryBased on PHP and MySQL, Coppermine Web photo gallery script offers a huge lineup of features including multiple languages, e-card creation, thumbnails, and many more. In order to use it, you need a Web server running Apache, PHP, MySQL, and either GD or ImageMagick. Operating System: OS Independent
772.
GalleryThis Web-based photo album organizer makes it easy to organize and share your digital photos. To use it, you'll need your own Web server, or the site recommends a number of hosts that are confirmed to be compatible with Gallery. Operating System: Windows, Linux
773.
HuginSometimes a single photo can’t capture the grandeur of a particular scene—that’s where Hugin comes in. Hugin makes it easy to combine multiple, overlapping photos of a single location into one huge panorama. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X
Open Source Apps: Physics
774.
StepKDE's physics program provides demonstrations of classical mechanics, particles, springs with dumping, gravitational and coulomb forces, rigid bodies, molecular dynamics and more. It can also do unit conversion and error calculation and propagation. (Note that in order to use Step on Windows, you'll have to download
KDE for Windows.) Operating System: Windows, Linux
Open Source Apps: Point-of-Sale (POS)
775.
Floreant POSUsed by the Denny's chain in New York, this restaurant-specific POS application offers a full set of capabilities to support fine dining, carry out, tax, discounts, food grouping, drawer pull, kitchen ticket, ESC/POS receipt, combined payment system and sales reports. Tow levels of commercial support are available, with prices varying based on response time and availability. Operating System: OS Independent
776.
Lemon POSDesigned for small or micro businesses, Lemon POS offers an easy-to-use interface, a price checker, search capabilities, and more. It can run multiple terminals from a single server and it includes role-based permissions and other security features. Operating System: Linux
777.
Openbravo POSOpenbravo's POS offering integrates with its ERP software. It's designed to work with touchscreens and includes master data management, warehouse management, reporting and restaurant management capabilities. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
778.
POSperThis app was designed for small retail stores and restaurants. It supports multiple touchscreens, scanners, card readers and ticket printers, and it integrates with all databases supported by Hibernate. Operating System: OS Independent
779.
SymmetricDSSymmetricDS is a data synchronization and replication tool designed to transmit data from POS databases to back office systems. Key features include guaranteed delivery, data filtering and rerouting, primary key updates, database versioning, and more. Operating System: OS Independent.
Open Source Apps: Portable Applications
780.
DemocrakeyFor privacy on the go, Democrakey bundles together apps for anonymous browsing, anonymous e-mail and IM, encryption, file shredding and anti-virus into a suite that runs from a thumb drive. You can also purchase a USB drive with Democrakey installed from
Democrakey.com. Operating System: Windows
781.
PortableApps.comYou don't have to be on your own PC to use your favorite open-source software—PortableApps.com packages many of the most popular apps so that you can take them with you on a thumb drive. The standard suite includes Firefox, OpenOffice.org, Pidgin and nine other apps, but dozens of other portable open source apps are also available on the site. Operating System: Windows
782.
Tor Browser BundleThe Tor project also makes a portable suite that you can take with you on a thumb drive. You can also download an IM version. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
783.
winPenPackWhile its not as well-known as PortableApps.com, winPenPack also offers dozens of open source apps in portable versions. You can download the apps individually or you can get the Full or the Essential suite. Operating System: Windows.
Open Source Apps: Presentations
784.
ImpressiveIf you want to make your presentations more, well, impressive, give this app a try. It takes presentations you create with PowerPoint or other apps and lets you add more interesting transitions, use a handy overview screen, and spotlight or highlight text on the screen as you give your talk. Operating System: OS Independent.
Open Source Apps: Privacy Protection
785.
AdBlock PlusUsed by more than 12.5 million Firefox users, AdBlock Plus can be configured to block all advertisements or only those originating from domains known to install malware. To use it, you'll also need to subscribe to one of the filters that provide the type of blocking you desire. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
786.
BetterPrivacyEven when you have your cookies disabled, Flash-enabled sites like YouTube, E-Bay and others can use Flash cookies (also called "SuperCookies") to track your activities. BetterPrivacy automatically disables those cookies. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
787.
HTTPS EverywhereMany websites have the ability to encrypt traffic via HTTPS, but don't turn on that feature by default. This Firefox add-on, a collaboration between the Tor Project and the Electronic Frontier Foundation, rewrites requests so that you will automatically use HTTPS whenever it is available. Operating System: OS Independent
788.
JAPLike Tor, JAP hides your IP address while you're browsing online. However, because it is a research project, the service occasionally experiences outages and downtime. Operating System: OS Independent
789.
MixmasterAvailable in both client and server versions, Mixmaster is a remailer that protects you from traffic analysis. With it, you can send e-mail anonymously or under a pseudonym. Operating System: Windows, Linux
790.
MixminionAnother anonymous remailer, Mixminion passes e-mail through a network of servers that mixes them up and encrypts them in order to protect privacy. It hasn't been updated in a while, but a stable version is available. Operating System: Windows, Unix, OS X
791.
Privacy DashboardThis Firefox add-on from W3C (the World Wide Web Consortium) alerts you to the data being collected by the various websites you visit. Users also have the option of contributing to a project that is tracking how websites are doing at protecting users' privacy. Operating System: OS Independent
792.
PrivoxyThis non-caching Web proxy server offers advanced filtering capabilities for removing ads and protecting your privacy. You can use it to protect an individual PC or an entire network. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
793.
ReclaimPrivacy.orgThis site scans your Facebook settings and alerts you to data which you may have unintentionally made public. It's still a good idea to check your privacy settings manually, but this tool gives you a good second check to make sure you haven't divulged personal information that you didn't want to make public. Operating System: OS Independent
794.
SafeCacheThis Firefox add-on helps prevent websites from accessing your browsing history. It works with your cookie settings to apply your desired level of privacy. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
795.
