204.
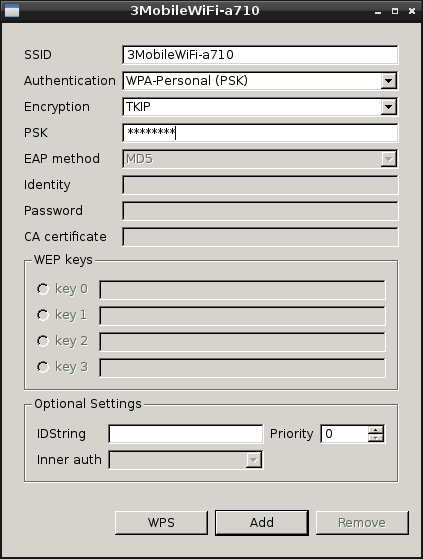
Java-based ConcourseSuite offers a 360° view of your customers, incorporating sales, marketing and customer service perspectives. Unlike most CRM apps, the cloud version is priced on storage and bandwidth, not per user. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
205.
This CRM solution promises to improve business productivity up to 30 percent while lowering costs. In addition to the open source server version, it's also available on an SaaS basis with prices in euros. Operating System: Windows, OS X, Unix
206.
Daffodil CRM provides a complete picture of the entire customer lifecycle and includes tools for sales force automation, sales forecasting, efficient opportunity tracking, customer satisfaction, and performance management. The Daffodil site primarily promotes the commercially supported version, but you can download the free, open-source version from
. Operating System: OS Independent.
207.
OpenCRX combines Web-based customer relationship management capabilities with groupware that will sync with smartphones and tablets. Track your sales and accounts from any browser. Operating System: OS Independent.
208.
Designed for non-profit organizations, Orange Leap offers "constituent relationship management" with specific features that aim to improve fundraising. It comes in an SaaS version, and commercial support is also available for the on-premise, open source version. Operating System: Windows.
209.
This CRM tool is designed primarily for your sales force rather than your customer service staff, and includes a phone client that is very helpful for mobile employees. Despite the "Win" in the name this is a multi-platform tool; in this case, "Win" refers to actual sales wins, not Windows. Operating System: OS Independent.
210.
SourceTap describes itself as "a highly flexible Sales Force Automation (SFA) tool that meets both the needs of sales managers and the sales rep." It's available under either a commercial or an open source license, and the company also offers an on-demand subscription service that also provides users with full access to the source code. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
211.
The community version of this software offers basic CRM features, but you'll need to purchase the professional or enterprise version if you want reporting, order management and other advanced features. Community, professional and enterprise versions can be deployed on-premise or used in the cloud. Operating System: Windows.
212.
Used by more than 250,000 customers, SugarCRM offers the full range of features you would expect in a top-notch CRM, plus better flexibility and no vendor lock-in as with commercial vendors. In addition to the free community version, it comes in several different paid versions that can be deployed on premises or in the cloud. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
213.
VTiger boasts that it is "one of the most dynamic and customizable CRM solutions with the lowest cost of ownership available today." It's also available in open source, on demand and mobile versions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, iOS, Android.
214.
X2Contacts offers sales management with a social-networking focus. It's aimed at SMBs and offers a blog-style interface that makes it easy to see and record sales contacts. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
215.
serious about your dancing, DanceCues can help you plot out your best moves ahead of time. It's suitable for professional choreographers and makes it much easier to create cue sheets than using a word processor. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
216.
This distributed database can run on a single system or scale to hundreds or thousands of machines. Features include dynamic sharding, high performance, high concurrency, high availability and more. Commercial support is available. Operating System: OS Independent.
217.
Originally developed by Facebook, this NoSQL database is now managed by the Apache Foundation. It's used by many organizations with large, active datasets, including Netflix, Twitter, Urban Airship, Constant Contact, Reddit, Cisco and Digg. Commercial support and services are available through
Operating System: OS Independent.
218.
Designed for the Web, CouchDB stores data in JSON documents that you can access via the Web or or query using JavaScript. It offers distributed scaling with fault-tolerant storage. Operating system: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android.
219.
This mature RDBMS offers many SQL standard features and released an updated version just last month. No commercial support is available directly from the project owners, but many third-party Firebird specialists do offer support. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X, Solaris
220.
Best known as Twitter's database, FlockDB was designed to store social graphs (i.e., who is following whom and who is blocking whom). It offers horizontal scaling and very fast reads and writes. Operating System: OS Independent.
221.
Another Apache project, HBase is the non-relational data store for Hadoop. Features include linear and modular scalability, strictly consistent reads and writes, automatic failover support and much more. Operating System: OS Independent.
222.
Used by many telecom companies, Hibari is a key-value, big data store with strong consistency, high availability and fast performance. Support is available through
. Operating System: OS Independent.
223.
Hadoop's data warehouse, Hive promises easy data summarization, ad-hoc queries and other analysis of big data. For queries, it uses a SQL-like language known as HiveQL. Operating System: OS Independent.
224.
This NoSQL database offers efficiency and fast performance that result in cost savings versus similar databases. The code is 100 percent open source, but paid support is available. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
225.
Infinispan from JBoss describes itself as an "extremely scalable, highly available data grid platform." Java-based, it was designed for multi-core architecture and provides distributed cache capabilities. Operating System: OS Independent.
226.
Intended as a replacement for Access and Filemaker, KDE's Kexi offers rapid database application development. Features include migration assistants for transition from other databases, support for parametrized queries, lookup columns, simple templates and visual designers for tables, queries and forms. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
227.
LucidDB claims to be "the first and only open-source RDBMS purpose-built entirely for data warehousing and business intelligence." Accordingly, it offers advanced analytics capabilities and good scalability. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
228.
us databases. It's a NoSQL database with document-oriented storage, full index support, replication and high availability, and more. Commercial support is available through
. Operating system: Windows, Linux, OS X, Solaris.
229.
The "world's most popular open source database," Oracle-owned MySQL offers high reliability, high scalability, security and ease of use. It's downloaded more than 65,000 times every day, and it's won numerous awards. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X.
230.
The "world’s leading graph database," Neo4j boasts performance improvements up to 1000x or more versus relational databases. Interested organizations can purchase advanced or enterprise versions from
. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
231.
This NoSQL database can store up to 150,000 documents per second and can load graphs in just milliseconds. It combines the flexibility of document databases with the power of graph databases, while supporting features such as ACID transactions, fast indexes, native and SQL queries, and JSON import and export. Operating system: OS Independent.
232.
Built to run in the cloud or other distributed environments, this database attempts to combine the benefits of traditional RDBMSes with the benefits of NoSQL. It comes in community and enterprise versions or Riak CS which provides a platform for
. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
233.
PostgreSQL might not be the most popular, but it does consider itself the "world's most advanced open source database." It's more than 15 years old and is standards-compliant. Support is available through third-party vendors. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X, Solaris
234.
Sponsored by VMware, Redis offers an in-memory key-value store that can be saved to disk for persistence. It supports many of the most popular programming languages. Operating System: Linux.
235.
Based on Terracotta, Terrastore boasts "advanced scalability and elasticity features without sacrificing consistency." It supports custom data partitioning, event processing, push-down predicates, range queries, map/reduce querying and processing and server-side update functions. Operating System: OS Independent.
236.
VoltDB describes itself as "the NewSQL database for high velocity applications." It was recently named one of Gartner's Cool Vendors for 2011. In addition to the free community version, it also comes in several commercially supported versions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
237.
This multi-function tool not only "shreds" deleted files, it also protects your privacy in a myriad of other ways like deleting cookies, erasing browsing history, deleting logs and cleaning up temp files. By getting rid of unwanted junk, it also helps speed your system and open up extra disk space. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
238.
While Eraser and Wipe delete single files, DBAN securely deletes entire disks. It's very helpful when donating or disposing of an old system. Operating System: OS Independent.
239.
This small utility cleans all the “junk” out of your temporary files, cache etc. It's also handy for protecting your privacy when using public machines. Operating System: Windows.
240.
When you simply "delete" a file from your drive, it can usually still be recovered with forensic tools. However, Eraser uses tools approved by the Department of Defense to eliminate all traces of a file from your drive, protecting your privacy and preventing the spread of sensitive or classified information. Operating System: Windows.
241.
Like Eraser, FileKiller "shreds" old files by rewriting over the stored data. It boasts fast performance, and it allows the end user to specify how many times to overwrite the file. Operating System: Windows.
242.
Wipe offers the same functionality as Eraser, but it's for Linux instead of Windows. The site also offers a wealth of information for those interested in learning more about how file "shredding" works. Operating System: Linux.
243.
Apatar makes it easier for enterprises to integrate data contained in on-premise or cloud-based applications, including many popular CRM tools. Users include Salesforce.com, Hotels.com, University of Maryland, Autodesk, Credit Suisse and others. In addition to the free download, Apatar offers an On-Demand version, as well as support, training, consulting and other paid services. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
244.
This data integration platform aims to "keep data in your business systems valuable, organized, and meaningful." They offer a range of commercial products based on the open source CloverETL Engine, which is available for download from
245.
The "premier open source data quality solution," DataCleaner is useful for data profiling and DQ analysis, data cleansing, detecting and merging duplicates, and lightweight ETL tasks. It's also available in a commercial edition. Operating System: OS Independent.
246.
Based on Kettle/Pentaho Data Integration, GeoKettle incorporates geospatial capabilities from a variety of other open source tools. It is owned by
, which offers commercial versions of the tools. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
247.
This scalable data warehouse supports data stores up to 50TB and offers "market-leading" data compression up to 40:1 for improved performance. Commercial products based on the same technology can be found at
. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
248.
Java-based KETL is a portable, scalable ETL tool with support for many popular security and data management tools. Commercial support is available through project owner
. Operating System: OS Independent.
249.
MailArchiva stores enterprise e-mail messages, allowing companies to meet compliance requirements, to search old messages quickly, to monitor content and to save on storage costs. The link above will connect you with the enterprise and ISP versions of the software; for the open source version, see
. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
250.
Java-based Scriptella offers a simple tool for performing ETL tasks and executing scripts. Note that this tool isn't quite as polished as some of the others on our list, and no enterprise version or commercial support is available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
251.
Named a "leader" in the Forrester Wave for ETL, Talend offers data integration, data quality, master data management and application integration tools used by companies around the world, including The Weather Channel, Xerox, Capgemini, Verizon, Infosys and others. The company offers quite a few different versions of its tools: it markets the open source versions under the name "Talend Open Studio," and it markets the commercial versions under the name "Talend Enterprise." Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix.
252.
OpenDLP is a "agent- and agentless-based, centrally-managed, massively distributable data loss prevention tool." It allows security or compliance managers to scan thousands of systems simultaneously via agents or perform agentless data discovery against a MySQL or Microsoft SQL server. Operating System: Windows.
253.
MyDLP can block credit card numbers, social security numbers, or sensitive files from being transmitted via e-mail, printers, the Web or removable devices. In addition to the free community version, it also comes in a paid enterprise version. Operating System: Windows, Linux, VMware.
254.
RapidMiner claims to be "the world-leading open-source system for data and text mining." RapidAnalytics is a server version of that product. In addition to the open source versions of each, enterprise versions and paid support are also available from the same site. Operating System: OS Independent.
255.
This Apache project offers algorithms for clustering, classification and batch-based collaborative filtering that run on top of Hadoop. The project's goal is to build scalable machine learning libraries. Operating System: OS Independent.
256.
This project hopes to make data mining "fruitful and fun" for both novices and experts. It offers a wide variety of visualizations, plus a toolbox of more than 100 widgets. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
257.
Short for "Waikato Environment for Knowledge Analysis," Weka offers a set of algorithms for data mining that you can apply directly to data or use in another Java application. It's part of a larger machine learning project, and it's also sponsored by Pentaho. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
258.
Also known as "jWork," this Java-based project provides scientists, engineers and students with an interactive environment for scientific computation, data analysis and data visualization. It's frequently used in data mining, as well as for mathematics and statistical analysis. Operating System: OS Independent.
259.
KEEL stands for "Knowledge Extraction based on Evolutionary Learning," and it aims to help uses assess evolutionary algorithms for data mining problems like regression, classification, clustering and pattern mining. It includes a large collection of existing algorithms that it uses to compare and with new algorithms. Operating System: OS Independent.
260.
Another Java-based data mining framework, SPMF originally focused on sequential pattern mining, but now also includes tools for association rule mining, sequential rule mining and frequent itemset mining. Currently, it includes 46 different algorithms. Operating System: OS Independent.
261.
Rattle, the "R Analytical Tool To Learn Easily," makes it easier for non-programmers to use the R language by providing a graphical interface for data mining. It can create data summaries (both visual and statistical), build models, draw graphs, score datasets and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
262.
This app performs de-duplication at the file level. In addition, it also offers bulk re-naming, bulk moving, file splitting and file joining capabilities. Operating System: Windows.
263.
Opendedup performs inline de-duplication to reduce storage utilization by up to 95 percent. It's available as an appliance for simplified setup and deployment. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
264.
Compiz can be used as either a compositing manager to add fancy effects to your windows or as a full windows manager. Included effects include drop shadows, the desktop cube and expo view. Operating System: Linux.
265.
For developers and others who like to work from the command line, Console adds capabilities that aren't available through cmd.exe. For example, it allows users to open multiple tabs, change the font and window style, use a text selection tool, and more. Operating System: Windows.
266.
If your file system is a mess, DropIt gives you an easier way to clean it up than using the file copy-and-paste capabilities of Windows Explorer. With this app, you can create an icon on your desktop that sends files to the folder of your choice. Just drag your file to icon and it will move the file where you want it to go. Operating System: Windows.
267.
Inspired by the Philip K. Dick novel
, this screensaver connects thousands of computers around the world to create unusual abstract designs known as "sheep." Vote for your favorite animations and they'll reproduce more often. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
268.
This replacement for the Windows shell offers a minimalist interface based on applets. It lets users access programs via a right click instead of the Start Menu, and it offers an application launcher and virtual desktop capabilities. Operating System: Windows.
269.
Compatible with both Gnome and KDE, Enlightenment is a fast, modular windows manager. The project also includes a large interface development library, some parts of which are usable on Windows, OS X and other OSes. Operating System: Linux.
270.
If you can't use your hands for some reason, or if you spilled Red Bull on your keyboard and are waiting for it to dry out, Florence can help you keep on typing. This app for the Gnome desktop puts a virtual keyboard on your screen that you can click with your mouse. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
271.
Although it's not too flashy, this window manager is lightweight and fast. Key features include tabbing, editable menus, an application dock and more. Operating System: Linux.
272.
If you don't like the way your Windows interface looks, GeoShell can replace it with skinnable versions of the start menu, taskbar, system tray, etc. It also requires fewer resources than Windows Explorer, and it has a whole host of plug-ins that can add other features like RSS readers, weather forecasts and more. Operating System: Windows.
273.
If you get bored having the same image on your desktop for more than five seconds or so, this app might be for you. You type in a keyword, an interval of time and whether or not you want to use "Safe Search." The app then pulls up random pictures from Google and uses them as your wallpaper for the period of time you set. Operating System: Windows.
274.
Icewm's stated goals include "speed, simplicity, and not getting in the user's way." It currently supports 25 different languages. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
275.
No window near your cubicle? This app automatically changes the background on your desktop to match current weather and time. Operating System: Linux.
276.
The default window manager for the KDE Plasma desktop, KWin puts an emphasis on reliability and good looks. The latest version supports compositing, that is, 3D window effects. Operating System: Linux.
277.
Much like Launchy (below), Kysrun starts your applications or opens bookmarks or documents with a couple of keystrokes. It also starts searches on Google, Wikipedia or IMDB and solves math problems. Operating System: Linux.
278.
If you hate to use the mouse, Launchy is for you. It lets you open applications, documents, folders, bookmarks and more with just a few keystrokes. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
279.
This app is a must have for Star Trek fans with an old PC sitting around in the garage or basement. It sets up your system with Star-Trek style graphics, a talking alarm clock and a file manager. Operating System: Windows, DOS.
280.
Fans of the artist M. C. Escher will enjoy this animated version of his Print Gallery drawing. If you like it, you may also like this developer's other screensavers: LotsaGlass, LotsaSnow and LotsaWater. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
281.
For those who love the Matrix movies, this screensaver features falling green characters that create images of characters from the The Matrix Reloaded. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
282.
The default window manager for Gnome 2.x, Metacity is designed to be as usable and unobtrusive as possible, and might be described as a little plain. The project owners themselves say, “Many window managers are like Marshmallow Froot Loops; Metacity is like Cheerios.” Operating System: Linux.
283.
This app generates new night-time cityscape artwork every time it runs. Check out the demonstration video link on the site to see how it works. Operating System: Windows.
284.
Much like real-world sticky notes, PNotes lets you leave virtual sticky notes for yourself on your computer. Interesting features of this app include audio notes, scheduling, password protection, encryption, transparency and more. Operating System: Windows.
285.
If you're looking for a screensaver that's a little bit out of the ordinary, check out Really Slick. It includes a dozen different colorful (and sometimes nausea-inducing) screensavers. Operating System: Windows.
286.
Sticker is a Windows 7-compatible electronic post-it note app. Unlike some similar apps, it lets you put notes directly on the desktop as if they were icons. Operating System: Windows.
287.
This screensaver's graphics aren't as impressive as some of the others on our list, but it's fun if you like Lego blocks. Operating System: Windows.
288.
If you prefer a screensaver that's a little more philosophical, check out this app. You type in a topic and press save, and it will pull up random Wikiquotes on the topic. Operating System: Windows.
289.
Like the Google Wallpaper app, Wally changes out the photo on your screen after a set period of time. But this app let's you pick photos from your own hard drive or from remote sources like Google, Flickr, Yahoo, Photobucket and many others. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
290.
Whorld generates interesting geometric patterns that can be used for a screensaver or for VJing. It gives you a huge number of options and controls, and you can even extend them by using one of the downloadable patches or creating a patch of your own. Operating System: Windows.
291.
Most Linux/Unix windows managers make it easy to switch between desktops, but to accomplish the same thing on Windows, you usually have to log out and log back in as another user. This app lets you save up to nine different desktops and switch between them quickly. It's helpful if you're multi-tasking and need one set of apps for one project and other set for a different project. Operating System: Windows.
292.
WindowsPager offers very similar functionality as VirtuaWin, with a different interface for switching between workspaces. Operating System: Windows.
293.
While definitely not as full-featured as commercial desktop publishing systems, MiKTeX is an excellent typesetting program based on the older app TeX. TeX was created by computer science legend Donald E. Knuth, who intended it to be used "for the creation of beautiful books -- and especially for books that contain a lot of mathematics." Operating System: Windows, Linux.
294.
Scribus offers the advanced features professional graphic designers need along with an intuitive interface that anyone can master. With it, you can create press-ready output or PDFs of documents you plan to publish online. However, you should note that Scribus cannot convert files made with proprietary formats. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
295.
After creating documents in the text editor of your choice, you can use SiSU (Structured information, serialized units) to publish them in the format of your choice and make them searchable. Supported formats include plain-text, HTML, XHTML, XML, ODF, LaTeX, and PDF. Operating System: Linux/Unix.
Developer Tools
296.
AllJoyn AllJoyn allows developers to create applications with OS-agnostic, proximity-based device-to-device communications. The company behind the project is currently running a contest where they plan to give away $170,000 in cash and prizes for great apps built with AllJoyn's framework. Operating System: Windows, OS X, iOS, Android.
297.
AML This XML-based language aim to makes it possible to build cross-platform, data-driven applications that run natively. However, currently it only supports Android. Operating System: Android.
298.
Anjuta DevStudio GNOME's IDE supports C and C++ development on Linux systems. It includes an application wizard, interactive debugger, source code editor, version control, GUI designer and more. Operating System: Linux.
299.
Appcelerator Titanium Appcelerator claims that Titanium is "the first mobile platform to combine the flexibility of open source development technologies with the power of cloud services." It supports the development of iOS, Android and mobile Web apps using JavaScript. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS, Android.
300.
ATPad This Notepad replacement includes a number of features for developers, like a tabbed interface, line numbering, word wrapping, text coloring and more. It's won a number of awards. Operating System: Windows.
301.
Cloud9 IDE This online IDE supports Javascript, Node.js, HTML, CSS, PHP, Java, Ruby and 23 other programming languages. The source code for the IDE is available through
GitHub, and the PaaS is free for open source projects or $15 per month for private projects. Operating System: OS Independent.
302.
Code::Blocks This cross-platform C++ IDE is highly extensible, making it easy to add the features you want. It includes built-in compiling and debugging capabilities, plus an easy-to-use interface. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
303.
Dev-C++ Dev-C++ is a C/C++ IDE with support for all GCC-based compilers. Key features include integrated debugging, project management, customizable syntax editor, code completion and others. Operating System: Windows.
304.
Eclipse In addition to the well-known Java IDE, the Eclipse site offers a number of other development tools and educational materials. You'll also find plug-ins that extend its capabilities to support C, C++, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby, and other programming languages. Operating System: OS Independent.
305.
Evolutility With Evolutility, users can build custom Web apps in just minutes, without writing any C#, HTML, CSS, Javascript, or SQL. If you have a database, this app can put it on the Web quickly and easily. Operating System: Windows.
306.
Game Editor If you're not really a programmer, but you think you have an idea for a game that might be the next big hit on the iPhone, this tool might help. It's a cross-platform game creator, and the site offers advice for those just starting out. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS, others.
307.
GCC The "GNU Compiler Collection" offers front ends and libraries for C, C++, Objective-C, Fortran, Java, and Ada. It's probably the most widely used compiler for code that will run on multiple operating systems. Operating System: OS Independent.
308.
Gestalt Gestalt offers a developers a way to write Ruby and Python scripts in in (X)HTML pages. It's SEO-friendly and lets you use some advanced HTML5 technologies on your Web apps. Operating System: OS Independent.
309.
Glade Glade lets developers quickly create interfaces for the GTK+ toolkit and the GNOME desktop environment. It saves those interfaces in XML so they can be accessed by applications written in a wide variety of programming languages. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
310.
Hibernate Part of the JBoss Enterprise Middleware Suite, Hibernate provides object/relational persistence for Java and .NET. It also includes the ability to write queries in SQL or the Hibernate version of SQL (HQL). Operating System: OS Independent.
311.
Intel Threaded Building Blocks This library helps C++ developers take advantage of the benefits of multi-core processing systems, even if they don't know a lot about threading. It's available in both a commercial and an open source version. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
312.
IPFaces Designed to make it easier for experienced Web developers build mobile apps, IPFaces excels at the creation of form-heavy mobile applications. Enterprise support and other professional services are available. Operating System: OS Independent for the developer; creates apps for iOS, Android, BlackBerry, others.
313.
Javadoc Javadoc uses the comments you embed in your Java code to create an HTML documentation file. By default it describes the public and protected classes, nested classes (but not anonymous inner classes), interfaces, constructors, methods and fields. It's included in Oracle's Java developer kits. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
314.
Jo Jo describes itself as a "simple app framework for HTML5." It allows you to build native-like apps in JavaScript and CSS. Operating System: iOS, Android, webOS, BlackBerry, Chrome OS.
315.
jQuery jQuery calls itself "the write less do more JavaScript library," and that's a pretty apt description. It simplifies HTML document traversing, event handling, animating, and Ajax interactions for rapid web development. Operating System: OS Independent.
316.
JQuery Mobile This HTML 5-based framework offers a simple drag-and-drop interface for creating cross-platform mobile Web applications and websites. Notable features include a theme roller and a download builder. Operating System: iOS, Android, BlackBerry, Windows Phone, others.
317.
JQTouch Want to do Web development from your iOS or Android device? JQTouch makes it possible. Notable features include easy setup, native WebKit animations, callback events, flexible themes, swipe detection and more. Operating System: iOS, Android.
318.
KDevelop This integrated development environment (IDE) from KDE that supports C and C++, as well as some other programming languages. It's based on the KDevPlatform, a set of open source libraries used by several IDEs. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
319.
Kurogo Created by Modo Labs, Kurogo is a mobile-optimized middleware platform that was based on the MIT Mobile Framework. It makes is easy to create portals, mobile websites and apps that aggregate data and content from multiple sources. Operating System: Windows, Linux, iOS.
320.
Lazarus Similar to Delphi, Lazarus is a rapid application development tool that includes an IDE and a compiler. It uses the FreePascal libraries to create write-once, compile-anywhere applications. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
321.
MinGW "Minimalist GNU for Windows" ports the GCC compilers and GNU Binutils for Windows. It allows you to use GNU tools to build Windows apps from Windows or Linux systems. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
322.
Moai Describing itself as "the mobile platform for pro game developers," Moai offers both an SDK for game development and cloud-based services like leaderboards, achievements, etc. In addition to the free open source version, it's also available in a number of fee-based versions, with prices depending on usage. Operating System: Windows, OS X, iOS, Android, Chrome.
323.
Mobl Based on HTML5 and JavaScript, mobl is a programming language designed specifically for creating mobile apps. It's statically typed and comes with an Eclipse-based IDE. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
324.
Molly This rapid development framework has a goal of making the creation of mobile portals as quick and painless as possible. Developed by Oxford University, it's a good option for other universities that also use the Sakai Virtual Learning Environment. Operating System: Linux.
325.
Mono Now sponsored by Xamarin, this IDE was specifically designed as an open source, cross-platform version of Microsoft's .NET development platform. The site also offers two related tools for mobile development: MonoTouch for iOS and Mono for Android. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS, Android
326.
MoSync SDK This cross-platform software development kit allows you write mobile apps in C/C++ or HTML5/JavaScript--or a combination of both. Developers can use it alongside MoSync Reload, an open source development tool that makes it easy to see how apps will look on various mobile platforms. Operating System: Windows, OS X, Android, iOS, Windows Mobile, Symbian.
327.
NetBeans Although known as a Java tool, NetBeans also supports PHP, JavaScript, Ruby, Groovy, Grails and C/C++. Its goal is to help users quickly develop web, enterprise, desktop, and mobile applications. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
328.
Nette Framework Nette Framework promises developers "you will write less, have cleaner code and your work will bring you joy." It's a PHP-based framework for writing Web applications, and it supports AJAX, SEO, DRY, KISS, MVC and code reusability. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
329.
NuGet This extension for Microsoft's Visual Studio makes it easy to install and update open source libraries for the .NET platform. And the
NuGet Gallery makies it easy to find those open source libraries. Operating System: Windows.
330.
Open64 Formerly known as Pro64, Open64 was created by Intel and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. It includes compilers for C, C++ and Fortran90/95 compilers for the IA-64 Linux ABI and API standards. Operating System: Linux.
331.
OpenBD Formerly known as Open BlueDragon, OpenBD offers Web app developers a free way to use the popular ColdFusion Markup Language (CFML). It makes it easy to deploy applications to the Google App Engine or anywhere else you choose. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
332.
OpenMEAP An enterprise-class HTML5 mobile application development platform, OpenMEAP boasts top-notch end-to-end security. It enables rapid application development and supports multiple mobile OSes. Operating System: Android, iOS, BlackBerry.
333.
OWASP The “Open Web Application Security Project” includes a number of documents, applications, and tools for developers concerned about app security. Key projects include WebGoat, ESAPI Security Library for Java, and numerous standards and guides. Operating System: OS Independent.
334.
PhoneGap Used by more than 400,000 developers, PhoneGap boasts that it's the "the only free open source framework that supports 7 mobile platforms": iOS, Android, Blackberry, Windows Phone, Palm WebOS, Bada and Symbian. With it, developers can build cross-platform mobile apps using HTML, CSS and Javascript. Operating System: Windows, iOS, Android, Blackberry, Windows Phone, others
335.
phpDocumentor Like Javadoc, phpDocumentor turns code comments into readable documentation for users, only in this case for the PHP language instead of for Java. It's very fast and includes a variety of templates. Operating System: OS Independent.
336.
phpMyAdmin Written in PHP, this utility handles the administration of MySQL over the Web. phpMyAdmin performs many database administration tasks like running SQL statements, adding and dropping databases, and adding, editing or deleting tables or fields. Operating System: OS Independent.
337.
Prototype This JavaScript framework tries to make it easier to create dynamic Web apps. It offers a class-style OO framework, easy DOM manipulation, and what it humbly calls "the nicest Ajax library around." Operating System: OS Independent.
338.
QuickConnectFamily Hybrid Boasting that it can speed mobile development by up to ten times, this app claims to be the "first full framework for JavaScript, CSS, and HTML development of installable, application store ready apps." It's highly modular and includes a built-in library for SQLite database calls. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS, Android.
339.
Qt Used for both mobile and desktop development, Qt is a cross-platform application and UI framework that supports both C++ and a JavaScript-like language called QML. Commercially licensed versions are available from
Digia. Operating System: Windows, OS X, Linux.
340.
Railo Railo claims to be the fastest open source CFML server available. Commercial consulting, training and services are available from
Railo Technologies. (And the name comes from an obscure Star Trek character, which boosts the project's geek cred.) Operating System: Windows, Linux.
341.
Restkit Restkit aims to simplify the process of building apps that interact with RESTful Web services. Features include a simple HTTP request/response system, integration with Apple’s Core Data framework, database seeding, object mapping system, pluggable parsing layer and more. Operating System: iOS.
342.
Rhodes Ruby-based Rhodes allows developers to write code once and turn it into native mobile applications for multiple platforms. An enterprise version with a commercial license and support is available for a fee. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iPhone, Android, BlackBerry, Symbian, Windows Phone.
343.
Ruby on Rails Designed for rapid application development using Agile methodologies, Ruby on Rails offers "Web development that doesn't hurt." It's used by the developers behind thousands of apps, including Twitter, Basecamp, Github and Groupon. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
344.
Sencha Touch Another JavaScript-based HTML5 framework, Sencha Touch is used by more than 500,000 mobile developers, including more than half of the Fortune 100 and 8 of the world's top 10 financial institutions. In addition to the free open source license, Sencha also offers a free commercial license and paid support. Operating System: OS Independent.
345.
SharpDevelop Another .NET alternative, SharpDevelop supports projects written in C#, VB.NET, Boo, IronPython, IronRuby and F#. It includes a debugger, code analysis, unit testing and a profiler, and it supports both Git and Subversion. Operating System: Windows.
346.
soapUI With more than 2 million downloads, soapUI claims to be the most popular Web services and SOA testing tool in the world. It performs functional testing of SOAP, REST, HTTP, and JMS services, as well as databases. Operating System: OS Independent.
347.
Sonar In its first year of release, this Web-based platform for managing code quality quickly racked up 30,000 downloads. Sonar is notable for its ease of use and excellent reporting tools. Operating System: OS Independent.
348.
Ultimate++ This rapid application development framework includes both a C++ library and an IDE designed to handle large applications. Its emphasis is on speeding up the development process and includes "BLITZ-build" technology that makes C++ rebuilds up to four times faster. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
349.
Wakanda According to its website, Wakanda is "an open source platform for building business Web applications with nothing but JavaScript." It's still in preview status, but is already getting kudos from end users for its ability to speed up and simplify the business application development process. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
350.
wxWidgets This cross-platform development toolkit enables programmers to write applications in C++, Python, Perl, and C#/.NET that work on several different operating systems. In addition to an easy-to-use GUI, wxWidgets offers online help, streams, clipboard and drag and drop, multithreading, database support, HTML viewing and printing, and many other features. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix, OS X.
351.
XML Copy Editor XML Copy Editor doesn't have as many features as some comparable apps, but it is very fast and lightweight. It's simplicity also makes it easier to use than some of the more feature-heavy applications. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
352.
Zend Framework The Zend Framework helps PHP developers create more secure, reliable, and modern Web 2.0 applications and services. Support and related products can be purchased through
Zend's corporate website. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
353.
ZK Downloaded more than 1.5 million times, ZK calls itself the "leading enterprise Java Web framework." It's known for allowing developers to build Web apps in Java alone--without knowing Ajax or JavaScript--and it can also be used to build mobile apps. Operating System: OS Independent.
Diet/Exercise/Fitness
354.
Cronometer If you're on a restricted calorie diet, this app can help you track the calories in the foods you eat as well as other health data. The link above will take you to the free Web app; you can find the source code at
SourceForge. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android, iOS
355.
eFit Calorie Counter With a database of nutrition information for 10,000 foods, this app helps you plan meals and count the calories you consume. It also includes a helpful recipe creator and a tool for tracking your body measurements. Operating System: Windows.
356.
iDiet This app supports multiple diets, including Atkins, Summer Fresh, The Zone and Body for Life. Simply input the diet you're following and your goal. The app calculates how many calories, fat, protein, carbs, etc. you should be eating and then tracks your actual food consumption to see if you are staying on your plan. Operating System: OS Independent.
357.
My Tracks This Android app uses your smartphone's GPS to trace your path when you go running, walking, biking or hiking. When you're finished, you can import your time, distance, speed and elevation change to a spreadsheet so that you can track your fitness or share your stats with others. Operating System: OS Independent.
358.
SportsTracker Whether you're training for a specific event or just want to track your progress toward a more healthful lifestyle, Sports Tracker makes it easy to set up a plan and track your statistics. It also integrates with several popular heart monitors. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
359.
TurtleSport If you have a Garmin fitness device like the Forerunner or the Edge, this app can retrieve your data and create reports. It also integrates with Google Earth and Google Maps so that you can see where you've been. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Document Management Systems (DMS)
360.
Epiware This document manager offers features like search, access history, version history, calendaring, project management and a wiki. Paid support is available. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
361.
LogicalDOC This DMS aims to reduce your document retrieval time from hours to just seconds. The cloud-based version adds the benefit of allowing users to access documents from any device, anywhere. Operating System: OS Independent.
362.
OpenDocMan This Web-based document management system complies with ISO 17025 and OIE standards. It comes as a free download, a commercial appliance or a hosted service, and additional paid services are also available. Operating System: OS Independent.
363.
OpenKM Designed for use by both small and large companies, OpenKM includes features like a Web 2.0 interface, document control version, content and metadata search, mobility support and more. It comes in community, professional or cloud versions, and the company also offers training services. Operating System: OS Independent.
364.
Xinco DMS Short for "eXtensible INformation COre," Xinco offers Web-based management of files, documents, contacts, URLs and more. Features include ACLs, version control and full text search. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
eBook Reader
365.
CoolReader CoolReader lets you read e-books on your desktop, laptop or Android device. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
366.
FBReader Want to read an e-book, but don't have a Nook, Kindle or iPad? This ebook reader supports multiple file formats and works on netbooks and Linux-based PDAs, as well as desktops. Operating System: Linux, Windows, BSD.
E-Commerce
367.
Broadleaf Commerce Used by companies like PepBoys, the Container Store, Ganz and Waste Management, Broadleaf offers a Java-based e-commerce platform with a sophisticated promotions engine and customization capabilities. The full software is free and open source, but Broadleaf also offers paid support and consulting services. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
368.
Eclime Based on osCommerce, Eclime offers fast performance and a template-based design that's difficult to mess up. It also offers SEO capabilities, media playlist support, wishlists and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
369.
eShop This WordPress plug-in offers good, basic e-commerce features, but lacks some of the more advanced features in other e-commerce solutions. It does integrate with most payment processing systems. Operating System: OS Independent.
370.
Fishop.NET Fishop describes itself as a "no frills" e-commerce solution. You can try a demo right from the site, and you can purchase it on an SaaS basis (with prices in euros). Operating System: Windows.
371.
Interchange Interchange has been around since 1995, and it supports a wide range of uses, including sales, content management, customer service, reporting and analysis, personalization, B2B, parts re-ordering, auctions, supply chain management, project management, online collaboration and even an MP3 jukebox. Professional support is available from a variety of third-party partners. Operating system: Linux, OS X.
372.
JadaSite Java-based JadaSite offers enterprise-class e-commerce features like BIRT reporting, product import/export, AJAX-based components, a WYSISYG editor, multi-currency, multiple language support and more. Paid support packages are not available, but JadaSite does offer consulting services for installation, customization, upgrades, etc. Operating System: OS Independent.
373.
Jigoshop Another plug-in for WordPress, Jigoshop boasts lightweight code, advanced reporting and "out-of-the box awesomeness." Paid support is available. Operating System: OS Independent.
374.
Magento Used by more than 100,000 merchants, including Office Max, Harbor Freight Tools, K-Swiss and others, eBay-owned Magento has been called "an emerging player to watch" by Forrester. In addition to the free community editions, it also comes in supported professional and enterprise editions, as well as a hosted turnkey version known as Magento Go. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
375.
MobileCartly This open source mobile shopping cart boasts PayPal integration, advanced management features, real-time statistics and "no programming skills required." It's also available as a WordPress plugin. Operating System: OS Independent.
376.
Modern Merchant Describing itself as "smart and simple," Modern Merchant offers a no-frills, easy-to-use e-commerce shopping cart. It's easy to install and extensible with a variety of plug-ins. Operating System: Linux.
377.
nopCommerce Based on Microsoft architecture and development tools, nopCommerce offers a stable, PCI DSS-compliant e-commerce solution. Check out the site to see a
demo of both its front-end and back-end tools. Operating System: Windows.
378.
OpenCart Nominated for a 2011 Packt Publishing award, OpenCart offers a long list of features and user-friendly operation. Commercial support is available from a variety of international third-party partners. Operating system: Windows, Linux, OS X.
379.
Order Portal Aimed at manufacturers, distributors and rental companies, Order Portal is best for established companies that are looking to add an online presence. It also integrates with a larger Web Business Suite available from the same company. Operating System: Linux.
380.
osCMax Another osCommerce fork (see below), osCMax aims to be easy enough for small startups and advanced enough for larger operations. It offers unlimited products and categories, vouchers and coupons, Web-based administration, support for multiple payment processors, spreadsheet-based data entry and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
381.
osCommerce Boasting a community 256,900 members strong, the award-winning osCommerce powers thousands of shops worldwide, including 12,700 that are linked on the site. More than 6,000 add-ons are also available on the site to help you customize the software for your specific needs. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
382.
Oxid eShop This flexible e-commerce solution offers marketing integration, search engine optimization, easy admin management, an integrated CMS, couponing, reviews, ratings and more. In addition to the community version, it also comes in paid professional and enterprise versions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
383.
Plici This French project offers a "powerful and extensible" e-commerce solution. Check out the website for a helpful demo of Plici in action. Be warned that much of the documentation is in French, but English translations are available. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
384.
PrestaShop One of the most popular eCommerce apps in Europe, PrestaShop boasts that it is used to open 30 new online stores every day. Paid support and training are available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
385.
Satchmo Django-based Satchmo calls itself "the webshop for perfectionists with deadlines." The site offers links to more than 100 stores created with the software, so you can see it in action for yourself. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
386.
Self Commerce A German project, Self Commerce is based on xt:Commerce (see above) and the Smarty template engine. Much of the website documentation is in German, but English versions of the software are available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
387.
SimpleCart (js) This very lightweight (under 20kb) JavaScript-based shopping cart offers very fast setup and doesn't require a separate database. However, in order to use it, you will need to know HTML. Operating System: OS Independent.
388.
Spree This newer e-commerce platform calls itself "the world's most flexible." In addition to the free download, it's also available as a Rackspace-powered SaaS solution, and the site also offers discounts and easy sign-up for payment processing. Operating System: OS Independent.
389.
Tomato Cart This fork of osCommerce includes unlimited product categories, a review and ratings system, search box with auto-completion, product image zoom, 26 built-in payment methods, one-page checkout and more. Hosting with support is available from several third-party partners. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
390.
Ubercart Ubercart is an e-commerce add-on for the Drupal content management system. It offers a configurable product catalog, single page checkout, anonymous checkout, an integrated payment system and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
391.
VirtueMart This add-on for the Joomla CMS offers advanced features like encryption, flexible tax models, shipping address management, multiple currencies and languages and more. The site has a demo and a number of links to live shops that use its shopping cart engine. Operating System: Winodws, Linux, OS X.
392.
WordPress eCommerce Plug-In Downloaded more than 1.3 million times, WordPress's eCommerce plug-in is a tried and true way to add e-commerce capabilities to your blog. Support, additional themes and other features and services are available for a fee. Operating System: OS Independent.
393.
X-Cart This feature-rich e-commerce solution touts itself as SEO-friendly, easy to customize, fast, secure and 100% PCI-DSS compliant. It comes in supported Gold and Pro editions, and hosting is also available from X-Cart. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
394.
xt:Commerce Smarty-based xt:Commerce is a mature, German e-commerce solution with an English version available. In addition to the free community version, it also comes in premium supported versions with prices in euros. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
395.
Zen Cart Designed in part by actual small business owners, this e-commerce tool is aimed at users without a lot of technical skills. The site includes plenty of tutorials and links to other services that are helpful when you're starting your own online business. Operating System: Windows, Linux
396.
ZenMagick This fork of Zen Cart (see below) offers features like unlimited products and categories, multi-currency and multi-language support, extensibility and simple PHP-based templates. Commercial support is available through Mixed Matter. Operating System: OS Independent.
397.
Zeuscart This open source shopping cart boasts a rich interface, good usability, comparison-driven shopping, SEO-friendly URLs, gift cards, coupons and more. Paid support services, including installation and upgrade help, are available. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
Educational Testing
398.
Safe Exam Browser If you're worried about your students cheating during a test, this app locks down the browser. While it's activated, it runs in fullscreen mode and prevents students from access other apps, the Internet, shortcuts, etc. Operating System: Windows.
399.
iTest With iTest, teachers can easily give students different versions of the same test because all questions can be drawn at random from a database. The website includes a large library of screenshots that show exactly how the software works. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
400.
TCExam Claiming to be "the most commonly used free CBA software in the world," this Web-based testing program greatly simplifies the process of creating, administering and grading tests. It's free for non-commercial use, or you can purchase a commercial license that includes support. Operating System: OS Independent.
Elementary Education
401.
ChildsPlay Designed for children under age six, ChildsPlay includes 14 different simple games. Some teach number and letter recognition, memory skills and keyboarding skills, and some of the games are just for fun. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
402.
GCompris GCompris collects more than 100 games and activities suitable for ages two to ten. It includes apps for telling time, chess, algebra, geography, sudoku, science and much more. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
403.
KLettres Because you're never too young for open source, KLettres teaches preschoolers to identify letters and their sounds. It also includes a "grown-ups" mode that aims to teach adults the basic building blocks of 25 different languages. (Note that in order to use KLettres on Windows, you'll have to download
KDE for Windows.) Operating System: Windows, Linux.
404.
Little Wizard If you’re the kind of parent who believes children are never too young to learn how to code, check out this development environment for the grade-school crowd. Using only the mouse, Little Wizard users learn about programming concepts like variables, expressions, loops, conditions, and logical blocks. Operating System: Windows.
405.
TuxMath To succeed at this game, kids must solve math problems in order to prevent Tux the Linux penguin from being hit by meteors. The user can choose the type of math problems and the level of difficulty. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
406.
Tux Paint Tux Paint is a drawing program designed for preschoolers and early elementary students. Drawing tools include brushes, line tools, stamps, shapes, an eraser, and a host of "magic" effects. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
E-mail
407.
Evolution Sometimes called "the Outlook of Linux," Evolution offers e-mail, calendar, to-do list and contact management for the Gnome desktop. The interface should feel very familiar for anyone who's ever used Outlook. Operating System: Linux.
408.
Thunderbird Made by Mozilla, the organization best known for the Firefox browser, Thunderbird offers e-mail with a tabbed interface and excellent customization capabilities. If you would like to add calendar functionality, you'll need to download Mozilla's
Lightning as well. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
409.
Zmail Zmail describes itself as a "fake e-mail program" that allows you to send e-mail from anyone to anyone. It's useful for testing mail servers or for sending e-mail without using your regular account. Operating System: OS Independent.
E-mail Marketing
410.
OpenEMM Downloaded more than 300,000 times, OpenEMM calls itself the "#1 open source application for e-mail marketing," and because it's been under development since 1999, it's also one of the oldest and most mature tools of its kind. The link above will connect you with the open source download, but commercial support, services, hosting and an SaaS version are available through project owner
Agnitas. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
411.
phpList With 10,000 downloads per month, phpList says it's "the world's most popular open source email campaign manager." The software also comes in a beta hosted version with fees based on the number of messages sent. Operating System: OS Independent.
Encryption
412.
APG APG (a.k.a. Android Privacy Guard) is an implementation of the OpenGPG encryption standard for Android. It's a work in progress, but already it allows users to encrypt, decrypt and sign messages, as well as to manage keys. Operating System: Windows.
413.
AxCrypt If you store personal information or data from your small business on your PC, you really should encrypt those files, especially if you are using a laptop. Downloaded more than 2.4 million times, AxCrypt integrates with Windows Explorer to make encrypting or decrypting individual files fast and easy. Operating System: Windows.
414.
Crypt At just 44KB, Crypt is one of the lightest weight encryption utilities available. And because it can encrypt 3MB worth of data in just 0.7 seconds, it's also one of the fastest. However, it doesn't have a GUI, so you'll need to be comfortable with the command line in order to use it. Operating System: Windows.
415.
FreeOTFE Like LUKS, this app encrypts an entire drive. With it you can create and encrypt virtual disks on your hard drive. It's also highly portable and can run from a thumb drive. Operating System: Windows.
416.
Gnu Privacy Guard This Gnu project is a command-line implementation of the popular OpenPGP encryption standard. It supports ElGamal, DSA, RSA, AES, 3DES, Blowfish, Twofish, CAST5, MD5, SHA-1, RIPE-MD-160 and TIGER encryption algorithms. Operating System: Linux.
417.
GPGTools Mac users can download this version of GPG for a more user-friendly way to encrypt e-mail and files. The website includes quite a bit of help and tutorials for new users, which make it even easier to get started using the app. Operating System: OS X.
418.
gpg4win And this version offers GPG for Windows users, complete with a GUI. It installs quickly and easily, and it protects both files at rest and mail messages. Operating System: Windows.
419.
LUKS/cryptsetup Short for "Linux Unified Key Setup," LUKS calls itself "the standard for Linux hard disk encryption." While many of the other apps on our list encrypt files one by one, LUKS encrypts your entire drive. Operating System: Linux.
420.
MailCrypt This app applies PGP or GnuPGP encryption to your e-mail and Internet usage. If you use Windows NT, be sure to read the warning note on the Web site. Operating System: OS Independent.
421.
MCrypt This replacement for the Unix crypt allows developers to add a wide range of encryption functions to their code, even if they don't know a lot about cryptography. The Web site contains a list of supported algorithms that are included in the Libmcrypt library. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix.
422.
NeoCrypt NeoCrypt supports multiple encryption algorithms, including AES, DES, Triple-DES, IDEA, RC4, RC5, CAST-128, BlowFish, SkipJack. It runs from an easy-to-use GUI, and it also integrates with the Windows Shell so that you can encrypt and decrypt files right from Windows Explorer. Operating System: Windows.
423.
Open Signature This digital signature project supports all Open SC cards and aims to be the first single app that can be used with cards from multiple countries. Open Signature originally focused on cards used in Italy but has branched out. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix.
424.
Steghide If you really want to feel like a spy, you can use Steghide to conceal hidden messages in audio or text files. It works with JPEG, BMP, WAV and AU files. Operating System: OS Independent.
425.
TrueCrypt If you don't want other people to be able to access any of the data on your drive, try TrueCrypt. It encrypts entire drives or partitions on the fly. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
426.
Apache OFBiz Apache's software suite for small businesses includes ERP, CRM, e-commerce, supply chain management, manufacturing resources planning, enterprise asset management, and POS from a single solution. Apache does not provide support directly, but the site does list a number of third-party service providers who can assist with deployment and ongoing support needs. Operating System: OS Independent.