TorbuttonThis Firefox add-on makes it easy to turn Tor (see above) on or off for anonymous browsing. Note that when you are using it, you will not be able to access sites that use JavaScript, some CSS features, or Flash. Operating System: OS Independent
796.
Web of Trust (WOT)Downloaded more than 23.5 million times, Web of Trust rates websites based on their reputation. While you're browsing, sites with a good reputation will show up with a green circle, bad sites get a red circle, and those in between will look more orange or yellow. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Programming Languages
797.
GoRecently developed by Google, Go aims to make developers more productive by providing them with a clean, simple programming language. And unlike many older languages, it offers garbage collection and parallel computation. Operating System: Linux, OS X
798.
JavaOriginally developed by Sun but now owned by Oracle, Java allows developers to write code that will run on multiple operating systems. According to Tiobe, it's the most popular programming language in the world. The link above offers extensive help for those new to the language and a large collection of tools for Java developers. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
799.
PerlPerl has been around for 22 years and runs on more than 100 different platforms. It's an ideal Web programming language and integrates easily with popular databases. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
800.
PHPThis general purpose scripting language is particularly suited to Web development, enabling developers to write dynamically generated pages quickly. A lot of its syntax comes from C, Java and Perl, and it can be embedded into HTML. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
801.
PythonPython's strengths are its speed, flexibility and readable syntax. It's often used in Web development but can be used for other types of applications as well. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
802.
RR is both a programming language and an environment for developing statistics and graphics applications. It's very similar to the commercially developed S language. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
803.
RubyDesigned to feel "natural," Ruby's creator Yukihiro “matz” Matsumoto blended parts of Perl, Smalltalk, Eiffel, Ada, and Lisp to create a new language that's been called both "handy" and "beautiful." It's ranked as the tenth most popular programming language in the world, due in no small part to the popularity of the Ruby on Rails framework. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Project Management
804.
AchievoDesigned for medium-sized organizations, Acheivo combines calendar, contacts, project management, time tracking and basic CRM and human resources management capabilities. It's Web-based, and the site offers a demo so that you can try it out before you download. Operating System: OS Independent.
805.
DigaboardFor Agile, Scrum or Kanban development teams, Digaboard is a digital version of your project whiteboard. Unlike a traditional white board, it saves everything you've done and you can access it from the Web, making it a good choice for geographically dispersed teams. Operating System: OS Independent.
806.
DotprojectThis Web-based app offers an e-mail based trouble ticket system, client/company management, project listings, hierarchical task list, file repository, contact list, calendar, discussion forum and resource-based permissions. To see it in action, check out the demo on the site. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
807.
GanttProjectLike OpenProj, GanttProject can also import and export from Project. As you would expect from the name, it creates Gantt charts, and it also creates PERT charts, generates reports and exports data to spreadsheet formats. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
808.
NavalPlanAs the name suggests, this Web-based project management system was originally created for the ship building industry, but its features make it useful for just about any industry. It helps organizations schedule resources, control costs, organize tasks and monitor progress, and it connects with many ERP systems. Operating System: Linux.
809.
OfuzThis cloud-based invoicing, project management and CRM solution was designed to help freelancers and small businesses manage their client interactions. You can run it on your own server for free or use the SaaS version called Ofuz Online. Operating System: OS Independent
810.
One pointOnepoint aims to combine a powerful set of features with an easy-to-use interface. It's available in a variety of editions: Basic and open editions are available with a free, open source license. Professional, master, group, and enterprise editions require a paid, commercial license. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
811.
OpenProjDownloaded more than 1.25 million times, OpenProj was specifically designed to replace Microsoft Project, and it opens both Project and Primavera files. Key features include Gantt charts, network diagrams (PERT charts), WBS and RBS charts, earned value costing and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
812.
openXprocess The app offers addresses the needs of process engineers, project managers and project participants. It imports from Microsoft Project and includes a number of features designed to meet the needs of Agile and Scrum teams. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
813.
PHPProjektPHPProjekt combines project management with a time tracker and some groupware functions, like a calendar, to do list and contact manager. It's Web-based, and the site provides a helpful demo so that you can see the features in action. Operating System: OS Independent.
814.
PlandoraPlandora meets the needs of a variety of kinds of teams with Gantt charts, a Balanced Scorecard view and an Agile development board. In addition, the latest release includes cost management, artifact management and new gadgets. Operating System: OS Independent.
815.
RedmineWeb-based Redmine offers Gantt charts, calendar, per-project wikis, an issue tracker, newsfeeds and more. It also integrates with most version control systems, making it a good choice for development teams. Operating System: OS Independent.
816.
TaskJugglerTaskJuggler calls itself "project managers' delight" and includes tools for project scoping, resource assignment, cost and revenue planning, and risk and communication management. It's designed for "serious project managers" and takes some effort to learn. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
817.
web2ProjectOffering "real project management for real business," this Web-based tool can manage multiple projects, companies, departments and users. Key features include a modular infrastructure, built-in security, role-based permissions, project- and group-wide Gantt charts, and group calendar. Operating System: OS Independent.
818.
XPlanner+Designed for development teams, this Java-based app includes project management, bug tracking and time tracking capabilities. It supports Agile methodologies and it can export to multiple formats, including Microsoft Project. Operating System: OS Independent.
Open Source Apps: Project Portfolio Management
819.
Onepoint ProjectOnepoint combines project management with project portfolio management capabilities, including supporting formal, Agile and JIRA projects within a single solution. The Basic and Community editions are available with a GPL license, while the supported editions for enterprise users have a proprietary license. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
820.
Project.NetThe first open source solution to be included in Gartner's "Magic Quadrant for IT Project and Portfolio Management Applications," Project.Net is a robust, but affordable alternative to commercial PPM software. It integrates with many BI systems, includes advanced social networking features and commercial support and services are available. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Property Management
821.