427.
EdgeERP A community-oriented fork of webERP, EdgeERP offers a similar feature set. It boasts reliability, accessibility and flexibility. Operating System: OS Independent.
428.
ERP5 ERP5 combines ERP functionality with CRM, supply chain management, material requirements planning and product data management. It's also available in a paid enterprise version and both free and paid SaaS versions. Operating System: Linux.
429.
Neogia This French ERP solution (with English translation available) caters to SMBs. It offers a modular design and ease of use. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
430.
Openbravo Used by more than 15,000 customers, Openbravo offers Web-based ERP capabilities, with a focus on agility and ROI. Besides the free community edition, it offers basic and professional versions which can be purchased through third-party partners. Operating System: OS Independent.
431.
Open ERP For mid-size and larger enterprises, Open ERP offers more than 700 accounting, ERP and other business modules that can be tailored to a specific company's needs. Both a supported version and an online hosted version are also available with a monthly subscription. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
432.
opentaps Opentaps incorporates e-commerce, customer relationship management, warehouse and inventory management, supply chain management, financial management and business intelligence features. The company boasts that you can deploy the software in just minutes with its Amazon Machine Images (AMI) for the Amazon Elastic Computing Cloud (EC2). Operating System: Windows, Linux.
433.
]project-open[ Project-open boasts more than 150,000 downloads and more than 32,000 active users. It offers project management and project portfolio management along with some ERP capabilities. Additional modules, consulting, support and automatic updates are available for a fee, and it also comes in an SaaS version. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
434.
xTuple PostBooks Open source xTuple PostBooks offers an integrated accounting, ERP and CRM solution. The xTuple software also comes in numerous commercial editions, and it's also available in a cloud version deployed on Amazon's infrastructure. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
435.
SQL-Ledger Another Web-based application, SQL-Ledger features double-entry accounting and ERP features and, as you might guess, stores data in a SQL database server. Paid support is available at a variety of price points. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
436.
webERP This Web-based solution allows small business owners and managers to keep tabs on their companies' operations using only a Web browser and a PDF reader. The site includes links to partners who offer third-party support and hosting services. Operating System: OS Independent.
Family Tracing and Reunification
437.
RapidFTR In crisis situations like earthquakes and other disasters, children often get separated from their families. This mobile app makes it easier to collect, share and manage information about these children so that they can be reunited with their families more quickly. Operating System: OS Independent.
File Managers
438.
Explorer++ Replaces Windows Explorer
Explorer++ extends the capabilities of the standard Windows Explorer with tabbed browsing, an improved interface, keyboard shortcuts, file merge, file split, and customization capabilities. Like the regular Windows Explorer, it also offers drag-and-drop functionality. Operating System: Windows.
439.
Krusader The KDE file manager, Krusader is a twin-panel commander-style file manager. It boasts extensive support for archived files, advanced search, batch re-naming, file content comparisons and more. Operating System: Linux.
440.
muCommander Java-based muCommander offers a dual-pane file management interface with a light footprint. It allows users to modify zipped files on the fly, and it supports multiple file transfer protocols. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
441.
Nautilus Nautilus, the file manager for the Gnome desktop, is available for most Linux distributions. The intuitive interface should feel familiar to anyone who's ever used a file manager. Operating System: Linux.
442.
PCManFM The standard file manager for the LXDE desktop, PCManFM also supports other Linux desktops. Its features include drag-and-drop support, thumbnails, icon view, tabbed windows and trash can support. Operating System: Linux.
443.
QTTabBar Similar to Explorer++, this very popular open source project extends the functionality of Windows Explorer with tabs and other interface improvements. Support for Windows 8 is planned. Operating System: Windows.
444.
SurF SurF brings a fresh approach to file management with a unique, tree-based list of files. Other features include brief highlighting of new and recently changed files, auto-complete for search terms and network support. Operating System: Windows.
445.
Thunar Used by the Xfce desktop environment, Thunar boasts a clean interface and very fast performance. It includes a bulk renamer and an extensions framework so that you can add any functionality you like. Operating System: Linux.
446.
TuxCommander Like other "Commander" style file managers, TuxCommander offers a two-paned interface. It also features support for large files, a tabbed interface, a customizable mounter bar, associations and more. Operating System: Linux.
File Sharing
447.
ABC (Yet Another BitTorrent Client) This BitTornado fork adds a queuing system. Other key features include multiple downloads in a single window, customization capabilities, super-seed mode and more. Operating System: Windows.
448.
ANts P2P ANts uses encryption and a host of other security features to enable anonymous file sharing. Note that the ANts network is smaller than many other file-sharing networks. Operating System: OS Independent.
449.
Ares P2P Ares has its own network with integrated chat, and it also supports BitTorrent protocol and Shoutcast radio stations. Key features include fast downloads, a built-in media player and a library organizer. Operating System: Windows.
450.
BitTornado As you might guess from the name, BitTornado is an alternative client for the BitTorrent network. It offers encryption and other enhanced security features. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
451.
BT++ This app aims at improving the original BitTorrent client. Current features include multiple downloads in a single window, minimize to the system tray, and automatic re-starting of interrupted torrents. In the future, developers plan to add enhanced bandwidth throttling and better OS/browser integration. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix.
452.
DC++ Downloaded more than 50 million times, DC++ offers a lot of help for first-time P2P users. It connects with the Direct Connect / Advanced Direct Connect network. Operating System: Windows.
453.
eMule/eMule Plus Considered by many to be the best P2P client available, eMule is now optimized for use with Windows 7. The eMule Plus version offers a slightly different interface, plus enhanced performance and IRC integration. Operating System: Windows.
454.
Mute Another P2P client with an emphasis on security, Mute uses indirect routing to help hide users' identities. Check out the site for an explanation of how its technology is based on the behavior of insects. Operating System: OS Independent.
455.
RetroShare Most file sharing networks open you up to all kinds of security and privacy concenrs, but RetroShare lets you set up a secure file sharing network only among those you trust. It encrypts all communication via OpenSSL and GPG, and it supports e-mail, chat, file sharing, streaming, VoIP, and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, BSD.
456.
Shareaza P2P Shareza calls itself the "ultimate P2P client" and boasts that it "just keeps getting better and better." It supports eDonkey2000, Gnutella, BitTorrent and Gnutella2 networks. Operating System: Windows.
457.
StealthNet Like MUTE, the StealthNet network routes file sharing requests through multiple network nodes in order to provide anonymity. It offers fast download speeds and a user-friendly GUI. Operating System: OS Independent.
458.
Vuze One of the most popular BitTorrent clients, Vuze makes it easy for novices to get started downloading hi-def video while offering plenty of features for advanced users. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix, OS X.
459.
Waste Waste allows small groups of users to chat and download files securely and anonymously. Transmissions are encrypted using RSA and Blowfish algorithms. Operating System: Windows, Linux, BSD, OS X.
File Transfer
460.
Connectbot Need to transfer files to an Android device? This SSH client will allow to move your files securely. Operating System: Android.
461.
FileZilla This project includes both an FTP server for Windows and a cross-platform FTP client. Both support FTP, FTPS and SFTP file transfer with an easy-to-use tabbed interface. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
462.
FireFTP This Firefox add-on has been downloaded more than 22 million times. It allows you to download files via FTP or SFTP right from your browser window. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
463.
WinSCP This award-winning FTP, SFTP, and SCP client comes with two different interfaces, so that you can pick the one that suits you best. Other notable features include an integrated text editor, authentication support, batch file scripting and more. Operating System: Windows.
Flashcards
464.
Anki Anki supports images, audio, videos and scientific markup, so you can use it to memorize anything from names and faces, geography, vocabulary, information for medical or law exams or even guitar chords. It also works with most mobile OSes, so you can use it on your smartphone or tablet. Operating System: OS Independent.
465.
FlashQard This learning tool is founded on two basic principles: different cards for different purposes and the Leitner System. Developed in the 1970s, the Leitner System is a proven methodology for spending more time on more difficult material and less time on materials that's already been mastered. As with many of the flashcard-type apps, this app lets you create your own cards or download sets that have already been created. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
466.
Genius If you need to memorize something—anything—Genius can help. It's a spaced repetition flashcard program that can help you pass a test, master a subject, prepare for a speech and more. Operating System: OS X.
467.
jVLT The Java Vocabulary Learning Tool, aka jVLT, aims to help users learn vocabulary for new languages. You can make up your own cardset or use the pre-built sets to learn French, English, Spanish, Thai, Chinese, German, Czech, Finnish or Russian. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
468.
The Mnemosyne Project Another flashcard-type study aid, The Mnemosyne Project relies on a sophisticated algorithm to determine which card shows up when. Users also have the option of transmitting their data and progress to the project's owners, who are conducting a research project about the nature of memory. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android
469.
Parley KDE's flashcard program can be used to learn any type of information, but it's particularly well adapted to learning new vocabulary. In addition to standard flashcards, it also offers anagram, multiple choice, fill in the blank, conjugation and other types of exercises. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
470.
Pauker This flashcard app claims to help strengthen your ultra-short-term, short-term, and long-term memory. You can make your own cards if you want to learn something in particular, or you can use one of the many pre-written lessons, which include foreign languages, states/provinces and capitals, chemical elements, multiplication tables, musical terms and even European license plates. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Foreign Language Instruction
471.
Pythonol Pythonol is designed to help English speakers learn Spanish. It includes multiple tools and games for learning vocabulary, conjugation, pronunciation, idioms, reading comprehension and more. Note that it comes in separate versions for adults and children. Operating System: Windows 98, Linux.
472.
Step Into Chinese This app can serve as both a Chinese-English dictionary and a flashcard system for mastering vocabulary. It includes pronunciation, translation and contextual information for more than 26,000 modern Chinese words and concepts. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
473.
Zkanji Zkanji is an elaborate English-Japanese dictionary. Included features can help you learn to write Japanese characters, study vocabulary or find meanings for words you don't know. Operating System: Windows.
474.
ZWDisplay ZWDisplay helps those studying Chinese learn to pronounce Chinese words and read Chinese text. Clicking the Chinese characters displays a pinyin pronunciation guide and an English translation. Operating System: Linux
Forensics
475.
Live View This Java-based tool creates a VMWare virtual image of the machine you are analyzing so that you can interact with it without changing the underlying image or disk. Developed by CERT and the Software Engineering Institute at Carnegie Mellon, it's an excellent tool for forensic examiners. Operating System: Windows.
476.
ODESSA The Open Digital Evidence Search and Seizure Architecture, aka "ODESSA," offers several different tools that for examining and reporting on digital evidence. This is an older project, but still valuable. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
477.
The Sleuth Kit/Autopsy Browser These two apps work together: The Sleuth Kit offers command line tools for conducting digital investigations, and Autopsy Browser offers a browser-based GUI for accessing those tools. The project also now includes a Hadoop framework for large-scale data analysis. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Games
478.
0 A.D. Now in its eighth alpha release, 0 A.D. is a real-time civilization-building strategy game that plays a lot like Age of Empires. It offers excellent graphics, six different civilizations to play, and several multiplayer modes. Operating System: Linux, Windows, OS X.
479.
Advanced Strategic Command This turn-based strategy game, which was "designed in the tradition of the Battle Isle series," pits military units against each other on a hexagonal grid. Play against the AI opponent or against other humans using hotseat or PlayByMail. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
480.
Alien Arena This self-described "furious frag fest" is a first-person shooter in the style of Quake III and Unreal Tournament. Boasting "one of the most active, loyal, and committed communities of any free game in existence," Alien Arena has a large user base that makes it easy to find online competitors any time of day. Operating System: Linux, Windows, OS X.
481.
AssaultCube This realistic first-person shooter runs in single- or multi-player mode and utilizes the same engine as Cube (see below). Thanks to its low latency and lightweight size, it can run on older systems and slow networks, and it offers fast gameplay. Operating System: Linux, Windows, OS X.
482.
AssaultCube Reloaded This fork of the popular first-person shooter integrates some of the best features of Battlefield, Quake and Call of Duty into AssaultCube, while maintaining a lightweight footprint. Other improvements include ricochet shots, new weapons, improved radar and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
483.
Battle for Wesnoth With plenty of elves, necromancers, orcs and warriors, this popular turn-based strategy game immerses players in a high-fantasy world with a number of scenarios to play. It includes more than 200 unit types from six different factions, and it supports online multiplayer games. Operating System: Linux, Windows, OS X, iOS.
484.
Billiards Billiards is designed to simply but accurately simulate the game for which it's named, so that players can practice when a pool table isn't available. It currently offers tables both with and without pockets, and you can play eightball, nineball and carom billiards. Operating System: Linux.
485.
BosWars In this futuristic real-time strategy game, you build your stores of energy and your economy while battling opponents for control of the map. You can play alone or against human opponents via a LAN or the Internet. Operating System: Windows, Linux, BSD, OS X.
486.
Brain Workshop Research suggests that dual n-back activities can improve working memory and fluid intelligence, and they also seem to help some ADHD/ADD sufferers. Downloaded more than 384,000 times, Brain Workshop lets you give your brain a workout by trying dual n-back exercises for yourself. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
487.
BZFlag Also known as "Battle Zone Capture the Flag," BZFlag is based on one of the most popular games ever created for Silicon Graphics machines. With nearly 200 servers available, it's fairly easy to find a group to play this multi-player 3D tank game. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
488.
CommanderStalin This game transports the action of Bos Wars away from the future and back to the Soviet era in Russia. Build up your economy and military so that you can withstand the inevitable attack from Nazi Germany. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
489.
Crossfire Explore 3000 maps and battle 150 monsters in this retro arcade adventure game. It includes 15 character types, an elaborate magic system and many, many treasures to find. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
490.
Cube Cube boasts excellent graphics and lots of brutal action in the tradition of games like Doom and Quake. Play alone or against up to 12 other players in multi-player mode. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
491.
Dakar 2011 In this newer racing game, you drive in the Dakar rally through 14 different stages based on real maps. It includes six different vehicles and 140 different opponents. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
492.
Domination Domination is a Java-based version of the board game Risk. The developers have recently completed a version for Android that can be downloaded through Google Play. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android.
493.
Egoboo This 3D dungeon-crawler challenges players to save Lord Bishop from the clutches of the evil Dracolich, slaying hordes of monsters along the way. Play with up to four other people as you make your way through 40 different dungeons. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
494.
Enigma Similar to the classic Oxyd and Rock'n'Roll games for Atari and Amiga, Enigma challenges uses to find pairs of matching Oxyd stones while avoiding traps, overcoming obstacles and solving puzzles. It's been downloaded hundreds of thousands of times and features more than 1,000 levels of gameplay. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
495.
Excalibur: Morganna's Revenge In this epic adventure game, you begin as a futuristic soldier on a starship but soon time-travel back to the age of King Arthur, where you must save the world from Morganna. It offers 42 levels of solo play and 27 levels you can play with your friends in network mode. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
496.
Extreme Tux Racer The classic Tux Racer (below) hasn't been updated in a while, but this version updates the original with better graphics and gameplay. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
497.
Fish Fillets NG Free the fish by solving a variety of puzzles. Along the way, the fish make funny comments and the other game denizens fight amongst themselves. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
498.
FlightGear FlightGear describes itself as "sophisticated, professional, open source." It includes realistic graphics for more than 20,000 real world airports, 3 DVDs worth of accurate world scenery, several aircraft options and the ability to model your own aircraft. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others
499.
Foobillard++ This is also a remake of an earlier open source game. Check out the screenshots on the site to see the excellent graphics for this billiards game. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
500.
FreeCol If you've played Civilization, FreeCol will feel very familiar. It's a turn-based strategy game where the objective is to build a successful civilization starting with just a few colonists. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
501.
FreeCiv Like many games in this genre, FreeCiv challenges players to manage a civilization from the Stone Age through the Space Age. The graphics and game play are fairly similar to Civilization I and II, but not as advanced as the more recent Civilization games. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
502.
FreeOrion Based on the Master of Orion games, this "turn-based space empire and galactic conquest game" involves both nation-building and combat elements. Both single- and multi-player games are available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
503.
Frets on Fire Very similar to Guitar Hero, Frets on Fire lets you use your keyboard of a guitar controller to play along with tracks. This project has a huge community of users who have composed songs for the game, or you can import Guitar Hero tracks or your own songs. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
504.
Frozen Bubble Known as "the most addictive game ever created," Frozen Bubble is a traditional bubble shooter where you try to make chains containing balls of the same color. It includes 100 levels for single players, or you can challenge your friends in two-player mode or online multi-player mode. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
505.
GBrainy Gbrainy helps keep you in top mental shape with a variety of logic, mental calculation, memory training and verbal analogy activities. It offers a variety of difficulty levels, making it appropriate for players of all ages. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
506.
The Genius The Genius is a chess app with a simple interface. Choose among four levels of game play ranging from "I dunno chess" to "Expert." Operating System: Windows.
507.
Get Sudoku Portable Stumped by a Sudoku puzzle? Enter the values you know into this app and it will help you keep track of the possible answers for all of the other boxes. Operating System: Windows.
508.
Glest The forces of Tech battle the forces of Magic in this award-winning 3D real-time strategy game. Check out the gallery on the website for plenty of screenshots and information about the tech tree and buildings. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
509.
GLtron As in the movie Tron, competitors in this game ride speeding lightcycles that trail walls behind them. The goal is to trap other players, forcing them to hit the wall, while you remain free. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
510.
GnomeGames Gnome's collection of casual "five-minute" games includes Chess, Sudoku, Mines, Four-in-a-row and 11 other simple games. The graphics and gameplay are basic but sometimes addictive. Operating System: Linux.
511.
GNU Backgammon Based on a neural network, this backgammon engine gets better with time. Test yourself against a computer opponent with the skills of a championship flight tournament player or use it to analyze backgammon moves and matches. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
512.
GNU Go This GNU project allows users to play Go, a 3,000-year-old Asian board game similar to chess. It's a two-player game where players attempt to control the most territory on the board. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
513.
Hedgewars Unlike a lot of strategy games, Hedgewars doesn't take itself too seriously. It describes itself as "a turn based strategy, artillery, action and comedy game, featuring the antics of pink hedgehogs with attitude as they battle from the depths of hell to the depths of space." Games can support up to eight players at once, and it includes 47 different weapons, including the piano strike and explosive robotic cake. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS.
514.
I Have No Tomatoes How many tomatoes can you smash in ten minutes? Find out with this off-beat and highly unusual puzzle game. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
515.
KDE Games The KDE desktop offers a much wider selection of casual games. It includes KBattleship, KMahjong, KBreakout, KSpaceduel, KMines, KSudoku and many more. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
516.
The Legend of Edgar On a dark and stormy night, Edgar's father fails to return home, leading Edgar to believe he has been captured by an evil sorcerer. In this 2D game, players help Edgar overcome obstacles, solve puzzles, defeat enemies and find his father. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
517.
LinCity NG LinCity NG offers an open source version of the original Sim City game. Win by building a sustainable economy or by evacuating your entire population in spaceships. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
518.
Liquid War One of the most unusual games available, Liquid War is a multiplayer strategy game with a twist. Instead of an army, you control a glob of liquid, and you win by eating your opponents. The graphics aren't particularly great, but the game itself is interesting. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
519.
Linley's Dungeon Crawl If you miss some of the really old dungeon crawlers like Rogue, Hack and Moria, this game is for you. The goal is to retrieve the Orb of Zot from deep in a subterranean cavern and return it to the surface. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
520.
MegaGlest Based on Glest, MegaGlest adds five more factions--Egyptians, Indians, Norsemen, Persian and Romans--to the Tech and Magic teams from the original. Play in one of 17 different settings, either alone or against up to seven other players. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
521.
Micropolis Another Sim City Clone, Micropolis (a.k.a. OLPC SimCity) was developed for the One Laptop Per Child project. It's based on the source code for the original version of Sim City. Operating System: Linux, Unix.
522.
Neverball To complete the levels of Neverball, you'll need to be able to solve puzzles and to be able to tilt the floor skillfully to move the ball where you want it to go. The download also includes Neverputt, a golf game based on the same engine. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
523.
Nexuiz One of the most popular open source first-person shooters ever, Nexuiz has been downloaded more than 6 million times. A team is currently working on re-making the game for consoles. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
524.
Oolite This space simulator challenges players to fly around the universe, establishing space stations and fending off enemy ships. The graphics are old-school (based on the classic game Elite), but many players same the game is highly addictive. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
525.
OpenArena Designed as a clone of Quake III Arena, Open Arena offers multi-player first-person shooter action and twelve different game types. Due to the nature of some of the content, its developers warn that it is unsuitable for kids under 17. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
526.
OpenCity Yet another city development simulator, Open City features 3D graphics and detailed terrain. The site includes helpful tutorials to get you started playing the game. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
527.
OpenTTD Although it was based on Transport Tycoon Deluxe, this game improves on the original with larger maps, support for up to 255 players, improved tools and the opportunity to bribe town authorities. Check out the site for a list of servers that host multiplayer games. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
528.
Performous For those who want to perfect their song and dance moves, Performous mashes together dancing, guitar playing and singing into one fun game. It's karaoke meets Dance Dance Revolution meets Guitar Hero—and all you need is a PC to play. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
529.
Pingus If you've ever played Lemmings, Pingus will feel very familiar. In this version you guide a horde of penguins through various levels by assigning some penguins to dig, bash, climb, etc. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
530.
PlaneShift This 3D fantasy role-playing game offers free play with no restrictions. It features six races, six "Ways of Magic," large worlds to explore and plenty of monsters to fight. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
531.
PokerTH Downloaded millions of times, this superb Texas Hold 'Em game features above-average graphics and an active community of players. Check out
Poker-heroes.com to see the rankings of current players. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android.
532.
Powermanga Similar to the old arcade game Galaga, Powermanga is a 2D space shooter with 41 levels to play. It's good for hours of shoot 'em up fun. Operating System: Linux.
533.
Pushover Guide your ant so that it knocks over the dominoes on the screen in the correct order. A remake of an older game, this version of Pushover includes several different levels and 11 different kinds of dominoes. Operating System: Windows.
534.
PySolFC PySolFC collects more than 1,000 solitaire games into a single download. In addition to games featuring the traditional 52-card deck, you'll find games for the 78-card Tarot deck, eight- and ten-suit Ganjifa games, Hanafuda games, Matrix games, Mahjongg games and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
535.
Red Eclipse Just over a year old, this Cube-based shooter includes unique gameplay features like Parkour, impulse boosts and dashing. It also includes an editor so you can build your own levels. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
536.
Rigs of Rods This very popular vehicle simulator uses a unique soft-body physics engine to provide very realistic behavior of vehicles that travel over land, water and air. An extremely active user community has created more than 2000 modifications for the app, and you can find numerous user videos online. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
537.
Rocks'N'Diamonds A definite oldie, Rocks'N'Diamonds is a multiplayer arcade game "in the tradition of" Boulder Dash, Emerald Mine, Supaplex and Sokoban. Thanks to an active user community, tens of thousands of levels are available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
538.
Ryzom Set 2000 years in the future on the plant Atys, Ryzom depicts a struggle for world domination between the nature forces of Kami and the technological forces of Karavan. Ryzom is a massively multiplayer online role-playing game (MMORPG) where players move up by gaining experience in fighting, magic, crafting and foraging. Note that while the download and basic play are free, unlimited play requires a subscription. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
539.
Scrabble In addition to the classic 15x15 crossword game, this version of Scrabble also lets you play SuperScrabble on a 21x21 word, Scrabble 3D or your own board. Compete against up to three online players at a time. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
540.
Scorched3D A modernized version of Scorched Earth, this turn-based artillery game offers excellent 3D graphics and easy-to-learn gameplay. Play online with up to 24 players at once and/or take on computer-generated opponents. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
541.
Secret Maryo Chronicles If you remember the old 2D Mario Bros. games fondly, you'll probably enjoy Secret Maryo Chronicles. It offers great old-school jump and run gameplay with plenty of levels. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
542.
Seven Kingdoms: Ancient Adversaries This is an updated version of the Seven Kingdoms real-time strategy game that was originally released in 1997. Choose your kindgom--Chinese, Egyptians, Greeks, Japanese, Maya, Mughuls, Normans, Persians, Vikings, Zulus--then begin training your army, building your economy and spying on your enemies in single-player or multi-player games. Operating System: Windows.
543.
ScummVM ScummVM allows you to port many classic point-and-click adventure games to nearly any platform you like, including many mobile platforms. Supported games include Simon the Sorcerer 1 and 2, Beneath A Steel Sky, Broken Sword 1 and Broken Sword 2, Flight of the Amazon Queen, Monkey Island, Day of the Tentacle, Sam and Max, and dozens of others. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, and many others.
544.
Simutrans Another Transport Tycoon Deluxe clone, Simutrans challenges players to create a successful transport network without going bankrupt. The website includes numerous PakSets, which offer new graphics and new worlds where you can play. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
545.
Slam Soccer 2006 Slam Soccer offers a comedic take on one of the world's most popular sports with slightly silly 3D graphics. It includes 80 teams, 20 stadiums, 10 referees, 9 commentators and the ability to play in a variety of weather conditions. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
546.
SlipStream Designed to support any type of vehicle that could be driven around a racetrack, SlipStream is more difficult to learn than some other vehicle simulators, but offers more realistic handling as a tradeoff. It's a young project that's early in development, but is already usable. Operating System: Linux.
547.
Smash Battle Based on the Mario Battle from Super Mario Bros. 3, Smash Battle is a newer game with old school 2D graphics. Fight against up to three other opponents in multi-player mode. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
548.
Spring: 1944 As you might guess from the title, this app is a WWII-theme real-time strategy game with period-accurate units and strengths. Play as the US, Germany, USSR or Britain. Operating System: Linux.
549.
SokoSolve SokoSolve offers a version of the classic Sokoban game which requires players to push one box at a time to achieve a desired configuration. In addition to the game, the download provides other tools for Sokoban fans, including a solver and a library. Operating System: Windows.
550.
Steel Storm Episode I Set in a futuristic world, Steel Storm is a top-down shooter with fast-paced action that doesn’t take too long to play. Note that while Episode I has an open source license, Episode II is a commercial product. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
551.
Stendhal This MORPG features simple, old-school graphics and friendly gameplay. Journey through a world full of villages, cities, dungeons, forests, mines, mountains and tropical islands, with plenty of adventures along the way. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
552.
StepMania This fun rhythm game works with your keyboards or dance pads (if you have them). You'll need to download songs separately from the game, but the site offers plenty of free songs. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
553.
Stunt Rally Stunt Rally is also a racing game, and it offers 57 tracks, 9 scenarios and 8 cars. There's also a track editor, so you can create your own courses, complete with loops and curves. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
554.
Summoning Wars This newer fantasy role-playing game offers four classes of characters, each with 24 unique magical abilities and other skills. Play on your own or with up to eight other people in multi-player mode. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
555.
SuperTux SuperTux is a classic 2D, side-scrolling jump-and-run game featuring Tux the Linux penguin. It offers 26 different levels where you can take on nine different enemies. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
556.
SuperTuxKart Tux the Linux penguin races around 3D tracks in this racing game. The latest version adds three new tracks, a battle arena, two new weapons and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
557.
T^3 Portable Play Tetris in 3D! It's simple, familiar and fun. Operating System: Windows.
558.
Teeworlds This side-scrolling 2D game features cartoonish graphics combined with multi-player shooting action. It supports up to 16 players at once in multiple game styles, including team deathmatch and capture the flag. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
559.
TORCS The Open Race Car Simulator (TORCS) offers realistic racing action that figures in tire and wheel properties, aerodynamics, collisions and more. It includes more than 50 cars, 20 tracks and 50 opponents. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
560.
Tremulous This award-winning game combines first-person shooter action with elements typically found in a real-time strategy game. Play as either the aliens or the humans, and rack up wins to become more powerful. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, XBox.
561.
Tux Racer Downloaded millions of times, this popular classic Linux game features Tux the penguin sliding downhill. It features 3D landscapes and changing weather conditions with fog, high winds and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
562.
UFO:Alien Invasion In the year 2084, you control a secret organization defending earth against brutal alien invaders. View the action from Geoscape mode, where you manage the battle from a high level, or Tactical Mode, where you lead a team in combat against the enemy. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
563.
Ultimate Stunts A remake of the DOS game Stunts, Ultimate Stunts takes racing to the next level by adding loops, corkscrews, jumps and more. It also makes it easy to build your own tracks. Note that it's still in the earlier stages of development. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
564.
Ultrastar Deluxe This karaoke games awards points based on how well you sing, similar to the game SingStar. You can use it with your own music files or you can download more than 10,000 songs available for the app. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
565.
Unknown Horizons In this 2D city-building strategy game, you start with a ship and a handful of resources on a desolate island. Can you build a thriving metropolis? Note that this is a newer game, and you may still run into some bugs. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
566.
VDrift This racing game was made with drift racing in mind. It features real-world tracks and vehicles and superb graphics. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
567.
Vega Strike This space simulator revolves around trading, exploration and combat with enemy ships. It plays in both single-player and multi-player modes and boasts excellent graphics. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
568.
WarMUX Now available for Android through Google Play, WarMUX describes itself as a game of "convivial mass murder" where you attempt to defeat your opponent's team using dynamite, grenades, baseball bats and bazookas. The 2D graphics feature penguins, gnus, firefoxes, and other mascots from well-known open source software. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android.
569.
Warsow No, that isn't a misspelling of "Warsaw." Warsow is a very fast-paced, cartoonish shooter featuring rocketlauncher-wielding pigs. Unlike most other shooters, Warsow goes easy on the gore, using stars and cubes to stand in for blood and guts. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
570.
Warzone 2100 Warzone 2100 challenges players to rebuild civilization after it's been destroyed by nuclear war. It offers real-time action in campaign, multi-player and single-player modes. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
571.
Widelands Inspired by The Settlers and The Settlers II, Widelands is another civilization-building real-time strategy game. It features four worlds, three tribes, a map editor and both single- and multi-player games. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
572.
WinBoard Portable Play the standard chess game you know or one of the variants like xiangqi (Chinese chess), shogi (Japanese chess), Makruk, Losers Chess, Crazyhouse, Chess960 and Capabanca Chess. You can play on your own or connect to other players on the Internet. Operating System: Windows.
573.
XMoto To complete the various levels on this 2D motocross game, you'll need to collect all the strawberries while overcoming various obstacles and avoiding wreckers. Hundreds of additional user-created levels are available on the site. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
574.
XM Solitaire This collection features 200 different cards games, including popular solitaire options like Freecell, Klondike, Fan, Spider, Pyramid and Gaps. The same site features a number of puzzle games, like Sokoban, Sudoku and others. Operating System: Windows.
Casual and Puzzle Games
575.
XPilot First developed in 1991, XPilot is a classic space game similar to Asteroids. It's multi-player only, so you'll need to join a game on an existing server or set up a server of your own. Multiple forked versions are also available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS.
576.
Yahtzo! As you might guess from the name, Yahtzo! is a computerized version of Yahtzee. The interface is fairly bare-bones, but play is just like the classic dice game. Operating System: Windows.
Card Games
577.
Yo Frankie! Built with the Blender open source 3D animation tool, Yo Frankie! features some of the best graphics you'll see on any open source game. It features characters from the open source movie Peach who run, jump, climb and glide their way across obstacles in a realistic landscape. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
578.
Zero-K This futuristic real-time strategy game offers plenty of action, streamlined economy controls and fast-moving games, with the average game lasting 20-30 minutes. It features battling robot armies with the ability to micro-manage individual units. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
579.
Zombies If you get tired of playing strategy games against the living, take a turn playing against the undead. The goal? Kill the zombies before they kill you. Operating System: Windows, OS X.
Gateway Security Appliance
580.
Endian Firewall Community With the Endian Community version, you can create your own network security appliance using an older PC. It offers firewall, antivirus, spam blocking, content filtering, a VPN and other security capabilities in a single package. Pre-configured hardware appliances and commercially supported software appliances are also available at the site. Operating System: Linux.
581.
Untangle Much like Endian, Untangle offers an integrated security appliance that you can deploy on your own hardware, or you can purchase a pre-configured hardware appliance from the company. Untangle also has a network of third-party partners who offer Untangle-based products and services. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
Genealogy
582.
GenealogyJ Like Gramps, GenealogyJ is a tool for viewing and editing your family history, but it was designed for amateurs, not professionals. Java-based, it creates family trees, timelines, maps, reports and more. Operating System: OS Independent.
583.
Gramps Short for "Genealogical Research and Analysis Management Programming System," Gramps is one of the best acronyms we've ever seen on an open source project. It's a professional-quality genealogical program with a very active user community and more than 1,100 pages of online documentation to help you trace your own family history. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
584.
PhpGedView Working on your family tree? PhpGedView makes it easy to collaborate online with the rest of your family to trace your genealogy. Note that you'll need your own Web server in order to set it up. Operating System: OS Independent.
Geography/GPS
585.
Marble Another KDE app, Marble is a combination atlas/virtual globe that integrates with Wikipedia so that students can learn more about places that interest them. It also includes topographic maps, a satellite view, street maps, earth at night and temperature and precipitation maps, and many teachers find it useful in the classroom. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
586.
WorldWind WorldWind was
originally packaged to be very similar to Google Earth. The link here takes you to an SDK that allows you to incorporate WorldWind into your own apps. It also includes links to several interesting apps that use WorldWind. Operating System: OS Independent.
Graphics Editors/Animation Tools
587.
Art of Illusion While not quite as robust as Maya, this 3D modeling and rendering studio still packs plenty of professional-quality features like subdivision surface based modeling tools, skeleton based animation, and a graphical language for designing procedural textures and materials. Check out the site for examples of artwork created with this open source tool. Operating System: OS Independent.
588.
Blender Designed for professionals, Blender is a complete 3D content creation suite with tools for modeling, shading, animating, rendering, and compositing both still and moving images. A number of motion pictures have been created using this software, and Blender even has an annual film festival to show off users' creations. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
589.
CinePaint Although it is a raster graphics editor, not a video editor, CinePaint is specifically designed to be used for motion pictures. It offers a similar set of tools as Gimp, but it supports high bit-depth, which allows this app to be used for touching up individual frames of a film. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
590.
Dia "Roughly inspired by Visio," Dia is perfect for creating org charts, network diagrams, flowcharts, and other simple diagrams. It saves diagrams in XML, or it can export to EPS, SVG, XFIG, WMF and PNG formats. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix
591.
Gimp There's no need to spend hundreds of dollars on Photoshop when Gimp offers the same features for free. It includes a full range of features, from photo re-touching capabilities for amateur photographers to advanced layers and photo manipulation tools for professional graphic designers. For the Windows version, see
Gimp-win. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
592.
Gmsh This app describes itself as a "3D finite element grid generator with a build-in CAD engine and post-processor." In layman's terms, it's a simple program for designing three-dimensional objects that offers some capabilities of a 3D graphics tool and some capabilities of a CAD tool. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
593.
Gnu Paint Also known as GPaint, Gnu Paint offers a basic set of graphic creation tools, including polygon shapes, ovals, freehand drawing tools, and fill and shadow features. It's essentially the same as Windows Paint, but it supports only the Linux Gnome desktop. Operating System: Linux.
594.
GrafX2 Originally created for DOS systems, this app traces its inspiration to programs like Amiga's Deluxe Paint and Brilliance. This updated open source version has been ported for multiple operating systems, but it's still best at creating old-school 256-color graphics. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
595.
gSculpt A fork of Wings 3D, gSculpt provides all the tools found in Wings 3D, plus a few additional improvements designed to improve workflow and reduce the time required for creating new graphics. In addition to the documentation available on the site, one gSculpt users has set up a
blog with extensive tutorials for those new to 3D graphics. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
596.
ImageJ Developed at the National Institutes of Health, this Java-based image manipulation program was intended to for use by doctors and scientists for use in analyzing images from clinical or laboratory settings. However, it can be used to modify many other types of images and artwork as well. Operating System: OS Independent.
597.
Inkscape Much like Illustrator and CorelDraw, Inkscape allows you to create, edit and save vector graphics. It provides a whole host of advanced features in a streamlined, intuitive interface. The website also offers lots of support and documentation, as well as a library of free clip art you can use in your creations. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
598.
JPatch This Java-based tool offers full modeling capabilities, but only basic animation capabilities. Sample work created with the app can be seen on the site. Operating System: OS Independent.
599.
K-3D Boasting that it is "easy, powerful, flexible and free," K-3D offers powerful 3D modeling and animation capabilities with an intuitive interface. The site offers plenty of help for new artists, including extensive tutorials. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
600.
KolourPaint This paint app for the KDE interface aims to be easier to use than Gimp with a better feature set than GPaint or Windows Paint. The site includes a helpful product comparison page that highlights some of the similarities and differences between the various painting programs available. Operating System: Linux.
601.
Krita KDE's painting app can help you edit existing photography or art or create new digital artwork of your own. The interface is designed to mimic real world art supplies and painting tools. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
602.
LaTeXDraw This simple drawing program creates images for use in documents created with LaTeX. It's best for mathematical or scientific images, charts, diagrams, etc. Operating System: OS Independent.
603.
Leonardo Sketch Leonardo describes itself as "named after the 15th century painter, but aimed for the 21st century user." It's a fairly new project, but offers a good list of basic features for vector graphics creation and editing. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
604.
Luminance HDR This project provides a workflow for high dynamic range (HDR) images. It supports multiple file formats, including raw formats, and it includes helpful wizards that walk users through common tasks. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
605.
Misfit Model 3D Although it's no longer in active development, you can still download and use this 3D modeling tool. Features include multi-level undo, skeletal animations, simple texturing and command-line batch processing. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
606.
MyPaint Designed for use with pressure sensitive graphic tablets, MyPaint is a fast powerful painting program. The interface disappears when not in use so that you can focus on your artwork. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
607.
Paintbrush Reminiscent of the old MacPaint software, Paintbrush offers Mac users a simple way to create basic images quickly. It supports multiple graphic file formats and includes tools like airbrush, rounded rectangle, eyedropper, zoom and a text tool. Operating System: OS X.
608.
Pencil If you'd like to try your hand at old-school hand-drawn animation, give Pencil a try. It offers an easy-to-use interface, and it supports both bitmap and vector graphics. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
609.
Pixelitor This Java-based photo editor offers more than 70 image filters and color adjustments, some of which aren't offered by any other tool. However, documentation for this project is a little light, so you'll need to have some experience with other photo editors in order to use it. Operating System: OS Independent
610.
Pinta Modeled after the freeware Paint.Net, Pinta offers advanced drawing tools and more than 35 adjustments and effects for manipulating your photos. Features include unlimited layers, full undo history and more. Operating System: Windows.
611.
Seashore Based on The Gimp, Seashore is a Mac-only graphics and photo editor designed to meet the needs of average users. It offers features like gradients, textures, anti-aliasing for both text and brush strokes, multiple layers and alpha channel editing. Operating System: OS X
612.
sK1 Developed as a replacement for Illustrator and CorelDRAW, sK1 offers professional pre-press features, such as CMYK color separations, ICC color management and press-ready PDF output. It currently works on Linux only, but the project owner plan to port it to Windows and OS X. Operating System: Linux.
613.
svg-edit This Java-based graphics editor will run in any browser. It offers more than enough features for amateur designers and illustrators, and it's been incorporated into many other open source projects. Operating System: OS Independent.
614.
Synfig Studio This 2D animation tool aims to make it possible to create professional-quality animation with fewer people and resources. It supports both vector and bitmap artwork. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
615.
Tux Paint Created for the younger set (primarily preschoolers and kindergarteners), Tux Paint helps kids create their own digital artwork. It offers basic drawing tools, plus fun stamps and special effects like sparkle, drip, rainbow and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
616.
Wings 3D Wings 3D creates still graphics, but not animation. Designed to be both powerful and easy to use, it offers a wide range of modeling tools, a customizable interface, support for lights and materials, and a built-in AutoUV mapping facility. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
617.
Xara Xtreme for Linux Based on the commercial Windows software by the same name, Xara Xtreme for Linus offers exceptional speed for a graphics editor. It also boasts an uncluttered interface and a well-developed library of documentation and support materials. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
Human Resource Management (HRM)
618.
Open Applicant Rather than a complete HR management tool, this app is specifically designed to assist with the hiring process. Besides the open source version, the company also offers a hosted version and commercial support. Operating System: OS Independent.
619.
Orange HRM Claiming more than a million users, OrganeHRM considers itself "the world’s most popular Open Source Human Resource Management Software (HRMS)." It also comes in a "Live" SaaS version that takes just 15 minutes to set up. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
620.
WaypointHR Similar to Orange, WaypointHR tracks personnel information, attendance and leave, contract details, discipline, performance reviews and more. It also comes in a hosted, on-demand version. Operating System: OS Independent.
Instant Messaging
621.
Adium Very similar to Pidgin (see below), this Mac-only software allows users to connect to multiple networks at once, including AIM, MSN, Jabber, Yahoo, and others. It offers a tabbed interface, and it integrates with your Address Book. Operating System: OS X.
622.
aMSN Designed to replace MSN Messenger (now known as Windows Live Messenger), aMSN is a skinnable client that works with Microsoft's IM network only. Noteworthy features include offline messaging, voice clips, custom emoticons, group support, multi-language support, webcam support, tabbed windows, display pictures and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
623.
Kopete KDE's IM client supports AIM, ICQ, Windows Live Messenger, Yahoo, Jabber, Gadu-Gadu, Novell GroupWise Messenger and other networks. It also offers tools for archiving and encryption and a unique notification system that only lets "important" message through. Operating System: Linux.
624.
Miranda IM Small and fast, Miranda is very light on system resources. Like many of the other IM clients on our list, it supports multiple networks, including AIM, Facebook, ICQ, IRC, Yahoo and others. Operating System: Windows.
625.
Pidgin This very popular open source IM clients connects with up to 16 different chat networks simultaneously. It supports file transfers, away messages, buddy icons, custom emoticons and typing notifications, and it has a large library of plug-ins that extend its capabilities further. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix
626.
Psi Psi is an open-source IM client for the Jabber network, which includes GoogleTalk, LiveJournal, and a number of international networks. It’s completely customizable and supports about 20 different languages. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Interior Design
627.
Sweet Home 3D Determined to spruce up your home this year? This app helps you create 2D and 3D layouts of your rooms, complete with a preview of how the finished product will look. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
IT Inventory Management
628.
GLPI Many users deploy OCS and GLPI together. OCS finds the resources connected to the network, and GLPI creates a database to help administrators track and manage those assets. Operating System: OS Independent.
629.
OCS Inventory NG Find out what hardware is connected to your network and how it is being used. OCS also includes a deployment system for distributing software and scripts across your network. Operating System: OS Independent.
Jewelry
630.
iNecklace This necklace for Mac fans slowly pulses with light. You can buy it premade or download the open source schematics from
GitHub to make it yourself. Operating System: N/A
Library
631.
LibLime Koha Koha humbly describes itself as "the most functionally advanced open source ILS on the market today." A variety of paid services, including hosting, support, implementation and consulting are also available on the site. Operating System: OS Independent.
632.
OpenBiblio This automated library system includes online public access catalog (OPAC), circulation, cataloging, and staff administration functionality. It's not as full-featured as some of the other library apps, but it gets the job done, and the site has lots of documentation. Operating System: OS Independent.
633.
VuFind Designed and developed "by libraries for libraries," VuFind aims to make searching your library's catalog easy and intuitive. Key features include modular design, faceted results, "more like this" suggestions, author biographies and more. Operating System: OS Independent.
Linux Desktop Environments
634.
Gnome One of the two most popular Linux desktop environments, Gnome is the default desktop for Fedora, Ubuntu, and several other distributions. It's best known for being easy to use. Operating System: Linux.
635.
KDE Plasma Desktop The second of the two most popular Linux desktop environments, KDE has a reputation for being "prettier" than some of the other desktop environments and feels very similar to Windows and OSX. The KDE community is one of the largest open source communities, so plenty of help is available for new (or experienced) users. Operating System: Linux.
636.
LXDE The "Lightweight X Desktop Environment" claims it has a "beautiful interface," but if truth be told, it's much more concerned about speed than looks. Because it uses so few computing resources, it's a good choice for netbooks and cloud-computing environments. Operating System: Linux.
637.
Xfce Another lightweight option, Xfce also offers very fast performance and doesn't make any claims about its beauty. It offers a modular design, so users can install just the components they choose in order to create a completely customized desktop experience. Operating System: Linux.
Log File Monitoring and Analysis
638.
Analog The "most popular logfile analyser in the world," Analog is an ultra-fast scalable log analysis tool for use with Web servers. Use it alone or with
Report Magic to generate prettier charts and graphs. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
639.
AWStats This free log file analysis tool creates graphs from Web, streaming, ftp or mail server statistics. Check out the helpful
comparison chart to see how its feature stack up against other open source and commercial applications. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
640.
BASE The "Basic Analysis and Security Engine," or BASE, use a Web-based interface to analyze alerts from Snort IDS. Features include role-based user authentication and Web-based setup. Operating System: OS Independent.
641.
IPtables Log Analyzer This app makes it easier to understand the log files from your Shorewall, or SUSE Firewall, or Netfilter-based firewall logs. It organizes rejected, acepted, masqueraded packets, etc. into an attractive HTML page. Operating System: Linux.
642.
Snare At this site, you'll find numerous open source Snare agents designed to analyze log files from a security perspective. InterSect Alliance, the organization behind the Snare agents, also offers a commercial server that incorporates the open source tools. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others.
643.
Webalizer This speedy Web log file analyzer claims to be able to process a log file with 2 million hits in 30 seconds. It supports both IPv4 and IPv6, and it is available in dozens of languages. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Logic/Debate
644.
Argumentative Similar to mind mapping software, Argumentative helps you create an "argument map" that outlines the premises of an argument in a visual way. It's particularly helpful for projects with a lot of writing – like creating a book, website, software documentation, etc. Operating System: Windows.
Mail Servers
645.
Citadel Citadel is a mail server that claims a reputation for being "easy to install, easy to use, easy to live with." The link above provides information about using Citadel in the cloud as a hosted service, but you can also download and deploy it on your own servers. Operating System: Linux.
646.
Exim This MTA was developed at the University of Cambridge and is still widely used in the UK. It's best for servers that are unlikely to have large volumes of mail because it doesn't have a central queue manager. Operating System: Linux, Unix.
647.
Postfix Originally developed by IBM Research, Postfix is a secure mail transfer agent that is very similar to Sendmail (see below). It's fairly fast and can handle a large volume of mail. Operating System: Linux, Unix, OS X, Solaris.
648.
Scalix Aimed at hosting providers and ISPs as well as enterprises and small businesses, Scalix offers an alternative to Microsoft Exchange servers for group e-mail and calendaring. It comes in numerous flavors, including the community, enterprise, small business and hosting editions. Operating System: Linux.
649.
Sendmail While it's not as widely used as it once was, Sendmail continues to be a very popular mail transfer agent. Newer features include support for filters, authentication and external database look-ups. Operating System: Linux.
650.
SOGo SOGo is a groupware server that allows users to access e-mail and shared calendar data via the Web, a BlackBerry device, or an e-mail client like Thunderbird. The latest version adds native Outlook support. Operating System: OS Independent.
651.
Zimbra Zimbra's open source edition provides an alternative to Microsoft Exchange, with e-mail, shared calendar, contact and document management capabilities that can be accessed from a variety of desktop clients. The company also offers a free desktop client of its own, plus paid network or appliance versions. Operating System: Linux, Unix, OS X.
Mapping
652.