SpaceBookerIf you're running a hotel, car rental company or a craft fair, SpaceBooker can help you keep track of reservations. It works both on- and offline, and it gives you a number of different views, including a graphical map, so that you can see what's reserved and what's available for various dates. Operating System: Windows.
Open Source Apps: Religion
822.
BibleTimeThis Bible study tool includes text from more than 200 free Bible texts and commentaries available through the Crosswire Bible Society. The interface is easy to use and it includes a helpful search capability. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
823.
GnauralIt already does everything else--now your computer can help you meditate. Using something called the “binaural beat principle,” Gnaural generates audio tones designed to get you in the right frame of mind for relaxation. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
824.
NoorNoor doesn’t offer a lot of bells and whistles, but it does let you access the text of the Quran from your PC. It includes both the original Arabic and translations. Operating System: OS Independent
825.
XiphosLike BibleTime, Xiphos offers access to hundreds of free Bible study tools. The tabbed interface makes it easy to cross-reference different texts, and Xiphos also allows you to create your own modules for journaling, prayer lists or writing your own commentary. Operating System: Windows, Linux
826.
ZekrZekr provides a searchable version of the Qur'an in Arabic and 20 other languages. You can read it yourself or have Zekr read it aloud for you. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Remote Access/VPN
827.
AndroidVNCThis TightVNC fork allows you to view and interact with your computer from your Android phone. Obviously, it's tough to do a lot of work from your phone, but it is useful for short and simple tasks. Operating System: Windows, Linux
828.
BO2KBased on Back Orifice, BO2K provides file-synchronization and remote operation capabilities for network administrators. Unlike most commercially available products, it's small, fast, free, and very extensible. Operating System: Linux
829.
OpenSSHDeveloped by the OpenBSD project, OpenSSH offers a set of SSH, SCP, and SFTP tools for secure remote access and file transfer. It encrypts all traffic, including passwords, to make hijacking nearly impossible. Operating System: Linux, Unix, BSD
830.
OpenVPNDownloaded more than 3 million times, this popular open source SSL VPN solution makes it possible for remote workers to access your corporate network securely. It's also available with commercial support or as a cloud-based solution. A number of other client front-ends are also available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
831.
PuTTYThis basic telnet/SSH client offers remote access for most Windows and Unix systems. Note that it does not support Vista. Operating System: Windows, Unix
832.
TightVNCWith TightVNC, employees can control their work computers while they are at home or traveling. It's lightweight and fast and conforms to RFB protocol specifications. Operating System: Windows, Linux
833.
UltraVNCUltraVNC provides similar functionality as TightVNC. Key features include file transfer, video driver, optional encryption plugins, text chat and multiple-monitor support. Operating System: Windows
834.
ZebedeeWhile it's not a true VPN tool, Zebedee does provide secure IP tunneling for TCP/IP or UDP data transfer between two systems. It not only provides security against snoopers, its compression capabilities save on network bandwidth. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix
Open Source Apps: Report Authoring
835.
WIKINDXDesigned to help researchers take notes and track bibliographic information, WIKINDX can be used by a single user or stored on a Web server for access by a team working together. It exports bibliographies in a variety of style guide formats, allows multiple attachments per resource and supports non-English characters. Operating System: OS Independent
836.
ZoteroZotero is a Firefox plug-in that makes it easy to track and cite your sources when doing research on the Web. It also includes a "Groups" feature that allows you to share your research with a team. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Robotics
837.
The Player ProjectMore middle and high school are offering classes in robotics, and The Player Project provides some of the software that supports instruction in robotics. It includes Player, a network server for robot control; Stage, a 2D multiple robot simulator; and Gazebo, a 3D multiple robot simulator with dynamics for simulating outdoor environments. Operating System: Linux, Unix.
838.
ROSShort for "Robot Operating System," ROS offers a set of open-source libraries for controlling robots. It includes device drivers, libraries, hardware abstraction and other capabilities. Operating System: Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Router Software
839.
VyattaVyatta's software and appliances offer enterprises an alternative to expensive networking hardware from companies like Cisco. The core software is available as an open source download, or you can purchase hardware, supported software or services from Vyatta. Operating System: Linux
840.
FREESCOWith FREESCO you can set up an Ethernet bridge or router, a dial-up or leased line router, or a http, dns, ftp, ssh, or print server. It also includes the standard Linux firewall and NAT to help protect your network. Operating system: Linux
Open Source Apps: RSS Readers
841.
FeedReaderFeedReader offers robust news aggregation while keeping the interface basic enough for novices to use. Upgrades to the FeedReader Connect and FeedReader OEM products are available for a fee. Operating System: Windows
842.
RSS OwlOne of the most popular feed readers available, RSS Owl aggregates headlines from all of your favorite media sites and makes them easy to browse. It has a ton of advanced features, like saved searches, news filters, labels, and news bins that set it apart from other similar apps. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: School Administration
843.
ClaSSClass describes itself as "a student information management system turned on its head." It takes a more teacher-centric approach, making it easy for classroom instructors to input information and access data about their students. Operating System: OS Independent
844.
Focus/SISThis newer SIS is completely Web-based and designed to make it as easy as possible to comply with state reporting requirements. It also streamlines attendance taking, scheduling, grading, and other administrative tasks. Operating System: OS Independent
845.
OpenAdminOpenAdmin's interface isn't particularly fancy, but it does provide a wide range of features for tracking grades, attendance, schedules, discipline, fees, IEPs and more. It was designed to meet the needs of both public and Catholic schools. Operating System: OS Independent
846.
openSISThis app includes all of the same features you would find in a much more expensive commercial SIS—demographics, contact information, scheduling, gradebook, reports, attendance, transcripts, health records, a parent portal, etc. The free community version is suitable for small or medium-sized schools with IT staff, and it's also available in commercially supported versions for individual schools and school districts. Operating System: Windows, Linux
847.