OpenLayers This alternative to Google Maps and Bing Maps provides free APIs that can put dynamic, JavaScript-based maps on any website. It's sponsored by the Open Source Geospatial Foundation. Operating System: OS Independent.
Math
653.
Apophysis If you're a math geek, you probably know what fractal flames are. If not, it's probably enough to know that this app lets you create and edit very strange algorithmically generated images. Operating System: Windows.
654.
Dr. Geo The award-winning Dr. Geo helps both elementary (age 10 and up) and more advanced students learn basic geometric principles by interacting with geometric shapes. Check out the video on the website to see it in action. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
655.
Genius Like Sage and Mathematica, Genius solves a wide of math problems, including calculus, statistics, trigonometric functions, modular arithmetic and more. It can also generate 2D and 3D graphs and output to TeX documents. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
656.
GeoGebra GeoGebra combines tools for learning dynamic geometry, algebra and calculus. It offers an intuitive GUI and a video tutorial which make it a little more user friendly than some of the similar math apps. Operating System: OS Independent
657.
gnuplot If you're comfortable working from the command line, you can use gnuplot to create 2D and 3D graphs of mathematical functions. Extensive help is available on the website, and there's even a book on Gnuplot that you can buy. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X, and others.
658.
GraphCalc Why buy a handheld graphing calculator, when GraphCalc will do all the same things (and more) for free. According to the website, "GraphCalc can be your first, last, and only line of offense against the mathematics that threaten to push you over the brink of insanity. It slices, dices, shreds and purees functions that leave other calculators wondering what hit them." Operating System: Windows, Linux.
659.
Kig This KDE app for geometry students and teacher makes it easy to draw and explore geometric shapes. It can also import files from Dr. Geo and Cabri. (Note that in order to use Kig on Windows, you'll have to download
KDE for Windows.) Operating System: Windows, Linux.
660.
Mandelbulber If you're geeky enough to know what a Mandelbulb is, you might enjoy this app which renders 3D fractals. More information about the app can also be found on the
FractalForums site. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
661.
Maxima This "computer algebra system," handles differentiation, integration, Taylor series, Laplace transforms, ordinary differential equations, systems of linear equations, polynomials, and sets, lists, vectors, matrices, tensors, and more. It also creates 2D and 3D graphs of mathematical functions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
662.
Sage Built from 100 different open source packages, Sage can perform a wide variety of mathematical operations from basic algebra and calculus to very advanced number theory, cryptography, exact linear algebra and more. To get the most out of its features, you'll need to be comfortable working from the command line and know the Python programming language. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
663.
Scilab Another good replacement for MATLAB, Scilab can perform hundreds of mathematical functions as well as generating 2D and 3D graphs. Commercial services and support are available through
Scilab Enterprises. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
664.
TTCalc If you need to work with numbers that are too big for the standard Windows calculator to handle, TTCalc is the solution. It includes most arithmetic and trigonometric functions, and it's accurate to 306 valid decimal digits. Operating System: Windows.
665.
Ultimate Calc This scientific and graphing calculator solves complex equations and offers an easy-to-use interface. It supports plug-ins and scripts to extend its capabilities. Operating System: Windows.
Microfinance
666.
Mifos This Web-based management information system (MIS) aims to help microfinance institutions streamline their operation. It offers portfolio and transaction management, on-the-fly financial product creation, in-depth client management, integrated social performance measurement, and a reporting engine. Operating System: OS Independent.
667.
Octopus Rated as "one of the most user-friendly solution with highly ergonomic windows display" by the World Bank/CGAP, Octopus offers a robust, secure MIS for microfinance organizations. It's available both in a free community version or a supported professional edition. Operating System: Windows.,?p>
Middleware
668.
JBoss Used by companies like Priceline.com, GEICO and NYSE Euronext, RedHat's JBoss line of middleware includes an application platform, Web platform, messaging, SOA platform, business rules management system and much more. All of the tools are available in open source and enterprise versions. Operating System: Linux.
Mind Mapper
669.
FreeMind This open source mind mapper program makes it easy to display the links between ideas. It's great for making outlines, brainstorming, making notes and more. Operating System: OS Independent.
670.
FreePlane This fork of FreeMind (see above) has been racking up thousands of downloads. It offers traditional mind-mapping features, plus some advanced functionality. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
671.
The Guide This tool lets you organize your notes in a hierarchical, tree-based format. It's similar to a mind mapper, but not as complex. Operating System: Windows.
672.
XMind Ideal for brainstorming and planning sessions, XMind makes it easy to see the connections between ideas—it's sort of like a white board for your computer. In addition to the free version, it comes in a pro version for individuals and an enterprise version for businesses. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Mobility Tools
673.
Akamai Mobitest Want to know how quickly your website will load on an iPhone 4 in Cambridge, Mass.? This testing tool lets you check website performance on various smartphones in different locations. You can use it for free directly from the website or download the source code and run it from your own server. Operating System: OS Independent.
674.
F-Droid This collection makes it easy to download and stay up to date with dozens of open source apps for Android. It provides details about all of the versions of the apps that are available and allows you to choose which apps you use. Operating System: Android.
675.
ForgeRock ForgeRock offers a platform of mobile identity management solutions for enterprises. The tools are also available on a subscription basis, which adds support and real-time access to software updates. Operating System: Linux.
676.
Funambol The open source Funambol software is a client-server solution for syncing contacts, calendars, tasks and notes. The company also offers commercial, cloud-based syncing solutions for mobile operators and personal use. Operating System: Android, iOS, Windows Mobile, Symbian.
677.
Knappsack This mobile application management platform offers tools for securely uploading, managing and sharing apps among a group of users. The open source version is free, and the company also offers both free and paid hosted versions. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS, Android.
678.
OpenMobster OpenMobster offers an open source mobile backed-as-a-service for enterprises and includes capabilities like syncing, HTML5 hybrid app development tools(based on PhoneGap) and push notifications. Fee-based consulting and integration services are also available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
679.
mAdserve The self-proclaimed "world's most powerful open source ad server," mAdserve offers tools for managing ad campaigns across 30 different ad networks. Premium services are also available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS, Android.
680.
QuincyKit This helpful kit collects and reports crash data and user feedback on your mobile apps. It's also available as a hosted service from
HockeyApp. Operating System: OS X, iOS.
Modeling
681.
ArgoUML The self-proclaimed "leading open source UML modeling tool" supports all standard UML 1.4 diagrams and comes in 10 different languages. Because it's based on Java, it runs on any platform, and it can export diagrams in six different file formats. Operating System: OS Independent.
682.
StarUML Designed as an alternative to Rational Rose and other commercial modeling tools, StarUML supports both the latest UML standards and Model Driven Architecture (MDA). It's very user-friendly and features a plug-in architecture. Operating System: Windows.
683.
Modelio The code behind Modelio has actually been in development for more than 20 years, but parent company Modeliosoft just recently released it under an open source license. It offers a UML modeler, BPMN support, Java code generator, and support for XML, HTML and Jython. Operating System: Windows, Linux
Multimedia Tools
684.
Ampache Want to set up your own streaming server? Ampache makes it easy and affordable and allows you to access your music and videos from any Internet-connect device. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
685.
AmpJuke While most of the other options on our list stream both audio and video files, AmpJuke focuses on music. It also connects to various Web services in order to provide lyrics, album covers and other data related to the songs being played. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
686.
AVStoDVD This helpful tool can convert various multimedia file types to DVD-ready formats and then burn them to DVDs. It supports multiple tracks and offers some audio and video editing capabilities. Operating System: Windows.
687.
Banshee Banshee can sync your multimedia library with your mobile device, connect with the Amazon store, play podcasts and Internet radio, shuffle smartly and retrieve cover art from the Internet. It also offers optional Last.fm integration, eMusic integration, import from iTunes and other services, and minimode. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android, iOS.
688.
Burn For Macs only, this burning tool can create data, audio or video CDs and DVDs. It can also copy discs, even if you only have a single optical drive. Operating System: OS X.
689.
CamStudio Many individuals and organizations need to make demonstration videos on occasion, but commercial screen video capture software can be very expensive. CamStudio can record your system's on-screen and audio activities, plus it offers some basic editing capabilities. Operating System: Windows.
690.
Darwin Streaming Server Based on the same code as the QuickTime Streaming Server, Darwin was also developed by Apple. It can stream live or pre-recorded content using RTP/RTSP protocols. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
691.
Data Crow If your resolution involved organizing a large collection of CDs, DVDs, books or other stuff, Data Crow can help. This self-proclaimed "ultimate media cataloger" connects to online services to provide detailed data about the items in your library, and it even includes a feature to help you keep track of who borrowed your things. Operating System: OS Independent.
692.
DVDStyler This app aims to make it easy for anyone to create professional-looking DVDs, complete with interactive menus. It includes tools for adding subtitles, mixing multiple audio tracks and creating photo slideshows. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
693.
FFmpeg More than just an audio and video player, FFmpeg also includes tools for recording, converting and streaming multimedia files. It humbly claims to be "the leading multimedia framework, able to decode, encode, transcode, mux, demux, stream, filter and play pretty much anything that humans and machines have created." Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
694.
InfraRecorder This Windows-only CD and DVD burner integrates directly into Windows Explorer. It can create audio, data or mixed-mode discs, and it offers four different methods for erasing rewritable media. Operating System: Windows.
695.
kPlaylist KPlaylist was also designed with music streaming in mind, but it can support both audio and video files. Features include multi-user support with authentication, Flash player support, Shoutcast support, randomizer function, shared playlists and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
696.
Krut Computer Recorder Java-based Krut can record screen video from nearly any system. Key features include timer control, the ability to move recording areas, two choices for frame rates and highly accurate audio/video synchronization. Operating System: Windows, Linux OS X.
697.
Media Converter This Mac-only converter supports avi, wmv, mkv, rm, mov and several other file types. A lot of its code is based on the Burn CD burning software (see above). Operating System: OS X.
698.
MediaInfo MediaInfo finds tags and technical data for audio and video files, as well as some text files. It supplies the title, artist, director, number of tracks, and much, much more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, and others.
699.
Media Player Classic Home Cinema This lightweight, customizable player looks and feels like older version of Windows Media Player. It supports numerous file types, and it has been translated into 23 languages. Operating System: Windows.
700.
MediaPortal Similar to XBMC, Media Portal also supports HTPCs and even turns ordinary PCs into advanced media centers. In addition to playing CDs, DVDs, multimedia files and streaming content, it lets you watch, schedule and record live TV like a TiVo, and it also works with most remote controls. Operating System: Windows.
701.
Miro This very attractive media player works on iOS and Android devices, including the Kindle Fire, as well as desktops. It offers easy import from iTunes, connections to Amazon and Google stores, conversion capabilities, sharing and very fast Torrent downloads. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android, iPad.
702.
Mplayer This award-winning player also supports a long list of audio and video file types and codes. The standard edition is a command-line tool for Linux, but variations are available for other operating system, and there are also GUI front-ends available. Operating system: Linux.
703.
Subsonic Subsonic can function as a streaming media server or a local jukebox. With apps available for Android, iPhone, Windows Phone, BlackBerry, Roku, PlayBook and others, it's easy to take your music and movies with your wherever you go. And if you don't have a server of your own, hosting services are also available. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android, iOS, Windows Phone, BlackBerry, Roku, others.
704.
Totem The official movie player for the Gnome desktop, Totem boasts features like playlists, full-screen mode, seek, volume control, keyboard navigation and a nautilus properties tab. It also includes a Firefox plug-in for watching movies through your browser. Operating System: Linux.
705.
UMPlayer The "Universal Media Player," UMPlayer includes more than 270 built-in codecs, so it can play nearly every kind of file, including incomplete or damaged files. Advanced features include a skinnable interface, subtitles search and sync, and a YouTube player and recording tool. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
706.
VideoLAN From the creators of the VLC Media Player, this is another option for setting up an audio/video streaming server. Like the Media Player, it supports a wide array of file formats. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
707.
VLC Media Player This very popular open source app can play most streaming video and media files, audio CDs, DVDs and more. It comes with a skinnable interface or it can run from the command line, and it supports tags, subtitles and closed captioning. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others.
708.
Webinaria In addition to downloadable screen capture software, this website also offers the opportunity to share your own creations and view other people's webinars and tutorials. A built-in rating system and discussion capabilities makes the site even more interesting. Operating System: Windows, Linux OS X.
709.
Wwidd Wwidd describes itself as "Del.icio.us for your video collection." It makes it easy to organize, tag and search your video library, and it integrates with VLC for playback. (Note that the source code is available through
GitHub. Operating System: Windows, OS X, Linux.
710.
XBMC Media Center This media player was designed to work with home theater PCs (HTPCs). It offers an attractive interface, support for most remote controls, support for most popular audio and video formats, and playlist and slideshow capabilities. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
711.
xine Xine also plays an impressive list of multimedia formats. It features a skinnable interface, extensible architecture, fast performance, navigation controls, playlists, image snapshots, aspect ratio conversion, full-screen mode and much more. Operating System: OS X, Linux.
Multiple Function Security Solutions
712.
ASEF Short for "Android Security Evaluation Framework," ASEF analyzes Android apps from a security standpoint. It can test multiple apps at once to determine if they include malware or aggressive adware or if they are using excessive amounts of bandwidth. Operating System: Android.
713.
Csipsimple Csipsimple offers secure calling and SIP features for Android devices. Video calling features are currently under development. Operating System: Android.
714.
The Guardian Project This project has developed multiple security-focused Android apps, including Orbot (a version of Tor for secure mobile Web browsing), Orweb (an enhanced browser that supports proxies), Gibberbot (private, secure IM), OscuraCam (private, secure camera app) and Ostel (encrypted phone calls). Operating System: Android.
715.
Network Security Toolkit (NST) Like INSERT, NST includes a whole lot of tools and a complete Linux distribution that fits on a CD-ROM. In this case, you get nearly 100 tools and the Linux copy is based on Fedora. Operating System: OS Independent.
716.
Security and Privacy Complete This app gives you control over a number of system settings and settings for Windows Media Player, Internet Explorer, and Firefox. A handy tooltip feature lets you know what each function does and why you might want to enable or disable it. Operating System: Windows.
Music Education
717.
GNU Solfege You might not have been born with perfect pitch, but you can get better with practice. This app will help you improve your ability to identify and sing intervals, chords, scales and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
718.
Impro-Visor Sometimes you get one really great line or phrase for a song, but just can't get the rest. The Impro-Visor can help you finish your composition by suggesting improvisations and solos built on your theme. (It's also a valuable educational tool for aspiring jazz musicians.) Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
719.
LenMus Phonascus Phonascus is a music theory and aural (ear) training program for musicians of all levels. It includes a wide variety of audio and written exercises, as well as a score editor for composing your own works. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
720.
ScoreDate First, let's make it clear that this app is not at all about dating—the "score" refers to musical scores. ScoreDate aims to teach anyone the basics of reading music. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Network/System Firewalls
721.
Devil-Linux Devil-Linux originated as a hardened version of Linux meant for use as a firewall/router. However, now it can also be used as an application server, as well as a network firewall. Operating System: Linux.
722.
Droidwall As you might guess from the name, Droidwall is a firewall for Android devices. It's based on IPtables and can also help you improve your battery life. Note that this app requires root access. Operating System: Android.
723.
FireHOL FireHOL describes itself as "a language to express firewalling rules." It lets you configure an iptables based firewall using four basic commands. Operating System: Linux.
724.
Firestarter Unlike most of the open-source firewalls, Firestarter can protect a single PC, as well as a network. Best of all, you can probably install it and be up and running in just a couple of minutes. Operating System: Linux.
725.
IPCop Aimed at home or SOHO users, IPCop also helps users configure a system as a Linux firewall for their network. Unlike some of the other Linux firewall options, it features a user-friendly Web-based interface. Operating System: Linux.
726.
LEAF The "Linux Embedded Appliance Framework" (aka LEAF) can be used as an Internet gateway, router, firewall, or wireless access point. This app requires a little more know-how than some of the other choices in the category, but is still a good option. Operating System: Linux.
727.
m0n0wall While most of the firewalls on our list run on Linux, this one runs on BSD. It was designed for appliances, but it can also be used on standard PCs. Operating System: FreeBSD.
728.
pfSense Downloaded more than 1 million times, this m0n0wall fork was designed for use on standard PCs. It functions as a firewall and a router for enterprise networks, small home networks and everything in between. Operating System: FreeBSD.
729.
Sentry Firewall This app can operate as a network firewall, server or IDS node. It boots directly from a CD, making it very easy to set up a firewall quickly. Operating System: Linux.
730.
ShellTer An iptables-based firewall, ShellTer offers quite a bit of customization capability. Features include port forwarding, blacklisting, whitelisting, and more. Operating System: Linux.
731.
Shorewall Another iptables-based firewall, Shorewall can be used on a PC used as a dedicated firewall, a multi-function gateway/router/server or on a standalone GNU/Linux system. It doesn't claim to be the easiest Linux firewall to use, but it does claim to be the most flexible and the most powerful. Operating System: Linux.
732.
Smoothwall You'll find the open source version of this firewall, Smoothwall Express, at
Smoothwall.org. At the main corporate site, Smoothwall offers more complete security and Web filtering products that incorporate the open source firewall. Operating System: Linux, Unix.
733.
Turtle Firewall Turtle allows administrators to configure iptables to set up a Linux-based firewall. It includes a Web interface, or you can directly modify XML files. Operating System: Linux.
734.
Vuurmuur Yet another iptables firewall, Vuurmuur boasts a simple-to-learn configuration tool that allows for very complex setups. Features include secure remote administration, traffic shaping and powerful monitoring capabilities. Operating System: Linux.
Network Management
735.
CloseTheDoor This tool allows network and security managers to identify all listening ports for their listening ports for IPv4 and IPv6 networks. It provides information and allows you to shut down remote attacks. Operating System: Windows.
736.
OpenNMS The "world's first open source, enterprise grade network management application platform," OpenNMS has been helping administrators monitor their networks for more than a decade. It's highly customizable and highly scalable, and it offers automated and directed discovery and provisioning, event and notification management, service assurance, and performance measurement capabilities. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, iOS.
737.
RANCID Short for "Really Awesome New Cisco confIg Differ," RANCID discovers and tracks configuration details for routers and other devices. It supports a variety of hardware, including Cisco routers, Juniper routers, Catalyst switches, Foundry switches, Redback NASs, and ADC EZT3 muxes. Operating System: Linux.
738.
Zenoss Zenoss helps IT departments monitor and manage their networks, applications and servers, and it includes support for virtualized and cloud environments. Commercial products based on the open source community version are available through
Zenoss, Inc. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
Network Monitoring/Scanning/Intrusion Detection
739.
AFICK Short for "Another File Integrity Checker," AFICK also offers very similar functionality to Tripwire. It quickly scans files and lets you know when data has changed.. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
740.
Cacti Cacti takes information from RRDtool and uses it produce more advanced graphs. It also offers an intuitive interface and some management capabilities. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
741.
Ganglia While most of the tools on our list are designed for run-of-the-mill networks, this tool from the University of California, Berkeley Millennium Project monitors high-performance computing systems such as clusters and grids. It's been around since 2000, and it's currently used on thousands of clusters around the world. Operating System: Linux, others.
742.
Kismet Kismet is a combination wireless network detector, packet sniffer, and IDS. Often used to detect unprotected or hidden networks, it's a valuable tool for checking the security of your wireless network, as well as monitoring network activity. Operating System: Windows, Mac, Linux, Unix, BSD
743.
Knocker This simple TCP security port scanner works on multiple platforms and is easy to use. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix.
744.
Munin Named for a Norse god of memory, Munin aims to help network administrators analyze trends and figure out why performance problems occur. It offers a Web interface, easy installation and easy use. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
745.
Nagios The self-described "industry standard in IT infrastructure monitoring," Nagios helps users "achieve instant awareness of IT infrastructure problems," by monitoring servers, switches, applications, and services. The link above will take you to the open source version; enterprise versions can be found at
Nagios.com. Operating system: Linux, Unix.
746.
NDT Short for "Network Diagnostic Tool," NDT is a client/server app that offers network performance testing. It can help identify problems such as duplex mismatch conditions on Ethernet/FastEthernet links, incorrectly set TCP buffers in the user’s computer, or problems with the local network infrastructure. Operating System: Linux.
747.
Net-SNMP This set of applications implements SNMP v1, SNMP v2c and SNMP v3 protocols for both IPv4 and IPv6. These are command line tools, so they're not quite as user friendly as some of the other network monitoring applications. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
748.
NSAT Short for "Network Security Analysis Tool," NSAT performs bulk scans for 50 different services and hundreds of vulnerabilities. It provides professional-grade penetration testing and comprehensive auditing. Operating System: Linux, Unix, FreeBSD, OS X.
749.
Open Source Tripwire Back in 2000, Tripwire released an open source version of its network monitoring software, and development on that project has continued since then. Like the commercial version of Tripwire, it alerts administrators when changes occur in specified files on your network. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
750.
Opsview With Opsview, enterprises can monitor their cloud, physical and hybrid infrastructure all from a single tool. It comes in both a free community download or a paid enterprise version, with an optional mobile module and other services available. Operating System: Linux.
751.
OSSEC In addition to file integrity checking, OSSEC also performs log analysis, policy monitoring, rootkit detection and real-time alerting to help prevent and detect intrusions into your network. It's downloaded more than 5,000 times per month and has won numerous awards. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
752.
Pandora FMS This "Flexible Monitoring Solution" can be set up to track anything from network status to website defacement to stock market trends. It generates real-time graphs, sends custom alerts, creates SLA reports and much more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
753.
RRDTool RRDtool calls itself "the open source industry standard, high performance data logging and graphing system for time series data." It's been incorporated into numerous other networking tools, including Endian and Cacti Operating System: Windows, Linux.
754.
SEC Although we put this app in the Network Monitoring category, the Simple Event Coordinator (SEC) actually works with many different applications. To use it, you set up a set of rules that specify what actions you want to occur whenever a particular event occurs. Operating System: OS Independent.
755.
SniffDet This tool implements a number of different open-source tests to see if any of the machines in your network are running in promiscuous mode or with a sniffer. Note that some of the documentation for this app is in Portuguese. Operating System: Linux.
756.
Snort With millions of downloads and more than 400,000 registered users, Snort claims to be "the most widely deployed IDS/IPS technology worldwide." Operating System: Windows, Linux OS X.
757.
tcpdump Although it lacks a user-friendly GUI, this command-line tool offers powerful packet analysis capabilities. Not that the same site also features the libpcap library for network traffic capture. Operating System: Linux.
758.
WinDump This is the version you'll need if you want to run tcpdump on Windows. It also includes the WinPcap library and drivers for traffic capture. Operating System: Windows.
759.
Wireshark The "world's foremost network protocol analyzer," Wireshark allows administrators to capture network traffic and browse it interactively. Features include deep inspection of hundreds of protocols, live capture and offline analysis, powerful display filters, VoIP analysis and much more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
760.
WinDump Managed by Riverbed Technology (which also owns Wireshark), WinDump ports tcpdump to the Windows platform. This site also includes the WinPcap library and drivers for traffic capture. Operating System: Windows.
761.
Zabbix Calling itself "the enterprise-class monitoring solution for everyone," Zabbix can monitor up to 100,000 networked devices for 1 million metrics, performing thousands of checks per second. It's completely open source, but Zabbix does offer paid support and other services. Operating System: Windows (agent only), Linux, OS X.
Network Simulation
762.
GNS3 This tool allows network engineers and administrators to simulate complex systems in order to design networks or to study for certification exams. There's a tutorial and extensive documentation on the site to help new users learn how to use the application. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Office Productivity
763.
AbiWord Similar to older versions of Word, AbiWord reads and writes most word processing document formats, including OpenOffice and Word formats, and it offers some advanced layout and mail merge capabilities. The latest version adds a lot of collaboration capabilities, and it integrates tightly with the free
AbiCollab.net service which allows users to store and edit documents in the cloud. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others
764.