SchoolToolCanonical's Edubuntu and the One Laptop Per Child project both include SchoolTool as their school administration program. It offers an online gradebook, calendar, attendance, competency tracking, demographics and contacts. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Screenplay Writing
848.
CeltxIf you have a great idea for a movie or a TV show, Celtx can help you format your screenplay properly, storyboard scenes and sequences, sketch setups, develop characters, breakdown and tag elements, schedule productions, and more. According to its owners, it’s "the world's first all-in-one media pre-production system." Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: SEO
849.
SEO PanelReleased in 2010, this app describes itself as the "world's first seo control panel for multiple websites." Key features include an automatic directory submission tool, keyword position checker, site auditor, Google and Alexa rank checker and more. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Small Business Server
850.
ClearOSIn addition to its networking and security gateway features, ClearOS acts as a groupware and mail server with support for Microsoft Outlook. The paid supported versions of the software and the pre-configured appliances from the Clear Foundation add other features useful for small businesses. Operating System: Linux.
851.
ZentyalThis all-in-one platform combines a communications server with a security gateway, backup, network monitoring, infrastructure management, file server, Web server and more. In addition to the basic, free edition, it also comes in paid professional and enterprise versions, with other add-ons available as well. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Smoking Cessation
852.
QuitCountNeed some motivation to help you stop smoking? Quit Count adds up how much money you've saved and how much time you've added to your life expectancy. Operating System: Linux
853.
No Smoke CounterLike QuitCount, the No Smoke Counter tracks your money saved by not smoking. However, this version is designed for your smartphone, so you can take it along with you. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: SOA
854.
TurmericVersion 1.0 of this eBay-owned SOA platform was released in May of 2011. It's Java-based, standards-based and offers quality-of-service features, monitoring capabilities, a repository library, a type library, an error library, local binding and more. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Social Networking
855.
BuddyPressMade by the WordPress team, BuddyPress offers "social networking in a box." Its used by thousands of organizations to create social networks for a variety of different groups. Operating System: OS Independent
856.
DiasporaLaunched as an alternative to Facebook, this open source social network has a long way to go to catch Facebook's user base. It offers greater control over your privacy and content. You can sign up to join a current Diaspora hub or create your own Diaspora server using the information from the site. Operating System: Windows, Linux
857.
LiveStreet CMSSimilar to BuddyPress, LiveStreet is a content management system for creating blogs or social networks. It boasts easy installation, extensibility and multilingual functionality. Operating System: Linux
858.
Pligg CMSPligg describes itself as "social publishing" software; that is, it creates websites that invite users to submit their own content and/or vote on current content. Hosting is available through several third-party partners. Operating System: Windows, Linux
859.
StoryltrStoryltr brings together all of your Web 2.0 posts from up to 18 different services, including Twitter, Flickr, StumbleUpon, Tumblr and others. It lets you tell the story of your life in your own way. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Speech
860.
eSpeakAlthough not as human-sounding as some other text readers, eSpeak provides clear audio of the text on your screen. It supports dozens of different languages, as well as several different English accents. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
861.
SimonIf you'd like to be able to talk to your computer, check out Simon. It accepts voice commands and turns audio into text. Operating System: Windows, Linux
Open Source Apps: Storage
862.
FreeNASBased on BSD, this app allows you to create network attached storage for sharing files across Windows, OS X, Linux and Unix-like systems. Key features include a Web-based interface, the Zettabyte File System, snapshots, thin provisioning and more. Operating System: FreeBSD
863.
OpenfilerDownloaded more than 250,000 times, Openfiler offers both file-based Network Attached Storage and block-based Storage Area Networking. Key features include volume-based partitioning, iSCSI (target and initiator), scheduled snapshots, resource quota, and a unified interface for share management. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Systems Administration Tools
865.
Inside Security Rescue ToolkitAlso known as INSERT, the Inside Security Rescue Toolkit packs dozens of helpful security and system administration apps into a single download. In addition to a complete, bootable Linux system (based on Debian), you'll get apps for anti-virus protection, network analysis, forensics, and more. Operating System: Linux.
866.
Networking Commands for WindowsIf you’d rather perform network configuration and maintenance activities from the command line instead of a GUI, check out Networking Commands for Windows. This collection of command-line tools lets you use a small list of short, easy-to-remember commands to perform day-to-day systems administration activities. Operating System: Windows XP
867.
No AutorunJust like the name suggest, this app prevents any malware on a thumb drive from auto-running when you plug it into your system. It also logs suspicious files so you can see the malware it's blocked. Operating System: Windows.
868.
ProShieldDesigned primarily for Debian and Ubuntu, ProShield scans your system to make sure your software is up-to-date and that you haven't picked up any malware. It also reminds you to backup your system, checks your available disk space, and performs other routine maintenance checks. Operating System: Linux
869.
Wake on LanThis helpful little app makes it easy to turn on or shut down Windows systems connected to your network. It also includes a scheduling feature and can be run from the command line or a GUI. Operating System: Windows.
870.
WebminThis interface allows you to set up Unix user accounts, change passwords, and perform other system admin tasks from any Web browser. You can perform more than 100 different functions. Operating System: Unix
Open Source Apps: Text Editors
871.
AkelPadDesigned to be small and fast, AkelPad offers basic text editing with numerous plug-ins that add other features. Standard features include multi-window mode, file preview, multi-level undo, and more
872.
EmacsEmacs-style text editors have been around since the mid-70s and are popular among programmers. The GNU version offers content-sensitive editing modes for HTML and other types of files. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
873.
jEditJava-based jEdit boasts auto indent and syntax highlighting for 130 programming languages. It has a huge list of features and more than 150 plug-ins that extend its capabilities. Operating System: OS Independent
874.