Edhita Edhita is a simple text editor for iPad only. It doesn't have advanced word processing capabilities or the highlighting features you would see in a good code editor, but it does a solid job of text editing. Operating System: iPad.
765.
Gnumeric Gnumeric describes itself as "free, fast and accurate," and an outside reviewer has praised it as more accurate than its commercial competitors. It opens files from most other popular spreadsheet programs (including Excel and Lotus), and it offers 583 different functions, including 194 you can only find in Gnumeric. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
766.
KOffice KDE's office productivity suite includes the KWord word processor, KCells spreadsheet, Showcase presentations, Kivio diagrams and flowcharts and the Artwork vector drawing program. The interfaces are intuitive but significantly different than Microsoft Office's interfaces, so they take a little getting used to. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
767.
LibreOffice When Oracle took over OpenOffice.org (see below), a group started this fork to continue community development. It offers all the same great features and capabilities of OpenOffice.org, plus a few improvements all its own. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
768.
LyX LyX lets you format your document based on its structure. You mark text as a title, subtitle, etc., and then worry about the formatting later. It makes it easier to ensure continuity throughout long documents and deal with some of the difficulty of creating a document on a netbook or other device with a very small screen. Operating System: Linux, Unix, Windows, OS X.
769.
NeoOffice Also very similar to OpenOffice.org (see below), NeoOffice offers an interface and features tailored for Mac users. The latest update supports Mac's versions, full-screen mode and resume features. Operating System: OS X.
770.
OI Notepad This note-taking app allows users to create, edit and share notes with other users. It also has an extension that allows users to add audio to the text. Operating System: Android.
771.
OpenOffice.org Now an Apache project, OpenOffice.org includes Microsoft-compatible word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, graphics and database software. At twenty years old, it's a mature project with all of the advanced capabilities and stability that home or business users need. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, others
772.
OpenOffice Document Reader This helpful app lets you view and read OpenOffice and LibreOffice documents from Android devices. It doesn't have editing capabilities, but does support spreadsheets. Operating System: Android.
773.
Sparklines for Excel Sparklines doesn't replace Excel--it extends its functionality with new functions that create simple, intense graphics known as Sparklines. See the user manuals for examples of the type of charts and graphs it can create. Operating System: Windows.
774.
Text Edit This simple text editor lets you write, edit and save short documents on your Android phone. You can select the font size and type, change colors and e-mail the documents you create. Operating System: Android.
775.
VuDroid With VuDroid, users can view PDF and DJVU documents from their Android devices. Features include zoom by slider drag, fast orientation change and more. Operating System: Android.
776.
WriteType If your children use your home office PC to write school reports (and of course, they do), you may want to check out WriteType. It's a word processor with special features for young students, like word completion, read back, highlighting, grammar and spell check, and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
777.
X-OOo4Kids OpenOffice.org for Kids offers a simplified version of OpenOffice.org designed to be used by those aged 7-12. The advantage of this version, even if you're not a kid, is that it loads and runs very quickly and requires very little space on your portable drive. Operating System: Windows.
Online Data Storage
778.
FTPbox FTPbox makes it easy to sync your files across multiple devices or share your files with others. It can use SFTP or FTPS protocol for secure file transmission. Operating System: Windows.
779.
iFolder Built with syncing, backup and file sharing in mind, iFolder works much like DropBox. Simple save your files locally as usually, and iFolder will update them on your server and the other workstations you use. It was originally founded by Novell and is now managed by Kablink. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
780.
SparkleShare Because it was built for developers, this
online storage solution includes version control software (Git, to be specific). It automatically syncs all files with the hosts, and it allows you to set up multiple projects with different hosts. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
781.
Syncany Syncany works with commercial
online storage solutions like Amazon S3 or Google Storage, adding better synchronization functionality (akin to DropBox) and improved security. It encrypts files locally, making it more feasible to use an online service to store sensitive data. Operating System: Linux (Windows and OS X versions planned.)
Online education/eLearning
782.
ATutor This standards-based course management system has been used by many educational institutions to create award-winning websites. It was designed with an emphasis on accessibility and is very easy to use. Operating System: OS Independent.
783.
Canvas Instructure's Canvas learning management system helps teachers and parents track the academic progress of K-12 students. The link above connects with the commercial and cloud versions, but you can download the source code from
GitHub. Operating System: Linux, Unix, OS X.
784.
Chamilo After just 18 months in existence, this open source learning management system racked up half a million users. The website includes a helpful demo so that you can try the software out before downloading. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X.
785.
Claroline Claroline has a very international community, with users in 93 different countries. It allows instructors to publish documents in nearly any format, and it's designed to foster collaborative learning. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
786.
CoFFEE Short for "Collaborative Face-to-Face Educational Environment," CoFFEE aims to help groups of students work together on problem-solving activities. It includes a set of tools for collaboration, shared work, individual work, and communication that can be managed and monitored by the instructor. Operating System: OS Independent.
787.
eFront Designed to be easy-to-use and visually appealing, eFront offers a very polished interface and all of the capabilities you would expect in an online course management system. In addition to the free version, it's also available in commercially supported versions with special features for educational institutions or enterprises. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
788.
ILIAS Another international favorite, the ILIAS website includes links to organizations using ILIAS in 20 different countries. It's standards-based and includes features like webcasting, tests and assessments, support for multiple authentication methods, a SOAP interface, online surveys, integration with Google maps and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
789.
Moodle One of the most popular online course management systems, Moodle currently has more than 43 million users accessing course content on more than 53,000 sites. It includes modules for wikis, forums, databases, assessments, document delivery and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
790.
Sakai Originally sponsored by Stanford, the University of Michigan, Indiana University and MIT, the Sakai CLE (collaboration and learning environment) is now used by more than 350 institutions. It is a combination learning management system, research collaboration system and ePortfolio solution. The source code is available for free, or you can purchase access to a hosted version through Sakai's commercial affiliates. Operating System: OS Independent.
OpenCourseWare
791.
eduCommons A number of universities around the world aren't just utilizing open-source software, they're "open-sourcing" the content of their courses by making it freely available online. EduCommons is a content management system designed for these OpenCourseWare projects. Operating System: OS Independent.
792.
OpenCourseWare The Open Courseware Consortium offers links to hundreds of "open source" university classes. Study nearly any subject you want with materials from institutions like MIT, Johns Hopkins, University of Michigan, University of California and dozens of others. Operating System: OS Independent.
Operating Systems and Kernel Modifications
793.
aLinux Formerly known as Peanut Linux, aLinux is designed to be both fast and multimedia-friendly. Its graphic interface provides an easy transition for former Windows users.
794.
andLinux A good option for Windows users who would like to try out some Linux applications, andLinux runs Linux applications on Windows 2000, 2003, XP, Vista, or 7 machines.
795.
Android Currently the most popular mobile operating system available, Google's Android is an open source project. Numerous manufacturers, including Samsung, LG, HTC and Motorola, offer Android-based smartphones and tablets.
796.
ArchBang This Arch variant uses the Openbox Window Manager. It's fast and lightweight, and offers many of the same customization capabilities as Arch.
797.
Arch Linux Arch is definitely not for Linux newbies, but its simple design makes it a favorite among long-time Linux users who are comfortable with the command line. By default, it installs a minimal base system but provides plenty of options for customization.
798.
Bodhi Linux Bodhi puts the focus on user choice and minimalism. It uses the Enlightenment desktop environment and a "software store" that makes it easy to find and install the open source applications you want to use.
799.
CentOS Short for "Community ENTerprise Operating System," CentOS is based primarily on Red Hat code. It's the most popular version of Linux for Web servers, accounting for about 30 percent of Linux-based Web servers.
800.
Chakra Based on ArchLinux, Chakra uses the KDE desktop. It uses a unique "bundles" system to let users access Gtk apps without actually installing them on the system.
801.
Chrome OS/Chromium OS Google's operating system goes by two names, which can make things confusing. Officially, "Chromium OS" is the open source version used primarily by developers, and "Chrome OS" is the name for the version of the operating system Google plans to include on netbooks for end users. And just to make things even more confusing, both projects share a name with Google's Web browser. For now, Chromium OS (the only version available for download) is really only suitable for advanced users and developers.
802.
CrunchBang Sometimes written #!, CrunchBang is a lightweight distribution based on Debian. It's a popular option for netbooks like the Asus Eee.
803.
Debian The basis for Ubuntu and several other Linux distributions, Debian is popular with hard-core open source enthusiasts. It includes more than 29,000 pre-compiled software packages. Operating System: Linux, FreeBSD
804.
DSL At just 50MB, this distro lives up to its name – Damn Small Linux (DSL). As you might expect, it's very fast and runs on older PCs, as well as fitting onto small USB drives and business card CDs.
805.
EasyPeasy Designed as a cloud OS, EasyPeasy is a very lean version of Linux that's ideal for netbooks or other devices used primarily to access the Internet. It offers low power consumption, social networking integration and more.
806.
Edubuntu This version of Ubuntu Linux was specifically designed for use in schools. It includes many of the education-related applications on this list, including the KDE education apps, GCompris and School Tool.
807.
eyeOS Built for cloud computing, eyeOS makes an entire desktop, including office productivity applications, accessible from a Web browser. It also serves as a platform for creating new Web apps.
808.
Fedora If you'd like to try
Red Hat Linux without paying the subscription fees, Fedora is a free community project based on the same code. It comes in several "spins" that are customized for the needs of gamers, engineers, designers or security professionals.
809.
Firefox OS Made by Mozilla, the group behind the Firefox browser, the Firefox OS promises to incorporate new Web standards and "free mobile platforms from the encumbrances of the rules and restrictions of existing proprietary platforms." The operating system isn't available on any handsets yet, but Mozilla has released an emulator that lets you try out the OS from a Web browser.
810.
Frugalware Like Slackware, Frugalware is best for users who aren't afraid of the command line, although it does have some graphical tools. It's designed with simplicity in mind.
811.
Fusion Fusion describes itself as a "pimp my ride" version of Fedora. It offers good multimedia support and an interesting look and feel. It's best for more advanced Linux users who are looking for cutting edge, experimental applications.
812.
Gentoo First released in 2002, Gentoo boasts "extreme configurability, performance and a top-notch user and developer community." It uses the Portage package management system, which currently includes more than 10,000 different applications.
813.
GoboLinux GoboLinux's claim to fame is that is doesn't use the Unix Filesystem Hierarchy Standard, but instead stores each program in its own sub-directory in the Program directory. That means that it's a little bit easier to use for Linux newbies or experienced Linux users who like to install applications from the original source code.
814.
gNewSense Supported by the Free Software Foundation, gNewSense is based on Ubuntu with a few changes, like the removal of non-free firmware. The name started as a pun on "Gnu" and "nuisance" and is pronounced guh-NEW-sense.
815.
Illumos When Oracle discontinued development of OpenSolaris, some of the developers who had been working on the project forked it to the Illumos project, where development and bug fixes continue. If you are looking for a free version of Solaris, this is the option for you. To download the software, visit the OpenIndiana page above.
816.
Joli OS Joli OS describes itself as "the ultimate desktop for the cloud." It aims to bring new life to old PCs with an extremely simple-to-use version of Linux that comes with 1,500 apps. It's used on more than 750,000 systems.
817.
Knoppix Suitable for beginners, Knoppix is an easy-to-use distribution based on Debian. It runs from a live CD, and if you don't want to go to the trouble to burn your own (or you don't know how), you can buy one for less than two bucks.
818.
Kubuntu As the name suggests, Kubuntu is a Ubuntu fork that uses the KDE desktop instead of the Unity desktop. It's an excellent choice for new Linux users.
819.
Linux Mint The fourth most popular home operating system, Linux Mint offers great ease of use for those new to Linux. It's based on Debian and Ubuntu and comes with a library of 30,000 free software applications
820.
Lubuntu Lubuntu is lighter, faster, and uses less energy than its namesake, making it a good choice for mobile devices, including netbooks. It uses the LXDE desktop instead of the Unity desktop.
821.
Mageia In 2010, a group of Mandriva developers began this community-driven fork following some ownership changes at the company that owns the Mandriva project. It's currently in beta, but the first official release is due in a few weeks.
822.
Mandriva Owned by a publicly traded French company, Mandriva claims more than 3 million users worldwide. It's available in several editions, desktop and server, paid and unpaid, including a unique Instant On version that boots up with minimal functionality in less than 10 seconds
823.
MEPIS Debian-based MEPIS (also known as simplyMEPIS) is particularly popular with those new to Linux. It's available in free downloadable versions, or you can purchase a CD which makes trying or installing the software easy.
824.
Musix GNU+Linux As its name implies, Musix is geared for multi-media enthusiasts, particularly those involved in audio editing. It can boot from a live disk or be installed on a system.
825.
openSUSE A free, community version of Novell's
SUSE, openSUSE describes itself as "Linux for open minds." It comes in desktop and server versions, and it includes 1,000 applications.
826.
PCLinuxOS Designed to be easy to use, PCLinuxOS can be run on a Live CD or installed on a desktop or laptop. It supports seven different desktops, including KDE, Gnome, Enlightenment, XFCE, LXDE, and others.
827.
Peppermint Another Linux distribution designed to be cloud- and Web-centric, Peppermint boasts that it is "sleek, user friendly and insanely fast." With a very small footprint, it loads and shuts down very quickly, and you don't have to be an uber-geek to use it.
828.
Pinguy OS Built for new Linux users who need something that's even easier to use than Ubuntu, Pinguy OS makes it easy to find and use the programs average users need most often. It's also available in a DVD version for $5.99.
829.
Puppy Linux Small and fast, Puppy is designed to be installed on a USB thumb drive that users can take with them and boot from any PC. It takes up about 100 MB, boots in less than a minute, and runs from RAM for maximum speed.
830.
Red Hat Probably the best known flavor of Linux, Red Hat comes in desktop and server versions that are suitable for enterprise users. Red Hat's software requires a paid support contract, or you can download the community version for free from
Fedora.
831.
Sabayon Named after an Italian dessert, Sabayon aims to be the "cutest" Linux distribution — "as easy as an abacus, as fast as a Segway." It's based on Gentoo, and it supports the KDE, Gnome, LXDE and Xfce desktop environments.
832.
Salix OS Salix compares itself to a bonsai tree in that it is "small, light and the product of infinite care." It comes in four different versions for the Xfce, LXDE, Fluxbox and KDE desktop environments.
833.
Scientific Linux Created by the folks at the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory and the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), as well as various scientists and universities, Scientific Linux (SL) aims to prevent scientists at each of these different institutions from having to recreate a Linux distribution that meets their needs. It's basically the same as Red Hat Enterprise Linux with a few slight modifications.
834.
Slackware First released in 1993, Slackware is one of the oldest Linux distributions. Popular with the geekiest of geeks, it relies heavily on command-line tools and is very similar to UNIX.
835.
SUSE Like Red Hat, SUSE is designed for enterprise users and requires a support contract. However, also like Red Hat, a free community version is available through
openSUSE.
836.
Tiny Core Linux One of the smallest Linux distros available, Tiny Core weighs in at just 10MB in its GUI version. The command line version, Micro Core, is even smaller – just 6MB.
837.
Tizen Governed by the Linux Foundation, this project aims to develop a mobile operating system that relies primarily on HTML5 technology.
838.
Ubuntu Suitable both for enterprise and home users, this extremely popular Linux distributions comes in desktop, server and cloud versions and now a TV version. It boasts 20 million users and offers fast performance, a stylish interface, ease of use and good security.
839.
Unity Instead of being built for end users, Unity is built to give developers or advanced Linux users some modular pieces they can use to create a customized distribution. Despite its name, it has nothing to do with the Unity desktop used by Ubuntu; instead, the Unity OS uses the OpenBox graphical environment.
840.
Vector Linux VectorLinux's credo is "keep it simple, keep it small and let the end user decide what their operating system is going to be." In addition to the free download, it's also available in a supported "deluxe" edition.
841.
Xubuntu And this is the version of Ubuntu that uses the Xfce desktop environment. It's available in both desktop and server versions.
842.
ZenWalk Originally based on Slackware and called "Minislack," ZenWalk has evolved to become a modern, fast, lightweight distribution that's easy to use. It's available in five versions: standard, core, live, Gnome and Openbox.
843.
Zorin OS Unlike most Linux distributions, Zorin was designed to look and feel as much like Windows as possible – only faster and without as many bugs. It's available in both free and paid verions.
Organization Management
844.
Artful.ly Designed for cultural and arts organizations, Artful.ly offers business management software with modules for ticket sales, accounting, donor and sponsor information, fundraising and marketing and more. The same software is available online with a subscription. Operating System: Linux.
Password Crackers
845.
Ophcrack Every network administrator needs to recover a lost or unknown password from time to time. Ophcrack uses the rainbow tables method to recover passwords, and it has a brute force module for cracking simple passwords. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
846.
John the Ripper John the Ripper can crack weak Unix passwords very quickly. It also comes in a paid Pro version. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Password Management
847.
Figaro's Password Manager This Linux-only password safe encrypts passwords with the blowfish algorithm. It also features a password generator and can act as a bookmark manager as well. Operating System: Linux.
848.
KeePass With KeePass, you no longer have to remember lots of different passwords. Instead, you'll only need to keep track of one master password, while KeePass stores your very strong passwords in an encrypted database, keeping you safe and secure. Operating System: Windows.
849.
KeePassDroid,
7Pas (KeePass for Windows Phone 7),
iKeePass,
KeePass for BlackBerry A perennial favorite among open source fans, KeePass is a password safe that allows users to utilize different passwords for every website or service they access, while only remembering a single master password. Versions are now available for every major mobile operating system--and some of the minor ones as well. You can find a complete list of mobile versions at
keepass.info/download. Operating System: Android, iOS, Windows Phone, BlackBerry.
850.
KeePassX If you use OS X or Linux, try this fork of KeePass. Plus, it adds a few features not in the original and runs on Windows as well. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
851.
PasswordMaker Using the same password all the time puts you at risk, but many people do it anyways because it's so difficult to remember a lot of different passwords. This browser add-on offers a better solution for the problem by creating unique passwords for each site you visit and storing them in an encrypted file that you access with a single master password. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
852.
Password Safe Downloaded more than 1 million times, Password Safe is another popular open source option for protecting your passwords. Like KeePass, it's lightweight and stores your encrypted passwords in a database so that you only need to recall one master password. Operating System: Windows.
853.
PWGen Using easy-to-guess passwords is just as bad as using the same password all the time. PWGen creates strong passwords for you, so you won't be tempted to use "password" or "123456." Operating System: Windows.
854.
Secrets for Android Similar to KeePass, Secrets for Android also stores all your passwords in an encrypted password safe behind a master password. However, this app also lets you store other "secrets" in encrypted notes. Operating System: Android.
855.
WebKeePass Have your own Web server? This version of KeePass lets multiple users access a KeePass database from any Web-connected system. It's ideal for small businesses. Operating System: OS Independent.
PDF Tools
856.
jPDF Tweak This Java-based program lets you merge, split, reorder, sign, and encrypt previously existing PDF files. Operating System: OS Independent.
857.
PDFCreator Adobe's Acrobat software is expensive, but you don't actually need that software to create PDFs. PDFCreator can write PDF files from any application capable of printing, and it includes features like encryption, digital signatures and more. Operating System: Windows.
858.
PDFedit You don't have to purchase expensive Adobe software in order to make modifications to existing PDF files. PDFedit lets you edit text, delete and renumber pages, add markup and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
859.
Sumatra PDF The free Adobe software isn't your only option for reading PDF files. The Sumatra PDF reader offers similar functionality with a lighter footprint for faster performance. Operating System: Windows.
Personal Financial Management
860.
Buddi While it's not as full-featured as Quicken, Buddi is a simple, understandable personal finance program designed for people with little or no financial experience. It's Java-based, so it works on nearly all operating systems, and the website has tutorials available for new users. Operating System: OS Independent.
861.
Financisto This open source Android app lets you track your budget from your smarphone or tablet. Key features include Quicken and CSV import, support for multiple accounts and currencies, recurring transactions, budgets and advanced reports. Operating System: Android.
862.
HomeBank Now nearly 17 years old, this personal finance solution boasts powerful filtering and graphing tools. It imports and exports data to other financial software, and it offers helpful features like auto-completion, transaction reminders and a "car cost" report that tallies up all your vehicle-related expenses. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
863.
iFreeBudget This extremely simple double-entry accounting budget is aimed at home or small business users. The interface is very basic, but the Android support is nice for tracking purchases as you make them. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Android.
864.
jGnash Java-based jGnash offers double-entry accounting for your home finances. It imports data from Quicken and Microsoft Money, and it tracks investments and supports multiple currencies. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
865.
JStock This portfolio manager offers near real-time data from 24 world stock markets. Two features that set this project apart are the cloud-based storage option and the integrated chat capabilities for exchanging tips with other investors. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
866.
KMyMoney This personal finance software from KDE features double-entry accounting and an intuitive GUI. The project's stated goal is "to be the best free software personal finance manager, period." Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
867.
Market Analysis System Ready to get really serious about investing? This app tracks a huge number of metrics and analyzes market data, flagging you when certain criteria are met. You can run it on a single PC or in a client/server setup. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
868.
Money Manager Ex Another personal finance manager with an emphasis on simplicity, Money Manager Ex aims to offer "all the basic features that 90% of users would want to see in a personal finance application." Key capabilities include budgeting, one-click reporting, charts and graphs, depreciation tracking, AES encryption support, bill reminders and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
869.
StockManiac StockManiac describes itself as an "investment time machine" for private investors. It tracks transactions and stores documents related to your portfolio, and it makes it easy to track multiple accounts and multiple portfolios. It automatically updates stock prices with Internet data, and it includes a feed reader that lets you keep up on relevant news. Operating System: OS Independent.
870.
UnkleBill One of the newer double-entry accounting apps on our list, UnkleBill offers a particularly attractive interface, complete with a cute UnkleBill cartoon character who offers tips and advice for new users. It supports multiple users and multiple accounts, and it creates PDF reports. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
871.
Yapbam Java-based Yapbam (short for "yet another bank account manager") is cross-platform, portable and extensible. It can import data from other software and online banking, automatically generates reports and includes a currency converter. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Photo Albums and Tools
872.
Album Shaper This app actually features three separate pieces: Presenter, a slideshow viewer; Reveal, an image viewer with limited editing capabilities; and Album Shaper, a tool for organizing, enhancing and sharing your photos. According to the site, it "strives to be the most friendly, easy to use, open source application" of its kind. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
873.
Comix Although it was built for viewing and organizing comic book collections, this app also functions well as a general image viewer. It offers basic image enhancement capabilities and tagging and bookmark capabilities that make it easy to see your library. Operating System: Linux.
874.
Coppermine Photo Gallery If you have your own Web server, you can use Coppermine to manage and share your photo collection with the world. It stores photo information in a MySQL database and allows you to organize your photos into online albums, upload photos, view slideshows and much more. Operating System: OS Independent.
875.
digiKam This powerful image manager for the KDE desktop aims to meet the photo organization needs of professional photographers. Key features include photo import, tagging, auto-transformations, a light table and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
876.
Eye of GNOME The official photo manager for the Gnome desktop, Eye of GNOME supports a wide variety of image file formats. It offers a basic set of capabilities that allow you to browse your images, view properties and metadata, and print your photos. Operating System: Linux.
877.
F-Spot This alternative photo viewer for the Gnome desktop offers a wider range of features than Eye of GNOME, including basic photo editing capabilities and tag icons. It also makes it easy to create a photo CD or export photos to Flickr, 23, Picasa Web or SmugMug. Operating System: Linux.
878.
Gallery Like Coppermine, Gallery requires that users have their own Web servers or Web hosting from a third-party provider. It provides a way to integrate large photo collections into existing websites. Click the link for examples of sites that use this software. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
879.
Gallery Mage Gallery Mage allows users to crop, resize and rotate images, while maintaining the original files. It integrates with several other viewers so that you can view slideshows and organize your photos. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
880.
gThumb Also for Gnome, gThumb includes an image browser, viewer, organizer and editor. Advanced features allow image import, slideshows, converting among file formats, removing duplicate images, creation of Web albums and more. Operating System: Linux.
881.
Gwenview Another photo viewer for KDE, Gwenview makes it easy to browse and view images, while also offering some basic editing capabilities. It displays image properties and meta information, and it can also play videos and animations. Operating System: Linux.
882.
jBrout The jBrout photo manager makes it easy to sort your photos into albums and later search to find one particular image. It includes integration with Picasa and Flickr. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
883.
imgSeek Although it’s a full-featured image viewer and manager, this app focuses on enabling content-based search. Quickly sketch an image or click on an existing photo to find other photos containing similar images. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
884.
KPhotoAlbum Also for KDE, KPhotoAlbum aims to make it possible to find any photo on your drive in five seconds or less. It offers automated tools for annotating, categorizing, searching and viewing your pictures. Operating System: Linux.
885.
KSquirrel KSquirrel is a fast, easy-to-use image viewer for KDE. Key features include disk navigator, file tree, multiple directory view, thumbnails and extended thumbnails, dynamic format support, DCOP interface and support for KEXIF and KIPI plugins. Operating System: Linux.
886.
Rawstudio Experts recommend saving your digital photos in their raw formats in order to preserve as much information as possible. Rawstudio handles batch processing of those images with features like image tagging and sorting, lens distortion correction, advanced noise reduction, intelligent sharpening, straightening and more. Operating System: Linux.
887.
RawTherapee Similar to Rawstudio, this two-year-old project also offers batch processing of raw photo files. It boasts "the most details and least artifacts from your raw photos thanks to modern and traditional demosaicing algorithms." Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
888.
Shotwell This photo manager for the Gnome desktop makes it easy to import, organize, edit and publish your pictures. It offers basic editing features like cropping, rotation, red-eye removal, saturation, tint and temperature, and it integrates with Facebook, Flickr, Picasa and YouTube. Operating System: Linux.
889.
UFRaw This utility can be used on its own or as a Gimp plug-in. It allows users to manipulate and view raw images and convert them to other formats. Note that like the other tools for working with raw images, you'll need to have some expertise to use this app. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Physics
890.
Step KDE's physics program provides demonstrations of classical mechanics, particles, springs with dumping, gravitational and coulomb forces, rigid bodies, molecular dynamics and more. It can also do unit conversion and error calculation and propagation. (Note that in order to use Step on Windows, you'll have to download
KDE for Windows.) Operating System: Windows, Linux.
Poetry
891.
Open Source Poetry This website offers tools to help you write your own poem or to collaborate with other poets on an open source creation. You can save your lines for your own reference or for others to use in creating new works. Operating System: OS Independent.
Point-of-Sale (POS)
892.
Floreant POS For restaurants only, this POS system works with touch screens and handles operations like split checks, kitchen print, drawer pull, tax, discounts and more. Its list of users includes the Denny's chain in New York. Operating System: OS Independent.
893.
Lemon POS Best for small or very small businesses, this Linux-based point of sale system offers features like role-based permissions, support for multiple terminals, sales suspension, custom orders and more. It stores all inventory data in a MySQL database and boasts excellent security. Operating System: Linux.
894.
Openbravo for Retail Formerly known as Openbravo POS, the retail version of Openbravo offers support for both Web and brick-and-mortar operations, compatibility with mobile devices, back office and analytics capabilities, and more. The website above primarily promotes the paid professional version, but you can find the free open source version at
Openbravo forge. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
895.
POSper This app was designed for small retail stores and restaurants. It supports multiple touchscreens, scanners, card readers and ticket printers, and it integrates with all databases supported by Hibernate. Operating System: OS Independent.
896.
SymmetricDS SymmetricDS is a data synchronization and replication tool designed to transmit data from POS databases to back office systems. Key features include guaranteed delivery, data filtering and rerouting, primary key updates, database versioning, and more. Operating System: OS Independent.
Portable Applications
897.
Democrakey For privacy on the go, Democrakey bundles together apps for anonymous browsing, anonymous e-mail and IM, encryption, file shredding and anti-virus into a suite that runs from a thumb drive. You can also purchase a USB drive with Democrakey installed from
Democrakey.com. Operating System: Windows.
898.
PortableApps.com This project also collects a ton of open source apps—only this time the apps are formatted so that you can put them on a USB thumb drive and take them with you wherever you go. The standard download comes with some of the most popular open source apps, but the site also includes a library of hundreds of other apps that you can add to your portable drive. Operating System: Windows.
899.
Tor Browser Bundle The Tor project also makes a portable suite that you can take with you on a thumb drive. You can also download an IM version. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
900.
winPenPack While its not as well-known as PortableApps.com, winPenPack also offers dozens of open source apps in portable versions. You can download the apps individually or you can get the Full or the Essential suite. Operating System: Windows.
Privacy Protection
901.
AdBlock Plus Used by more than 12.5 million Firefox users, AdBlock Plus can be configured to block all advertisements or only those originating from domains known to install malware. To use it, you'll also need to subscribe to one of the filters that provide the type of blocking you desire. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
902.
BetterPrivacy Even when you have your cookies disabled, Flash-enabled sites like YouTube, E-Bay and others can use Flash cookies (also called "SuperCookies") to track your activities. BetterPrivacy automatically disables those cookies. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
903.
HTTPS Everywhere Many websites have the ability to encrypt traffic via HTTPS, but don't turn on that feature by default. This Firefox add-on, a collaboration between the Tor Project and the Electronic Frontier Foundation, rewrites requests so that you will automatically use HTTPS whenever it is available. Operating System: OS Independent.
904.
JAP Like Tor, JAP hides your IP address while you're browsing online. However, because it is a research project, the service occasionally experiences outages and downtime. Operating System: OS Independent.
905.
Mixmaster Available in both client and server versions, Mixmaster is a remailer that protects you from traffic analysis. With it, you can send e-mail anonymously or under a pseudonym. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
906.
Mixminion Another anonymous remailer, Mixminion passes e-mail through a network of servers that mixes them up and encrypts them in order to protect privacy. It hasn't been updated in a while, but a stable version is available. Operating System: Windows, Unix, OS X.
907.
Privacy Dashboard This Firefox add-on from W3C (the World Wide Web Consortium) alerts you to the data being collected by the various websites you visit. Users also have the option of contributing to a project that is tracking how websites are doing at protecting users' privacy. Operating System: OS Independent.
908.
Privoxy This non-caching Web proxy server offers advanced filtering capabilities for removing ads and protecting your privacy. You can use it to protect an individual PC or an entire network. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
909.
SafeCache This Firefox add-on helps prevent websites from accessing your browsing history. It works with your cookie settings to apply your desired level of privacy. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
910.
Torbutton This Firefox add-on makes it easy to turn Tor (see above) on or off for anonymous browsing. Note that when you are using it, you will not be able to access sites that use JavaScript, some CSS features, or Flash. Operating System: OS Independent.
911.
Web of Trust (WOT) Downloaded more than 33 million times, this popular add-on for Firefox, Internet Explorer, Chrome, Safari or Opera lets users know when they've strayed into websites that are questionable or insecure. It utilizes user ratings to identify sites that perpetuate scams, collect personal information or include unsuitable content, and it ranks them with a green-yellow-red classification system. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Programming Languages
912.
Dart First unveiled in October of 2011, Dart is Google's new programming language designed as an alternative to JavaScript. Currently, the company is seeking feedback on the language, which is still in the very early stages of development. Operating System: OS Independent.
913.
ECL ECL ("Enterprise Control Language") is the language for working with HPCC. A complete set of tools, including an IDE and a debugger are included in HPCC, and documentation is available on the HPCC site. Operating System: Linux.
914.
Go Recently developed by Google, Go aims to make developers more productive by providing them with a clean, simple programming language. And unlike many older languages, it offers garbage collection and parallel computation. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
915.
Java Originally developed by Sun but now owned by Oracle, Java allows developers to write code that will run on multiple operating systems. According to Tiobe, it's the most popular programming language in the world. The link above offers extensive help for those new to the language and a large collection of tools for Java developers. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
916.
Perl Perl has been around for 22 years and runs on more than 100 different platforms. It's an ideal Web programming language and integrates easily with popular databases. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
917.
PHP This general purpose scripting language is particularly suited to Web development, enabling developers to write dynamically generated pages quickly. A lot of its syntax comes from C, Java and Perl, and it can be embedded into HTML. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
918.
Pig/Pig Latin Another Apache Big Data project, Pig is a data analysis platform that uses a textual language called Pig Latin and produces sequences of Map-Reduce programs. It helps makes it easier to write, understand and maintain programs which conduct data analysis tasks in parallel. Operating System: OS Independent.
919.
Python Python's strengths are its speed, flexibility and readable syntax. It's often used in Web development but can be used for other types of applications as well. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
920.
R R is both an environment and a programming language for statistical calculations. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
921.
Ruby Designed to feel "natural," Ruby's creator Yukihiro “matz” Matsumoto blended parts of Perl, Smalltalk, Eiffel, Ada, and Lisp to create a new language that's been called both "handy" and "beautiful." It's ranked as the tenth most popular programming language in the world, due in no small part to the popularity of the Ruby on Rails framework. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Project Management
922.
Achievo Designed for medium-sized organizations, Acheivo combines calendar, contacts, project management, time tracking and basic CRM and human resources management capabilities. It's Web-based, and the site offers a demo so that you can try it out before you download. Operating System: OS Independent.
923.
Dotproject Conceived in 2000 as an alternative to Microsoft Project, this application offers a clean interface and a focus on project management without extraneous groupware functions. Key features include an e-mail based ticket/trouble system, hierarchical task list, discussion forum, file repository and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux
924.
GanttProject Similar to OpenProj (see below), GanttProject can also import and export data from Microsoft Project. Other key capabilities include Gantt charts, PERT charts and collaboration features. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
925.
NavalPlan As the name suggests, this Web-based project management system was originally created for the ship building industry, but its features make it useful for just about any industry. It helps organizations schedule resources, control costs, organize tasks and monitor progress, and it connects with many ERP systems. Operating System: Linux.
926.
Onepoint Project Onepoint Project offers enterprise-class project management with fast deployment and quick ROI. It comes in a variety of open source and commercial editions; the group and enterprise editions can be deployed on-premise or used on demand. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
927.
OpenProj Very similar to Microsoft Project, this popular app lets you assign resources, schedule tasks and handle the other aspects of managing an ongoing project. It also imports and exports Microsoft Project files. However, note that the export to PDF function in the software is shareware, not open source. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS X.
928.
openXprocess A good choice for application development teams, openXprocess has some tools for using Agile and Scrum methodologies, and Xprocess also offers training for using the app to support Agile and Scrum development. The company also offers paid support. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
929.
PHPProjekt PHPProjekt combines project management with a time tracker and some groupware functions, like a calendar, to do list and contact manager. It's Web-based, and the site provides a helpful demo so that you can see the features in action. Operating System: OS Independent.
930.
Plandora Plandora meets the needs of a variety of kinds of teams with Gantt charts, a Balanced Scorecard view and an Agile development board. In addition, the latest release includes cost management, artifact management and new gadgets. Operating System: OS Independent.
931.
Redmine Web-based Redmine offers Gantt charts, calendar, per-project wikis, an issue tracker, newsfeeds and more. It also integrates with most version control systems, making it a good choice for development teams. Operating System: OS Independent.
932.
TaskJuggler TaskJuggler calls itself "project managers' delight" and includes tools for project scoping, resource assignment, cost and revenue planning, and risk and communication management. It's designed for "serious project managers" and takes some effort to learn. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
933.
web2Project Offering "real project management for real business," this Web-based tool can manage multiple projects, companies, departments and users. Key features include a modular infrastructure, built-in security, role-based permissions, project- and group-wide Gantt charts, and group calendar. Operating System: OS Independent.
934.
XPlanner+ Designed for development teams, this Java-based app includes project management, bug tracking and time tracking capabilities. It supports Agile methodologies and it can export to multiple formats, including Microsoft Project. Operating System: OS Independent.
Project Portfolio Management
935.
Onepoint Project Onepoint combines project management with project portfolio management capabilities, including supporting formal, Agile and JIRA projects within a single solution. The Basic and Community editions are available with a GPL license, while the supported editions for enterprise users have a proprietary license. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
936.
Project.Net The first open source solution to be included in Gartner's "Magic Quadrant for IT Project and Portfolio Management Applications," Project.Net is a robust, but affordable alternative to commercial PPM software. It integrates with many BI systems, includes advanced social networking features and commercial support and services are available. Operating System: OS Independent.
RAID Controllers
937.
Mdadm Part of the Linux kernel, Mdadm is software that makes it possible to build your own RAID array with standard hardware. It can also monitor and report on RAID arrays. Operating System: Linux.
938.
Raider Raider allows users to convert any Linx disk system into a RAID array. It supports RAID levels 1, 4, 5, 6 or 10. Operating System: Linux.
939.
RaidEye Just as Raider and Mdadm allow you to turn Linux systems into RAID arrays, RaidEye does the same thing for Macs. It's a monitoring tool that works with the built-in RAID capabilities in OS X. Operating System: OS X.
940.
Salamander Another Linux project, Salamander simplifies the process of turning a multi-disk system into a RAID system. As for the name, the website explains, "Salamanders are the only vertebrates that can regenerate limbs. In the same way, a system installed with Salamander can regenerate after a hard-drive failure." Operating System: Linux.
941.
SnapRAID SnapRAID is a non-standard RAID level for storage arrays. It uses snapshot backup capabilities to provide redundancy that protects against the failure of up to two disks in an array. Operating System: OS X.
Religion
942.
BibleTime The BibleTime free Bible study software includes data from more than 100 Bibles, commentaries and other reference materials. It's a good alternative to similar commercial software which can cost hundreds of dollars. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
943.
Gnaural It already does everything else--now your computer can help you meditate. Using something called the “binaural beat principle,” Gnaural generates audio tones designed to get you in the right frame of mind for relaxation. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
944.
Noor Noor doesn’t offer a lot of bells and whistles, but it does let you access the text of the Quran from your PC. It includes both the original Arabic and translations. Operating System: OS Independent.
945.
Xiphos This app works much like BibleTime and even links to the same set of free reference materials. However, Xiphos' modular design allows for user-built add-ons, including some that add journaling and prayer list features. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
946.
Zekr Zekr brings the text of the Qu'ran to your PC with advanced search, read aloud and other functions. It's open source because the project owners believe you should "never profit off the prophet." Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Remote Access/VPN
947.
Android-VNC-Viewer This VNC client allows you to use an Android device to connect to a VNC server. It allows you to view another system screen remotely. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
948.
BO2K Based on Back Orifice, BO2K provides file-synchronization and remote operation capabilities for network administrators. Unlike most commercially available products, it's small, fast, free, and very extensible. Operating System: Linux.
949.
OpenVPN OpenVPN is available as a open source community download, a commercially supported enterprise solution or as a cloud-based service. All three versions offer a secure, private way to access the Internet or your organization's network. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
950.
TightVNC This remote control application allows users to interact with a system in one location while using a system in another location. In addition to its telecommuting uses, it's also useful in many help desk situations. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
951.
UltraVNC UltraVNC offers similar capabilities as TightVNC. Key features include file transfer, video driver, optional encryption plugins, MS logon, text chat, viewer toolbar, viewer auto scaling, multiple monitor support, auto reconnection and more. Operating System: Windows.
952.
Zebedee While it's not a true VPN tool, Zebedee does provide secure IP tunneling for TCP/IP or UDP data transfer between two systems. It not only provides security against snoopers, its compression capabilities save on network bandwidth. Operating System: Windows, Linux, Unix.
Recipe Management
953.
Gourmet Gourmet helps you organize your recipes. It imports recipes from multiple formats, including websites, plus it generates shopping lists and counts the calories in the meals you're making. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
954.
Recipe Tools This set of tools can help you find (and share) great recipes on the Web. With the RecipeFox Firefox add-on, you can easily grab recipes off the Internet and save them for use later. You can then store the recipe in a recipe manager like MasterCook or Gourmet (see below). Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Report Authoring
955.
WIKINDX Designed to help researchers take notes and track bibliographic information, WIKINDX can be used by a single user or stored on a Web server for access by a team working together. It exports bibliographies in a variety of style guide formats, allows multiple attachments per resource and supports non-English characters. Operating System: OS Independent.
956.
Zotero Zotero is a Firefox plug-in that makes it easy to track and cite your sources when doing research on the Web. It also includes a "Groups" feature that allows you to share your research with a team. Operating System: OS Independent.
Robotics
957.
The Player Project More middle and high school are offering classes in robotics, and The Player Project provides some of the software that supports instruction in robotics. It includes Player, a network server for robot control; Stage, a 2D multiple robot simulator; and Gazebo, a 3D multiple robot simulator with dynamics for simulating outdoor environments. Operating System: Linux, Unix.
958.
ROS Short for "Robot Operating System," ROS offers a set of open-source libraries for controlling robots. It includes device drivers, libraries, hardware abstraction and other capabilities. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
Router Software
959.
Vyatta Used by dozens of Fortune 500 companies, Vyatta allows users to create their own enterprise-grade networking appliance from any x86 system. You can find commercial products based on the same technology at
Vyatta.com. Operating System: Linux.
960.
FREESCO This Linux-based software lets you set up your own router or a Web, FTP, DNS or SSH server. It incorporates firewalling and NAT capabilities. Operating system: Linux.
961.
Tomato While the other projects in this category allow you to create your own routers from standard PCs, this project is a replacement for the firmware on routers you may already own, specifically Linksys' WRT54G/GL/GS, Buffalo WHR-G54S/WHR-HP-G54 and other Broadcom-based routers. It includes some more advanced management capabilities, raises the maximum connections for P2P and enables additional wireless features.
RSS Readers
962.
FeedReader FeedReader offers robust news aggregation while keeping the interface basic enough for novices to use. Upgrades to the FeedReader Connect and FeedReader OEM products are available for a fee. Operating System: Windows.
963.
RSS Owl One of the most popular feed readers available, RSS Owl aggregates headlines from all of your favorite media sites and makes them easy to browse. It has a ton of advanced features, like saved searches, news filters, labels, and news bins that set it apart from other similar apps. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
School Administration
964.
Focus/SIS This newer SIS is completely Web-based and designed to make it as easy as possible to comply with state reporting requirements. It also streamlines attendance taking, scheduling, grading, and other administrative tasks. Operating System: OS Independent.
965.
OpenAdmin OpenAdmin's interface isn't particularly fancy, but it does provide a wide range of features for tracking grades, attendance, schedules, discipline, fees, IEPs and more. It was designed to meet the needs of both public and Catholic schools. Operating System: OS Independent.
966.
openSIS OpenSIS boasts that it can save school systems 75 percent compared to closed source student information systems. It comes in three versions: community, school, and district. The school and district options are also available as a hosted solution. Operating System: OS Independent.
967.
SchoolTool Canonical's Edubuntu and the One Laptop Per Child project both include SchoolTool as their school administration program. It offers an online gradebook, calendar, attendance, competency tracking, demographics and contacts. Operating System: Linux.
Screenplay and Novel Writing
968.
Celtx Planning to tackle writing a screenplay or producing your own film? This "all-in-one movie pre-production system" can help you write scripts, produce storyboards, and much more. It boasts more than 1.5 million users in 170 countries. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
969.
Storybook If writing a novel is on your to-do list for this year, Storybook can help you get started. It keeps an overview of characters and scenes in one place, helps you organize your book and includes features to help you maintain continuity. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Small Business Server
970.
ClearOS This software allows small business owners to set up their own networks with a server that offers file and printer sharing, anti-virus, Web server, mail server, firewall, content filtering, VPN, multi-WAN and many other features. It also comes in a professional version with paid support and additional apps. Operating System: Linux
971.
SME Server Also aimed at small and medium-sized enterprises, SME Server is based on CentOS and RedHat Linux. It offers easy administration, file and print sharing, mail server, firewall, directory services, Web application server and more. Operating System: Linux
972.
Zentyal Small businesses can use this app as a gateway, infrastructure manager, unified threat manager, office server, unified communication server or all of the above. It's goal is to provide "a single, easy-to-use platform to manage all your network services." Operating System: Linux
Smoking Cessation
973.
QuitCount This Linux-only app helps keep you motivated to stop smoking. You tell it the day you quit, and it keeps a running total of how much money you've saved, how much tar you didn't put into your body and how much time you have added to your life expectancy. Operating System: Linux.
974.
Smoke Reducer Smoke Reducer keeps track of how long it's been since your last cigarette. It plays an alarm when it's time to smoke again, gradually lengthening out the time between smoking sessions until you stop completely. Operating System: Android.
SOA
975.
Turmeric Version 1.0 of this eBay-owned SOA platform was released in May of 2011. It's Java-based, standards-based and offers quality-of-service features, monitoring capabilities, a repository library, a type library, an error library, local binding and more. Operating System: OS Independent.
Social Networking
976.
BuddyPress Made by the WordPress team, BuddyPress offers "social networking in a box." Its used by thousands of organizations to create social networks for a variety of different groups. Operating System: OS Independent.
977.
Diaspora Launched as an alternative to Facebook, this open source social network has a long way to go to catch Facebook's user base. It offers greater control over your privacy and content. You can sign up to join a current Diaspora hub or create your own Diaspora server using the information from the site. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
978.
LiveStreet CMS Similar to BuddyPress, LiveStreet is a content management system for creating blogs or social networks. It boasts easy installation, extensibility and multilingual functionality. Operating System: Linux.
979.
Pligg CMS Pligg describes itself as "social publishing" software; that is, it creates websites that invite users to submit their own content and/or vote on current content. Hosting is available through several third-party partners. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
980.
Storyltr Storyltr brings together all of your Web 2.0 posts from up to 18 different services, including Twitter, Flickr, StumbleUpon, Tumblr and others. It lets you tell the story of your life in your own way. Operating System: OS Independent.
Speech
981.
eSpeak Although not as human-sounding as some other text readers, eSpeak provides clear audio of the text on your screen. It supports dozens of different languages, as well as several different English accents. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
982.
Simon If you'd like to be able to talk to your computer, check out Simon. It accepts voice commands and turns audio into text. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
Stamp Collecting
983.
Numismatic Yes, there's even an open source project for coin collectors. Numismatica stores data related to your collection in a MySQL database that you can access through a Web app. Operating System: OS Independent
Storage
984.
Ceph Ceph is a distributed file system that offers unified object, block and file-level storage. Professional support and services are available through
InkTank. Operating System: Linux.
985.
FreeNAS This open source storage platform allows end users to store and share files across Windows, Mac, Linux and Unix-like systems. Key features include thin provisioning, backup and restore, snapshots, zettabyte file system and a Web interface. Operating System: FreeBSD.
986.
Gluster FS This distributed file system can scale up to 72 brontobytes while handling thousands of clients. A commercial version of the same software is available through Red Hat. Operating System: Linux.
987.
Libvirt Storage Management This open source API provides an array of virtualization management capabilities, including storage management capabilities. It supports multiple hypervisors, including, KVM, Xen, VMware, Hyper-V and others. Operating System: Linux.
988.
Lustre Oracle-owned Lustre boasts that it can handle very large and complex storage needs, "scaling to tens of thousands of nodes and petabytes of storage with groundbreaking I/O and metadata throughput." Note that although the name is similar to "Gluster," the two are completely independent projects. Operating System: Linux.
989.
NAS4Free A fork of FreeNAS, this project also creates a BSD-based NAS system. Key features include ZFS, Software RAID (0, 1, 5), disk encryption and reporting. Operating System: FreeBSD.
990.
OHSM Short for Online Hierarchical Storage Manager, OHSM automatically moves data between high- and low-cost storage media in accordance with the policies set up by the administrator. It allows policies for allocation (where to put a new file) and relocation (when to move an existing file). Operating System: Linux.