Notepad++This mature text editor offers fast performance and a lightweight file size. It's been downloaded more than 20 million times, has won numerous awards, and offers a number of features that make it an excellent option for developers. Operating System: Windows
875.
TEATEA combines a small file size with hundreds of functions, including syntax highlighting for more than 20 languages. Other key capabilities include a spellchecker, code snippets, built-in ZIP packager, bookmarks, tabbed layout engine and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
876.
VimSometimes considered an IDE, Vim is a "programmer's editor" with extensive syntax assistance, code completion, split screens, undo/redo, and many other features. It's won a number of awards, but does have a reputation for being difficult to learn. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
877.
ZileShort for "Zile is Lossy Emacs," Zile is a small text editor that looks very similar to the popular Emacs editor. It packs many features into just 100KB, including multi-level undo, multi-window display, killing, yanking, register, and word wrap. Operating System: Linux/Unix
Open Source Apps: Time Tracking
878.
eHoureHour was designed for firms that work on multiple projects and bill by the hour. It's great for lawyers, consultants and freelancers of all kinds, and it offers a user-friendly, Web-based interface. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
879.
RachotaWhile the other apps in this category are designed to track time for invoicing and payroll purposes, Rachota tracks your time so that you can see how you can become more efficient. You can take it with you on a mobile device and track work on multiple projects. Operating System: OS Independent
880.
timeEditionThe minimalist interface on this app makes it very easy to track the amount of time workers spend on various tasks. It also integrates with iCal, Outlook and Google Calendar, and exports into spreadsheet formats. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
881.
TimeTrexIn addition to tracking employee time and attendance, this app includes scheduling, estimating and document management modules that are helpful for project managers. The site offers a helpful demo, and you can also purchase the app on an SaaS basis. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
882.
TodomooTodomoo combines a hierarchical task manager with a time tracker that allows you to bill for your time on multiple projects. It's also available in a portable edition that you can run from a USB drive. Operating System: Windows.
Open Source Apps: To-Do Lists/Schedulers/Calendars
883.
AstridAstrid describes itself as a "social productivity" tool. Basically, it's a to-do list and reminder system that you can use individually or with groups. Operating System: Android
884.
BORG CalendarNo need to worry about being assimilated, this "BORG" stands for "Berger Organizer." It combines basic calendar functionality with a sophisticated to-do list that actually works more like most project management software. Operating System: OS Independent.
885.
MakagigaLike RedNotebook (below), Makagiga includes a to-do list, calendar, and text editor, but it also adds a feed reader and a sticky-note widget. You can also import and export documents from other applications. Operating System: Windows, Linux
886.
RedNotebookRedNotebook combines a calendar/to-do list with a text editor that use can use to create a journal, track progress on projects or make notes on upcoming events. If you need something more freeform than traditional project management software, this app might be for you. Operating System: Windows, Linux
887.
Task CoachWhile it's very simple, this to-do list includes the helpful ability to divide tasks into smaller subtasks. It's also available in mobile versions for use on your smartphone. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS
888.
ThinkingRockThis app helps you put into practice the "Getting Things Done" methodology featured in books by David Allen. Different screens help you collect your thoughts, process thoughts, then organize, review, and do. Operating System: Windows, Linux
Open Source Apps: Transit
889.
OpenTripPlannerThis one-year-old project aims to make it easy for government entities to communicate information about public transit schedules, walking and biking routes and other travel-related information. Portland's TriMet, one of the sponsors of the project, currently has a
working demo of the software in action. Operating System: OS Independent
Open Source Apps: Typing
890.
KlavaroKlavaro offers a much more comprehensive program that includes a basic course, adaptability exercises, fluidity exercises, velocity exercises, progress charts and more. Unlike many other programs, you can also use it to learn alternative keyboard layouts in addition to the standard QWERTY keyboard. Operating System: Windows, Linux
891.
TypeFaster Typing TutorTypeFaster also includes touch typing lessons and a 3D typing game for extra practice. It comes in standard, accessible, and Spanish versions, as well as a multiple user version that allows instructors to assign certain lessons each day and track student progress. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
892.
TuxTypeThis app for younger kids includes some basic typing instruction and two fun games for increasing your typing speed. It's not a comprehensive typing instruction program, but does offer fun supplemental activities and helps elementary students learn where all the letters are on the keyboard. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Utilities
893.
AppetizerAppetizer is a dock-style application launcher for Windows (2000, XP or Vista). It supports the PortableApps.com file format, so it will automatically detect any other portable apps you have on your thumb drive and include them on the dock. Operating System: Windows
894.
BarnacleThis WiFi tethering app lets you turn your Android phone into a wireless router that will connect your other devices to the Internet. Note that this app requires root access. Operating System: Android
895.
Bulk File ManagerThis helpful utility finds duplicate files and gives users the options of deleting or moving them. It also offers bulk file moving, re-naming and secure deletion capabilities. Operating System: Windows
896.
Copy HandlerIf you're re-organizing or cleaning up your hard drive, Copy Handler can help. It's faster than the standard Windows copy and move features, and it gives you more options, like task queuing, filtering files according to specific criteria, pausing and resuming copying files and changing the copying parameters on the fly. Operating System: Windows
897.
Explorer++This utility doesn't so much replace Windows Explorer as enhance it. It adds tabbed browsing, a preview window, keyboard shortcuts and other features to the familiar interface. Operating System: Windows
898.
Folder MenuThis handy tool makes it easier to jump to your favorite files and folders. It works with Windows Explorer, open/save dialog boxes, or the command prompt. Operating System: Windows
899.
GnuWin32This site offers native Windows ports of lots of different open-source apps offered under the GNU license. There are dozens of apps, tools, and libraries available, but many of them fall under the "utilities" category, which is why we put it here on our list. Operating System: Windows
890.
HDGraphWondering how in the world you managed to fill up 300 GB worth of hard drive space? HD Graph lets you see the reasons in a flash by drawing a multi-level pie chart that details how much space each directory and subdirectory is consuming. Operating System: Windows
891.
KShutdownNeed to turn off, turn on, or restart your computer at a later time? This app lets you schedule all those functions so they happen automatically and adds several other features as well. Operating System: Windows, Linux
892.
KysrunOriginally designed for the Eee, Kysrun lets you open applications, link to bookmarks, or perform other operations by typing a few letters instead of hunting through menus. As you begin typing one letter at a time, Kysrun brings up a list of all applications on your system with those letters in the name, and you simply click on the one you want. Operating System: Linux
893.
Open ManagerOpen manager is an open source file manager for Android smartphones and tablets. It allows you to cut, copy, paste, rename, delete, sort, zip and backup files and folders. Operating System: Android
894.
QTTabBarLike Explorer++, QTTabBar adds tabs to the Windows Explorer interface. It's technically still in alpha, but has a large and enthusiastic user base. Operating System: Windows
895.
Standup TimerKeep your standup meetings short and sweet with this helpful timer. It displays both the amount of time elapsed and the time left before you need to wrap up your meeting. Operating System: Android
896.
Startup ManagerTired of waiting forever while Windows starts up? This app gives you control over which applications and services launch when you start up your system, so that you get better performance and greater security. Operating System: Windows.
897.
UltraDefragNeed to defrag your hard drive? Unlike the defragmenter tool that comes with Windows, UltraDefrag lets you defrag on startup for maximum speed. You can also configure it to shut down your system when it's finished, so you can leave it working at night after you go to bed. Operating System: Windows
898.
Unrar Extract and RecoverIf you need to extract a lot of RAR archive files and you're not exactly sure what all the passwords are, this tool can help. It "handles password-protected, multi-part and encrypted archives with ease," and it requires no installation. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
899.
Windows Leaks DetectorThis no-frills app can attach to any running Windows process and detect memory leaks. It groups leaks together by call stack for easier debugging. Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: User Authentication
900.
SourceAFISThe "AFIS" in this app name stands for "Automated Fingerprint Identification System." It works with a variety of fingerprint readers to authenticate users. Operating System: OS Independent.
901.
Smart SignSmart Sign offers several different modules that help you use smart cards for user authentication and digital signatures. It supports a number of different card types and readers, as well as the Open CA certification authority. Operating System: Linux.
902.
WiKIDWiKID offers open-source, two-factor authentication that utilizes software tokens for remote access, online banking and other applications that require strong authentication. The enterprise version adds some proprietary code not included in the community version, as well as support. Operating System: OS Independent
903.
CoffeeThis helpful app keeps your system "awake" during downloads, file transfers, etc. It's very helpful if you don't want your system going into standby mode while it completes a particular activity. Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Version Control
904.
BazaarThis cross-platform, distributed version control system is used by numerous organizations, including open source heavyweights like the GNU project, Ubuntu, MySQL, Bugzilla, Debian and LaunchPad. It boasts great usability and calls itself "version control for everyone." Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
905.
GitUsed for the Linux kernel, Perl, Eclipse, Ruby on Rails, Gnome, KDE and many other open source projects, this distributed version control system is fast and efficiently handles large projects. It offers strong support for non-linear development and cryptographic authentication of history. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
906.
MercurialThis distributed version control system aims to help teams work together faster and more easily. It's easy to learn, and it's speed makes it particularly good at handling large projects. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
907.
908. TortoiseSVNIf you'd like to use Subversion on Windows, you might want to use the TortoiseSVN client. It lets you use commands and see the status of files from within Windows Explorer. Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Video Tools
909.
AvidemuxBest for amateurs, Avidemux offers basic cutting, filtering and encoding capabilities. It also offers some task automation capabilities. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others
910.
CinelerraThis "movie studio in a box" invites users to "unleash the 50,000 watt flamethrower of content creation in your UNIX box." It offers many advanced compositing, editing and special effects features. Note that there is also a community version of the project at
Cinelerra.org. Operating System: Linux
911.
DivXRepairExperiencing problems playing AVI files? DivXRepair may be able to help. Operating System: Windows
912.
DVD FlickNot quite as full-featured as DVDx, DVD Flick focuses on allowing you to create DVDs from the videos on your PC. It supports more than 60 video codecs and 45 file formats. Operating System: Windows
913.
DVDxThis powerful audio/video encoder can copy multimedia content to and from a wide variety of formats. It's easy to use, and the website includes a number of tutorials for popular uses, like copying a DVD to DivX or QuickTime files. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
914.
FFDShowThis codec decodes numerous file formats. It provides excellent video quality while consuming few computing resources. Operating System: Windows
915.
Kaltura Community EditionKaltura is home to a number of video-related projects, including a player, editor, widgets, processing, and much more. Their latest release is a Joomla extension that makes it easy to add video to your Joomla-based Web site. Operating System: OS Independent.
916.
KdenliveAlthough primarily for home users, Kdenlive offers enough advanced features that its suitable for some professional projects. It's extremely versatile and makes it very easy to edit your video projects. Operating System: Linux, OS X
917.
LiVESLiVES (short for "LiVES is a Video Editing System") offers both non-linear editing and real-time editing capabilities for VJs. It's a professional-quality tool with an intuitive interface and advanced special effects. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
918.
MiroWhile most video players also play audio (and thus ended up in the multimedia category), this one just plays video. It's claim to fame is its support for HD, as well as its library of 6,000 free movies and TV shows. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
919.
OpenShot Video EditorVery popular with Linux users, OpenShot offers a simple, user-friendly interface, but doesn't skimp on features. Check out the website for videos showing this software in action. Operating System: Linux
920.