991.
Openfiler Openfiler offers unified storage incorporating both NAS and SAN features. Its customers include Motorola, Pratt & Whitney, BillMeLater and the London Metropolitan Police. Commercial support and plug-ins are available. Operating System: Linux.
992.
OpenSMT Like Openfiler, OpenSMT also allows users to turn standard system hardware into a dedicated storage device with some NAS features and some SAN features. It uses the ZFS filesystem and includes a convenient Web GUI. Operating System: OpenSolaris.
993.
oVirt Like Libvirt, oVirt can manage many different types of virtualized environments, including virtualized storage. It supports the KVM hypervisor only. Operating System: Linux.
994.
Turnkey Linux File Server Turnkey offers a wide variety of Linux-based software that you can use to create your own appliance. The File Server version creates a simple NAS device. Operating System: Linux.
995.
ZFS Originally developed by Sun, this file system supports very high storage capacities and offers features like error checking, RAID capabilities and data deduplication. It has been incorporated in many other open source projects, including FreeNAS and NAS4Free. Operating System: Solaris, OpenSolaris, Linux, OS X, FreeBSD.
Systems Administration Tools
996.
Inside Security Rescue Toolkit Also known as INSERT, the Inside Security Rescue Toolkit packs dozens of helpful security and system administration apps into a single download. In addition to a complete, bootable Linux system (based on Debian), you'll get apps for anti-virus protection, network analysis, forensics, and more. Operating System: Linux.
997.
Networking Commands for Windows If you’d rather perform network configuration and maintenance activities from the command line instead of a GUI, check out Networking Commands for Windows. This collection of command-line tools lets you use a small list of short, easy-to-remember commands to perform day-to-day systems administration activities. Operating System: Windows XP.
998.
ProShield Designed primarily for Debian and Ubuntu, ProShield scans your system to make sure your software is up-to-date and that you haven't picked up any malware. It also reminds you to backup your system, checks your available disk space, and performs other routine maintenance checks. Operating System: Linux.
999.
Wake on Lan This helpful little app makes it easy to turn on or shut down Windows systems connected to your network. It also includes a scheduling feature and can be run from the command line or a GUI. Operating System: Windows.
1000.
Webmin This interface allows you to set up Unix user accounts, change passwords, and perform other system admin tasks from any Web browser. You can perform more than 100 different functions. Operating System: Unix.
Text Editors
1001.
Emacs Emacs-style text editors have been around since the mid-70s and are popular among programmers. The GNU version offers content-sensitive editing modes for HTML and other types of files. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1002.
jEdit Java-based jEdit boasts auto indent and syntax highlighting for 130 programming languages. It has a huge list of features and more than 150 plug-ins that extend its capabilities. Operating System: OS Independent.
1003.
Notepad++ This mature text editor offers fast performance and a lightweight file size. It's been downloaded more than 20 million times, has won numerous awards, and offers a number of features that make it an excellent option for developers. Operating System: Windows.
1004.
TEA TEA combines a small file size with hundreds of functions, including syntax highlighting for more than 20 languages. Other key capabilities include a spellchecker, code snippets, built-in ZIP packager, bookmarks, tabbed layout engine and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1005.
Vim Sometimes considered an IDE, Vim is a "programmer's editor" with extensive syntax assistance, code completion, split screens, undo/redo, and many other features. It's won a number of awards, but does have a reputation for being difficult to learn. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1006.
Zile Short for "Zile is Lossy Emacs," Zile is a small text editor that looks very similar to the popular Emacs editor. It packs many features into just 100KB, including multi-level undo, multi-window display, killing, yanking, register, and word wrap. Operating System: Linux/Unix.
Time Tracking
1007.
eHour If you're a freelancer, consultant or other professional who bills by the hour, eHour can help you track and bill for the time you spend on projects. It also has some multi-user capabilities suitable for small offices. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1008.
Rachota One way to make sure you're being as efficient as possible is to track the amount of time you spend on tasks. Rachota does just that—for both work and home situations. It's also portable, so you can take it with you. Operating System: OS Independent.
1009.
timeEdition The minimalist interface on this app makes it very easy to track the amount of time workers spend on various tasks. It also integrates with iCal, Outlook and Google Calendar, and exports into spreadsheet formats. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1010.
TimeTrex This open source solution handles scheduling, employee time tracking, job estimates and payroll tasks. It's also available in a cloud-based "On Demand" version. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1011.
Todomoo Todomoo combines a hierarchical task manager with a time tracker that allows you to bill for your time on multiple projects. It's also available in a portable edition that you can run from a USB drive. Operating System: Windows.
To-Do Lists/Schedulers/Calendars
1012.
Astrid Astrid describes itself as a "social productivity" tool. Basically, it's a to-do list and reminder system that you can use individually or with groups. Operating System: Android.
1013.
BORG Calendar No need to worry about being assimilated, this "BORG" stands for "Berger Organizer." It combines basic calendar functionality with a sophisticated to-do list that actually works more like most project management software. Operating System: OS Independent.
1014.
Makagiga Makagiga offers the same schedule/journal functionality as RedNotebook, plus it adds a sticky notes widget and a feedreader. Other optional add-ons are also available. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1015.
qOrganizer Like several of the other options in this category, qOrganizer offers a calendar, to-do list and an integrated journal. However, this one also adds special student-focused features, such as a booklet for tracking grades and attendance, a timetable for tracking classes and an extra loud alarm in case you've dozed off while studying. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1016.
RedNotebook This innovative app adds a text editor to a calendar/to-do list app. The result is perfect for keeping a diary or making notes about upcoming events. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1017.
Task Coach Unlike many similar to-do list managers, Task Coach allows you to break tasks down into smaller sub-tasks. It also allows you to tag and organize tasks, and it integrates with some of most well-known e-mail clients, including Outlook and Thunderbird. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1018.
ThinkingRock This app helps you put into practice the "Getting Things Done" methodology featured in books by David Allen. Different screens help you collect your thoughts, process thoughts, then organize, review, and do. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
Transit
1019.
OpenTripPlanner This one-year-old project aims to make it easy for government entities to communicate information about public transit schedules, walking and biking routes and other travel-related information. Portland's TriMet, one of the sponsors of the project, currently has a
working demo of the software in action. Operating System: OS Independent.
Typing
1020.
Klavaro Klavaro offers a much more comprehensive program that includes a basic course, adaptability exercises, fluidity exercises, velocity exercises, progress charts and more. Unlike many other programs, you can also use it to learn alternative keyboard layouts in addition to the standard QWERTY keyboard. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1021.
TypeFaster Typing Tutor TypeFaster also includes touch typing lessons and a 3D typing game for extra practice. It comes in standard, accessible, and Spanish versions, as well as a multiple user version that allows instructors to assign certain lessons each day and track student progress. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1022.
TuxType This app for younger kids includes some basic typing instruction and two fun games for increasing your typing speed. It's not a comprehensive typing instruction program, but does offer fun supplemental activities and helps elementary students learn where all the letters are on the keyboard. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Utilities
1023.
Appetizer Appetizer is a dock-style application launcher for Windows. It supports the PortableApps.com file format, so it will automatically detect any other portable apps you have on your thumb drive and include them on the dock. Operating System: Windows.
1024.
Barnacle Barnacle allows you to use your Android device as a WiFi hotspot, so that you can connect your PCs to the Internet via your wireless data connection. Note that this app requires root access. Operating System: Android.
1025.
Coffee This helpful app keeps your system "awake" during downloads, file transfers, etc. It's very helpful if you don't want your system going into standby mode while it completes a particular activity. Operating System: Windows.
1026.
Copy Handler If you're re-organizing or cleaning up your hard drive, Copy Handler can help. It's faster than the standard Windows copy and move features, and it gives you more options, like task queuing, filtering files according to specific criteria, pausing and resuming copying files and changing the copying parameters on the fly. Operating System: Windows.
1027.
Folder Menu This handy tool makes it easier to jump to your favorite files and folders. It works with Windows Explorer, open/save dialog boxes, or the command prompt. Operating System: Windows.
1028.
GnuWin32 This site offers native Windows ports of lots of different open-source apps offered under the GNU license. There are dozens of apps, tools, and libraries available, but many of them fall under the "utilities" category, which is why we put it here on our list. Operating System: Windows.
1029.
HDGraph Wondering how in the world you managed to fill up 300 GB worth of hard drive space? HD Graph lets you see the reasons in a flash by drawing a multi-level pie chart that details how much space each directory and subdirectory is consuming. Operating System: Windows.
1030.
KShutdown Need to turn off, turn on, or restart your computer at a later time? This app lets you schedule all those functions so they happen automatically and adds several other features as well. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1031.
Kysrun Originally designed for the Eee, Kysrun lets you open applications, link to bookmarks, or perform other operations by typing a few letters instead of hunting through menus. As you begin typing one letter at a time, Kysrun brings up a list of all applications on your system with those letters in the name, and you simply click on the one you want. Operating System: Linux.
1032.
Open Manager This project offers an alternative file manager for Android that makes it easy to cut, copy, paste, delete, rename, backup and zip files, as well as to install apps that don't come from Google Play. It comes in both smartphone and tablet versions. Operating System: Android.
1033.
Standup Timer Keep your standup meetings short and sweet with this helpful timer. It displays both the amount of time elapsed and the time left before you need to wrap up your meeting. Operating System: Android.
1034.
Stuff Organizer Stuff Organizer makes it easy to organize and find any kinds of files on your computer—whether they're music, video, or just documents. Features include a compression extracting utility, tagging support and integration with several Web services that provide data about multimedia files. Operating System: Windows.
1035.
UltraDefrag Need to defrag your hard drive? Unlike the defragmenter tool that comes with Windows, UltraDefrag lets you defrag on startup for maximum speed. You can also configure it to shut down your system when it's finished, so you can leave it working at night after you go to bed. Operating System: Windows.
1036.
Unrar Extract and Recover If you need to extract a lot of RAR archive files and you're not exactly sure what all the passwords are, this tool can help. It "handles password-protected, multi-part and encrypted archives with ease," and it requires no installation. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1037.
Windows Leaks Detector This no-frills app can attach to any running Windows process and detect memory leaks. It groups leaks together by call stack for easier debugging. Operating System: Windows.
User Authentication
1038.
Smart Sign Smart Sign offers several different modules that help you use smart cards for user authentication and digital signatures. It supports a number of different card types and readers, as well as the Open CA certification authority. Operating System: Linux.
1039.
WiKID WiKID boasts "two-factor authentication without the hassle factor." In addition to the free community version, it also comes in a supported enterprise version which also adds additional functionality. Operating System: OS Independent.
Version Control
1040.
Bazaar This cross-platform, distributed version control system is used by numerous organizations, including open source heavyweights like the GNU project, Ubuntu, MySQL, Bugzilla, Debian and LaunchPad. It boasts great usability and calls itself "version control for everyone." Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1041.
Git Used for the Linux kernel, Perl, Eclipse, Ruby on Rails, Gnome, KDE and many other open source projects, this distributed version control system is fast and efficiently handles large projects. It offers strong support for non-linear development and cryptographic authentication of history. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1042.
Mercurial This distributed version control system aims to help teams work together faster and more easily. It's easy to learn, and it's speed makes it particularly good at handling large projects. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1043.
Subversion Subversion describes itself as "Enterprise-class centralized version control for the masses." Its features and feel are very similar to CVS. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1044.
TortoiseSVN If you'd like to use Subversion on Windows, you might want to use the TortoiseSVN client. It lets you use commands and see the status of files from within Windows Explorer. Operating System: Windows.
Video Tools
1045.
Amara From the same group behind the Miro multimedia player, award-winning Amara aims to make it easier to subtitle and translate video. The project includes both downloadable software and a website for working on projects collaboratively. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1046.
Avidemux Although it's not quite as powerful as some of the other open source video editors, Avidemux offers basic editing capabilities for amateurs, and it's one of the few open source apps in this category that runs on Windows and OS X. The site offers a wiki and a helpful forum for new users who need help getting started. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1047.
Cinelerra Describing itself as a "movie studio in a box," this professional-quality compositing and editing tool invites users to "unleash the 50,000 watt flamethrower of content creation in your UNIX box." There's also a community fork of the project at
Cinelerra.org. Operating System: Linux.
1048.
CinelerraCV The standard version of Cinelerra doesn't get updated very regularly, but this community-managed fork has added features and bug fixes more recently. It claims to be "the most advanced non-linear video editor and compositor for Linux." Operating System: Linux.
1049.
DivXRepair Experiencing problems playing AVI files? DivXRepair may be able to help. Operating System: Windows.
1050.
DVD Flick This app focuses on converting video or audio files saved on your system into playable DVDs. It offers the options of adding a menu and subtitles as well. Operating System: Windows.
1051.
DVDx Convert DVDs to any of the popular file formats with DVDx. It can also correct some file errors, split videos into smaller files or merge several files into one larger file. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1052.
FFDShow This codec decodes numerous file formats. It provides excellent video quality while consuming few computing resources. Operating System: Windows.
1053.
HandBrake This newer conversion tool also helps convert DVDs or BluRay disks to other formats. Features include chapter selection and markers, subtitles, support for numerous filters and live video preview. Operating System: Windows.
1054.
Kaltura Community Edition Kaltura is home to a number of video-related projects, including a player, editor, widgets, processing, and much more. Their latest release is a Joomla extension that makes it easy to add video to your Joomla-based Web site. Operating System: OS Independent.
1055.
Kdenlive This video editor aims to "answer all needs, from basic video editing to semi-professional work." It's easy-to-use, highly versatile and supports a wide variety of file formats. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
1056.
LiVES LiVES, which stands for "LiVES is a Video Editing System," is both a tool for VJs and a non-linear video editing tool. It's frame and sample accurate, supports the latest standards and includes dozens of special effects. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1057.
Miro While most video players also play audio (and thus ended up in the multimedia category), this one just plays video. It's claim to fame is its support for HD, as well as its library of 6,000 free movies and TV shows. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1058.
OpenShot Video Editor This video editor for Linux includes capabilities like unlimited tracks, clip resizing and scaling, video transitions, compositing and overlays, 3D titles, rotoscoping and more. It boasts an easy-to-use interface that makes it suitable for beginning filmmakers and hobbyists. Operating System: Linux.
1059.
PhotoFilmStrip While it's not a full-featured video editor like Premiere, PhotoFilmStrip is a good option for amateurs who want to make a movie out of existing photos. It uses the "Ken Burns" effect on your photos to make a much more interesting show than you could with PowerPoint or similar presentation software. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1060.
VirtualDub Another "lite" offering, VirtualDub offers basic video capture and processing. It works best with AVI files. Operating System: Windows.
1061.
Windows Essentials Codec Pack Having trouble playing a video file you've downloaded from the Internet? This download gives you the tools you need to play 99 percent of files available, including a simple media player. Operating System: Windows.
Virtualization
1062.
KVM Short for "Kernel-based Virtual Machine," KVM is owned by Red Hat and included in the main Linux kernel. Unlike Xen, it only runs on x86 systems. Operating System: Linux.
1063.
OpenVZ OpenVZ takes a different approach to virtualization: unlike VMware, VirtualBox and many other virtualization solutions which use VMs, OpenVZ offers container-based virtualization through VEs or VPSs. Commercial products based on OpenVZ are sold as
Parallels Virtuozzo Containers. Operating System: Linux.
1064.
VirtualBox VirtualBox offers virtualization for x86 and AMD64/Intel64 servers and desktops. Pre-built VirtualBox appliances are available for download from
Oracle. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Solaris, others.
1065.
Xen Xen has become the industry standard open source hypervisor, and it's used by many public cloud computing services, including Amazon and Rackspace. It's operating system-neutral, lightweight, secure and offers good performance. Operating System: OS Independent.
Vulnerability Assessment
1066.
BackTrack BackTrack's website describes it as "a Linux-based penetration testing arsenal that aids security professionals in the ability to perform assessments in a purely native environment dedicated to hacking." It's won numerous awards and has been downloaded more than 4 million times. Operating System: Linux.
1067.
Metasploit This well-known penetration testing tool simplifies network discovery and vulnerability verification. In addition to the free community version, it also comes in paid pro and express versions that add more capabilities. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1068.
Nexpost Often used alongside Metasploit, Nexpose offers vulnerability scanning for very small organizations or individuals. It also comes in paid express, consultant and enterprise versions. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1069.
Nmap This powerful network scanner helps with numerous administrative tasks, such as network inventory, managing upgrades and monitoring uptime, as well as with performing security audits. It's very flexible, portable and it's won numerous awards. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1070.
Nikto Nikto scans Web servers for thousands of dangerous files and server-specific problems. Optional automatic updates are available. Operating System: Windows, Mac, Linux, Unix, BSD.
1071.
OpenVAS The "world's most advanced open source vulnerability scanner and manager," OpenVAS is a framework with several tools for security testing and management. As of May 2012, it now includes more than 25,000 network vunlerability tests. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1072.
Paros This Java-based scanner intercepts all http and https data transmitted between server and client to help evaluate the security of Web applications. It includes a spider, proxy-chaining, intelligent scanning for XSS and SQL injections, and more. Operating System: OS Independent.
1073.
Samurai Find out how well your Web site will stand up to attack with this penetration testing framework. It incorporates a number of well-known open source tools, including e Fierce domain scanner, Maltego, WebScarab, ratproxy, w3af, burp, BeEF, AJAXShell and many others. Operating System: Linux.
1074.
Sara Short for "Security Auditor's Research Assistant," Sara integrates with the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and performs SQL injection and XSS tests. It's no longer under active development, but you can still download the code from this link. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
Web Filtering
1075.
DansGuardian This content filtering tool uses phrase matching, PICS filtering and URL filtering to block objectionable material from your network. Highly flexible, it allows the user to define what is an what is not objectionable, with the default settings designed to be appropriate for young children. Operating System: Linux, OS X.
1076.
iSAK The "Internet Secure Access Kit" (iSAK) lets you view reports on what type of sites your users are visiting and when. Of course, it also gives you the option to block specific sites or categories of sites for security or to prevent access to objectionable sites. It also incorporates anti-virus and anti-spam protection. Operating System: Linux.
Web Page Editors
1077.
Amaya Originally developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) in 1996, Amaya promotes two-way Web communication by incorporating both a Web page viewer and a Web page editor. It supports multiple Web languages, including HTML, CSS, XML, XHTML, MathML and SVG. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1078.
Aptana A better option for professional Web application developers, Aptana supports HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript, Ruby, Rails, PHP and Python. It also offers Git integration and easy deployment to Heroku or EngineYard. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1079.
Bluefish Created with more experienced Web developers and designers in mind, Bluefish is a lightweight, fast editor that can be used with multiple programming languages, including HTML, PHP, Python, Ruby, JavaScript and others. Key features include a powerful search and replace function, side bar snippets, multiple document interface, unlimited undo/redo, and a spellchecker that supports many programming languages. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1080.
BlueGriffon Just over a year old, BlueGriffon is a next-generation Web page editing tool based on the Gecko rendering engine that Firefox also uses. The easy-to-use interface also makes it a good choice for non-technical users, and it supports HTML5. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1081.
Firebug If you're comfortable editing code, Firebug is a fabulous tool for editing your Web pages live. It integrates with Firefox and makes it easy to search, edit, and find errors in your HTML, CSS, or JavaScript. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1082.
Kompozer A good choice for novice Web developers, Kompozer offers an easy-to-use WYSIWYG page editor as well as an HTML editor. Key features include an FTP site manager, color picker, tabbed interface, CSS editor, forms, spellchecker and more. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1083.
SeaMonkey This "all-in-one Internet application suite" includes a Web browser, e-mail client, feed reader, chat client and HTML editor. It's powered by Mozilla source code, and has a large library of add-ons for more features. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1084.
XML Copy Editor For XML only, this editor is lightweight and fast. It validates your code as you type and offers a simple, basic interface. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
Web Servers
1085.
Apache HTTP Server Used by 63 percent of all websites, Apache has been the most popular Web server for more than a decade. It prides itself on being secure, efficient and extensible. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1086.
AppServ The goal of the App Serv project is simple: allow users to set up a Web server with Apache, MySQL and PHP in one minute or less. Note that this project originated in Thailand so some of the English documentation reads a little strange. Operating System: Windows, Linux.
1087.
EasyPHP EasyPHP lets you set up a WAMP (Windows, Apache, MySQL and PHP) environment on a system or a thumb drive in just minutes. It also includes optional modules for WordPress, Spip, PrestaShop, Drupal, Joomla, and other apps. Operating System: Windows.
1088.
Nginx Nginx (pronounced "engine X") is both an HTTP and a mail proxy server. Currently powering about 8 percent of all websites, it's the third most popular Web server. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1089.
XAMPP Most of them time when you want to install the Apache Web server, you'll also need other tools, like MySQL, PHP and Perl. This group of downloads bundles together all of those tools—along with a variety of other open source software that's helpful for running a Web server—in an easy-to-deploy package customized for each of the major operating systems. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X, Solaris.
Wikis
1090.
DokuWiki This simple-to-use wiki was designed for developer teams and other small groups. Key features include unlimited revisions, recent changes viewing, section editing, anti-spam capabilities, multiple language support and more. Operating System: OS Independent.
1091.
FOSWiki A split from the TWiki project, FOSWiki distinguishes itself with support of embedded macros to enhance content and allow end-users to create their own applications. The Web site includes considerable support for new users, as well as a number of extensions to the basic application. Operating System: OS Independent.
1092.
MediaWiki Because it's the software used by Wikipedia, MediaWiki should feel familiar to most users. It's scalability makes it a good choice for large wikis. Operating System: Windows, Linux/Unix, OS X.
1093.
TikiWiki TikiWiki calls itself "Groupware" because it offers features like blogs, forums, an image gallery, map server, bug tracker and feed reader to standard wiki capabilities. The software is completely open source, but support, consulting, hosting and other services are available through third-party partners listed on the site. Operating System: OS Independent.
1094.
TWiki As a structured wiki, TWiki combines the benefits of a wiki with the benefits of a database. It can be used for project management, document management, as a knowledge base, or to collaborate on virtually any type of content for intranets or the Internet. Operating System: OS Independent.
1095.
XWiki XWiki combines an enterprise-grade wiki, a wiki manager (for those who have multiple wikis), a generic wiki platform and an RSS Reader. It's a second-generation wiki, meaning that it gives users the ability to create and deliver apps from within the wiki. Operating System: OS Independent.
Wine and Beer
1096.
CellarBoss For those with a large wine collection, CellarBoss helps keep track of the bottles you own and what you'd like to try next. It's Java-based and doesn't require a separate database, so it's easy to get started. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.
1097.
Brewtarget If you're more of a beer person than a wine person, Brewtarget can help you craft the perfect drink. This beer calculator helps home brewers track recipes and calculate the end results. Operating System: Windows, Linux, OS X.





 Money
Money because it is the default Linux shell, and you'll need to know it no matter what other languages you learn. Don't make yourself crazy trying to decide which scripting or programming language to learn first-- just pick one. Everyone has their own ideas which ones are essential, and you can overthink yourself right out of even trying to start. Javascript, Python, Ruby, and PHP are all popular, fairly easy to learn, and well-documented. C is an oldtimer that is not going away anytime soon. Basic programming concepts are the same no matter what language you're using, so as soon as you develop some proficiency with one it's easier to learn additional languages.
because it is the default Linux shell, and you'll need to know it no matter what other languages you learn. Don't make yourself crazy trying to decide which scripting or programming language to learn first-- just pick one. Everyone has their own ideas which ones are essential, and you can overthink yourself right out of even trying to start. Javascript, Python, Ruby, and PHP are all popular, fairly easy to learn, and well-documented. C is an oldtimer that is not going away anytime soon. Basic programming concepts are the same no matter what language you're using, so as soon as you develop some proficiency with one it's easier to learn additional languages.