VirtualDubNot as full-featured as the other apps on this list, VirtualDub primarily offers video capture and processing capabilities for AVI files. Operating System: Windows
921.
Windows Essentials Codec PackHaving trouble playing a video file you've downloaded from the Internet? This download gives you the tools you need to play 99 percent of files available, including a simple media player. Operating System: Windows.
Open Source Apps: Virtualization
922.
XenUsed by many commercial cloud services, the Xen hypervisor is included in most Linux distributions and is also available as an appliance. Many commercial virtualization products, including the Citrix XenServer, are built on top of Xen. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Solaris, others
923.
VirtualBoxVirtualBox offers virtualization for x86 and AMD64/Intel64 servers and desktops. Pre-built VirtualBox appliances are available for download from
Oracle. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Solaris, others
924.
OpenVZOpenVZ takes a different approach to virtualization: unlike VMware, VirtualBox and many other virtualization solutions which use VMs, OpenVZ offers container-based virtualization through VEs or VPSs. Commercial products based on OpenVZ are sold as
Parallels Virtuozzo Containers. Operating System: Linux
925.
KVMShort for "Kernel-based Virtual Machine," KVM allows users to run multiple Linux or Windows virtual machines on a single server. Like Xen, it's included in many Linux distributions. Operating System: Windows, Linux
Open Source Apps: Vulnerability Assessment
926.
BackTrack LinuxThe "most widely adopted penetration testing framework in existence," BackTrack includes a complete Linux distribution with an up-to-date set of tools for penetration testing. Easy instructions for downloading it to a USB drive are included on the site. Operating System: Linux
927.
MetasploitMetasploit can be used both to determine any weakness in your network or by black or white hats to create new exploits. For less knowledgeable users, it's also now available in a commercial "Metasploit Express" penetration testing version with an easy-to-use GUI. Operating System: Windows, Unix
928.
NmapNmap (Network Mapper) is useful for monitoring which devices are connected to your network and for detecting possible security holes. It can run from the command line or a GUI, and also includes Ncat for debugging and data transfer and Ndiff for spotting the differences between two scans. It's also the open source equivalent of a movie star, having been featured in
The Matrix Reloaded,
Die Hard 4,
The Bourne Ultimatum, and several other movies. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
929.
NiktoNikto scans Web servers for thousands of dangerous files and server-specific problems. Optional automatic updates are available. Operating System: Windows, Mac, Linux, Unix, BSD
930.
OpenVASSeveral years ago, the Nessus vulnerability scanner moved from an open source license to a proprietary one. OpenVAS is an open source fork that continues development of the original Nessus scanner. The scanner requires a feed of network vulnerability tests in order to work, but the project also includes an open source daily feed of more than 18,000 of such tests. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
931.
ParosThis Java-based scanner intercepts all http and https data transmitted between server and client to help evaluate the security of Web applications. It includes a spider, proxy-chaining, intelligent scanning for XSS and SQL injections, and more. Operating System: OS Independent
932.
SamuraiFind out how well your Web site will stand up to attack with this penetration testing framework. It incorporates a number of well-known open source tools, including e Fierce domain scanner, Maltego, WebScarab, ratproxy, w3af, burp, BeEF, AJAXShell and many others. Operating System: Linux.
Open Source Apps: VoIP
933.
QuteComFormerly known as Wengo, this project enables free VoIP calls from one PC to another. This is still a developing project, so it's not as easy to use yet as Skype or some other VoIP solutions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
Open Source Apps: Web Analytics
934.
HummingBirdAlthough it's still a pre-alpha release, this app is interesting for its ability to let you view your website visitor statistics in real time. It refreshes 20 times per second, giving you immediate insight into what's happening on your site. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Web Filtering
935.
DansGuardianDansGuardian runs on a Linux or OS X server to block objectionable content from any PC connected to the network (including Windows PCs). It uses URL and domain filtering, content phrase filtering, PICS filtering, MIME filtering, file extension filtering and POST limiting to block pornography and other content that you don't want your children or employees accessing. Operating System: Linux, OS X
936.
iSAKThe "Internet Secure Access Kit" (iSAK) lets you view reports on what type of sites your users are visiting and when. Of course, it also gives you the option to block specific sites or categories of sites for security or to prevent access to objectionable sites. It also incorporates anti-virus and anti-spam protection. Operating System: Linux
Open Source Apps: Web Page Editors
937.
AmayaOriginally developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) in 1996, Amaya promotes two-way Web communication by incorporating both a Web page viewer and a Web page editor. It supports multiple Web languages, including HTML, CSS, XML, XHTML, MathML and SVG. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
938.
BluefishCreated with more experienced Web developers and designers in mind, Bluefish is a lightweight, fast editor that can be used with multiple programming languages, including HTML, PHP, Python, Ruby, JavaScript and others. Key features include a powerful search and replace function, side bar snippets, multiple document interface, unlimited undo/redo, and a spellchecker that supports many programming languages. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
939.
BlueGriffonFirst released this year, BlueGriffon uses Gecko, the same engine used by Mozilla products, so it makes it easy to see how your Web pages will look on Firefox. While the core software is free, several add-ons require a fee. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
940.
FirebugIf you're comfortable editing code, Firebug is a fabulous tool for editing your Web pages live. It integrates with Firefox and makes it easy to search, edit, and find errors in your HTML, CSS, or JavaScript. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
941.
KompoZerKompoZer aims to make it easy for novices to create Web pages thanks to an intuitive Web file management system and an excellent WYSIWYG editor. The interface is similar to Dreamweaver's, and like BlueGriffon, it's powered by the Gecko engine. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
942.
SeaMonkeyThis "all-in-one Internet application suite" includes a Web browser, e-mail client, feed reader, chat client and HTML editor. It's powered by Mozilla source code, and has a large library of add-ons for more features. Operating System: Windows, Linux
943.
XML Copy EditorFor XML only, this editor is lightweight and fast. It validates your code as you type and offers a simple, basic interface. Operating System: Windows, Linux
Open Source Apps: Web Servers
944.
Apache HTTP ServerUsed by 63 percent of all websites, Apache has been the most popular Web server for more than a decade. It prides itself on being secure, efficient and extensible. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
945.
Apache TomcatOften used alongside the Apache HTTP server, Tomcat offers a "pure Java" HTTP web server for running Java code. Well-known websites that use Tomcat include Walmart, E*Trade, The Weather Channel and many others. Operating System: Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
946.
AppServThe goal of the App Serv project is simple: allow users to set up a Web server with Apache, MySQL and PHP in one minute or less. Note that this project originated in Thailand so some of the English documentation reads a little strange. Operating System: Windows, Linux
947.
EasyPHPEasyPHP lets you set up a WAMP (Windows, Apache, MySQL and PHP) environment on a system or a thumb drive in just minutes. It also includes optional modules for WordPress, Spip, PrestaShop, Drupal, Joomla, and other apps. Operating System: Windows
948.
NginxNginx (pronounced "engine X") is both an HTTP and a mail proxy server. Currently powering about 8 percent of all websites, it's the third most popular Web server. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X
949.
WampServerThis is another project that bundles together Apache, MySQL and PHP into an easy-to-install package. However, this one only supports Windows. Operating System: Windows
950.
XAMPPMost of them time when you want to install the Apache Web server, you'll also need other tools, like MySQL, PHP and Perl. This group of downloads bundles together all of those tools—along with a variety of other open source software that's helpful for running a Web server—in an easy-to-deploy package customized for each of the major operating systems. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Solaris
951.
Z-WAMPAnother option for creating a portable WAMP stack, Z-WAMP aims to be lightweight and easy to install. Additional applications included in the package include Adminer, MongoDB Admin, MemCached, SQLite, eAccelerator, and Alternative PHP Cache (APC). Operating System: Windows
Open Source Apps: Wikis
952.
DokuWikiThis simple-to-use wiki was designed for developer teams and other small groups. Key features include unlimited revisions, recent changes viewing, section editing, anti-spam capabilities, multiple language support and more. Operating System: OS Independent
953.
FOSWikiA split from the TWiki project, FOSWiki distinguishes itself with support of embedded macros to enhance content and allow end-users to create their own applications. The Web site includes considerable support for new users, as well as a number of extensions to the basic application. Operating System: OS Independent
954.
MediaWikiBecause it's the software used by Wikipedia, MediaWiki should feel familiar to most users. It's scalability makes it a good choice for large wikis. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix, OS X
955.
TikiWikiTikiWiki calls itself "Groupware" because it offers features like blogs, forums, an image gallery, map server, bug tracker and feed reader to standard wiki capabilities. The software is completely open source, but support, consulting, hosting and other services are available through third-party partners listed on the site. Operating System: OS Independent
956.
TWikiAs a structured wiki, TWiki combines the benefits of a wiki with the benefits of a database. It can be used for project management, document management, as a knowledge base, or to collaborate on virtually any type of content for intranets or the Internet. Operating System: OS Independent.
957.
XWikiXWiki combines an enterprise-grade wiki, a wiki manager (for those who have multiple wikis), a generic wiki platform and an RSS Reader. It's a second-generation wiki, meaning that it gives users the ability to create and deliver apps from within the wiki. Operating System: OS Independent.


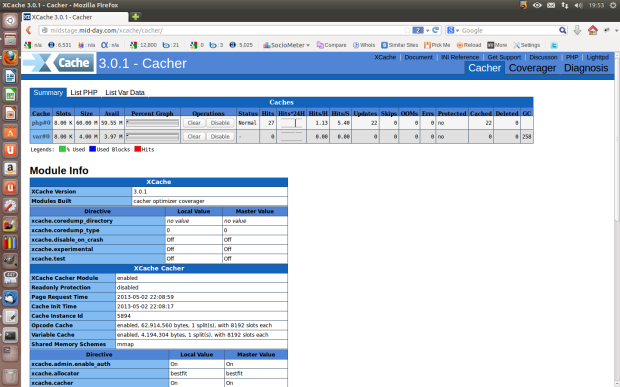





















































 Figure 1. The Main Login Screen
Figure 1. The Main Login Screen  Figure 2. First View of the Data Center
Figure 2. First View of the Data Center Figure 3. Our New Server Group
Figure 3. Our New Server Group  Figure 4. Real-Time Performance Stats on One of Our KVM Servers
Figure 4. Real-Time Performance Stats on One of Our KVM Servers Figure 5. Provisioning a Guest from the Linux Template
Figure 5. Provisioning a Guest from the Linux Template  Figure 6. Mounting an .iso to the Guest CD-ROM
Figure 6. Mounting an .iso to the Guest CD-ROM Figure 7. Provisioning Settings to Clone the Golden Image
Figure 7. Provisioning Settings to Clone the Golden Image  Figure 8. Shared Storage Details
Figure 8. Shared Storage Details  Figure 9. Server Pools That Can Use This Storage
Figure 9. Server Pools That Can Use This Storage 





 For the business person, the answer is that Xen is a safe, stable, well-tested choice for virtualization which is used by industry giants (Amazon, Rackspace, Verizon, etc.). It has a
For the business person, the answer is that Xen is a safe, stable, well-tested choice for virtualization which is used by industry giants (Amazon, Rackspace, Verizon, etc.). It has a 


